Chapter 15 - Atmosphere Study Guide
advertisement

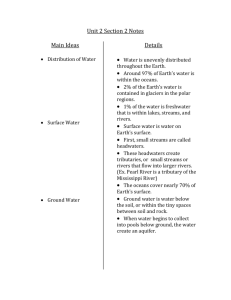
Chapter 15 - Atmosphere Study Guide Layers of the atmosphere (the thin layer of gases that surrounds the Earth) in order- what is found in each? (refer to drawing) Troposphere – lowest layer of the Earth’s atmosphere, where weather occurs Stratosphere – the layer above the troposphere (has ozone) & airplanes Mesosphere – asteroids Thermosphere – the top layer of the atmosphere Composition of the atmosphere (gases): the air you breathe 21% oxygen 78% nitrogen 1% other gases What is relative humidity? Ratio comparing the amount of H2O vapor the air contains to the maximum amount air can hold at that temperature Convection vs. Conduction vs. Radiation All are heat transfer methods Convection = warm air rise, cold air fall/ conduction =transfer through touch / radiation = energy move through air What is air pressure? – the force exerted by air on the area below it What is air pressure measured by? How does air pressure change as altitude increases? -barometer -air pressure goes (down) as altitude goes (up) How does temperature change as you increase in altitude? -temperature (up) or (down) depending on layer What are some natural sources of air pollution? (Releasing of damaging materials into the atmosphere) -fires, dust storms, volcanic ash What is the main source of human air pollution? -burning (combustion) of fossil fuels Smoke & fog combining = smog What is the difference between primary and secondary air pollution? Primary – released directly into air ex. soot secondary – reacts to create a product that is a pollutant ex. sulfuric acid Explain how air pollution can affect health? -irritate respiratory system & make people cough, develop bronchitis and asthma -carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin & interferes with the bodies ability to deliver oxygen to cells -exhaust from cars & trucks contain benzene, linked to cancer What is a temperature inversion? Why are they more likely to be around cities? When cold air is stuck under warm air. This holds pollutants close to Earth -cities produce more pollution, hence the yellowish haze appearance How does the ozone layer help life on Earth? Keeps UV rays from reaching Earth What is the source of energy that drives weather and climate? SUN What are CFC’s? Chlorofluorocarbons – responsible for O3 hole -were found in refrigerants & aerosol spray cans What is acid deposition? Examples? What are the effects of acid deposition? -precipitation that deposits acid -dust, snow, rain -animal reproduction rates go down, kills vegetation, etc. What was the goal of the Clean Air Act? (passed in 1963) -protect & improve air quality to safeguard human health and environment -limits motor vehicle emissions (substances released into the air such as carbon dioxide) A provision of the Act was to set aside funds for research into pollution control. How do catalytic converters and scrubbers help stop air pollution? Catalytic converters = reduces some air pollution from car emissions Scrubbers = stop some pollution from leaving factory smoke stacks What was the goal of the Montreal Protocol? Called for major cuts in CFC manufacture Understand the pH scale- What is considered an acidic pH? *below 5.6 = acid deposition acid rain could have a pH of 4.6 acidic = anything below 7 Where is the ozone hole located? Over Antarctica hint* wind does not have boundaries – it goes with the flow Other vocab: Front – the boundary between air masses that differ in temperature and moisture Climate – average weather conditions over a longer period of time Weather – daily changes in temperature, pressure, etc. Emission – particulate matter ex: soot & smog Gases ex: carbon monoxide Fossil Fuel – coal, oil, natural gas