http://esl.about.com/od/grammarstructures/ig/Tenses-Chart/spresent.htm 9/13/2012 8:47 PM
©2012 About.com. All rights reserved. A part of The New York Times Company.
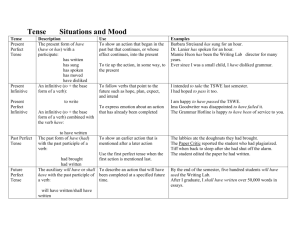
Present Simple
Structure and Usage
The present simple is used to express daily routines and habits. Adverbs of frequency such as
'usually', 'sometimes', 'rarely', etc. are often used with the present simple.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
always, usually, sometimes, etc.
... every day
... on Sundays, Tuesdays, etc.
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + Present Tense + object(s) + time Expression
Frank usually takes a bus to work.
Negative
Subject + do / does + not (don't / doesn't) + verb + object(s) + time Expression
They don't often go to Chicago.
Question
(Question Word) + do / does + subject + verb + object(s) + time Expression
How often do you play golf?
Present Continuous for Action at the Moment
Structure and Usage
One use of the present continuous tense is for action that is occurring at the moment of speaking.
Remember that only action verbs can take the continuous form.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... at the moment
... now
... today
... this morning / afternoon / evening
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + be + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
She's watching TV at the moment.
Negative
Subject + be + not (isn't, aren't) + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
They aren't having fun this morning.
Question
(Question Word) + be + subject + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
What are you doing?
Present Continuous for Current Projects
Structure and Usage
Use the present continuous to describe projects and actions that are happening around the present
moment in time. Remember that these projects have begun in the recent past and will end in the
near future. This usage is especially popular for talking about current projects at work or for
specific hobbies.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... at the moment
... now
... this week / month
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + be + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
We're working on the Smith account this month.
Negative
Subject + be + not (isn't, aren't) + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
He isn't studying French this semester.
Question
(Question Word) + be + subject + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
Which account are you working on this week?
Present Continuous for Scheduled Events
Structure and Usage
One use of the present continuous tense is for scheduled future events. This usage is especially
useful when talking about appointments and meetings for work.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... tomorrow
... on Friday, Monday, etc.
... today
... this morning / afternoon / evening
... next week / month
... in December, March, etc.
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + be + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
I'm meeting our CEO at three o'clock this afternoon.
Negative
Subject + be + not (isn't, aren't) + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
Shelley isn't attending the meeting tomorrow.
Question
(Question Word) + be + subject + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
When are you discussing the situation with Tom?
Past Simple
Structure and Usage
The past simple is used to express something that happened a past point in time. Remember to
always use a past time expression, or a clear contextual clue when using the past simple. If you
do not indicate when something happened, use the present perfect for unspecified past.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... ago
... in + year / month
...yesterday
...last week / month / year
... when ....
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + Past Tense + object(s) + time Expression
I went to the doctor's yesterday.
Negative
Subject + did + not (didn't) + verb + object(s) + time Expression
They didn't join us for dinner last week.
Question
(Question Word) + did + subject + verb + object(s) + time Expression
When did you buy that pullover?
Past Continuous for Exact Times in the Past
Structure and Usage
The past continuous tense is used to describe what was happening at a specific moment in time
in the past. Do not use this form when referring to longer periods of time in the past such as 'last
March', 'two years ago', etc. Use the past continuous with times of the day in the past.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... at 5.20, three o'clock, etc.
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + was / were + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
We were meeting with Jane at two o'clock yesterday afternoon.
Negative
Subject + was / were + not (wasn't, weren't) + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
They weren't playing tennis at five o'clock on Saturday.
Question
(Question Word) + was / were + subject + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
What were you doing at two-thirty yesterday afternoon?
Past Continuous for Interrupted Action
Structure and Usage
Use the past continuous to express what was happening when something important happened.
This form is almost always used with the time clause '... when xyz happened'. It is also possible
to use this form with '... while something was happening' to express two past actions that were
occurring simultaneously.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... when xyz happened
... while xyz was happening.
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + was / were + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
Sharon was watching TV when she received the telephone call.
Negative
Subject + was / were + not (wasn't, weren't) + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
We weren't doing anything important when you arrived.
Question
(Question Word) + was / were + subject + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
What were you doing when Tom gave you the bad news?
Future with Going to for Future Plans
The future with 'going to' is used to express future plans or scheduled events. It is often used
instead of the present continuous for future scheduled work events. Either form can be used for
this purpose.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... next week / month
... tomorrow
... on Monday, Tuesday, etc.
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + be + going to + verb + object(s) + time Expression
Tom is going to fly to Los Angeles next on Tuesday.
Negative
Subject + be not (isn't, aren't) + going to + verb + object(s) + time Expression
They aren't going to attend the conference next month.
Question
(Question Word) + be + subject + going to + verb + object(s) + time Expression
When are you going to meet Jack?
Future with Will for Promises
and Predictions
Structure and Usage
The future with 'will' is used to make future predictions and promises. Often the precise moment the
action will occur is unknown or not defined.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... soon
... next month / year / week
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + will + verb + object(s) + time Expression
The government will increase taxes soon.
Negative
Subject + will not (won't) + verb + object(s) + time Expression
She won't help us much with the project.
Question
(Question Word) + will + subject + verb + object(s) + time Expression
Why will they reduce taxes?
Future with Going to for Future Intent
Structure and Usage
The future with 'going to' is used for future intent. Remember that you can express a future intent
without expressing the exact future time that something will occur. This use of the future with
'going to' can be used to discuss future study plans, career plans, and more.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... next week / month
... tomorrow
... on Monday, Tuesday, etc.
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + be + going to + verb + object(s) + time Expression
Anna is going to study medicine at university.
Negative
Subject + be not (isn't, aren't) + going to + verb + object(s) + time Expression
They aren't going to develop any new projects for the next few years.
Question
(Question Word) + be + subject + going to + verb + object(s) + time Expression
Why are you going to change your job?
Present Perfect for Past to Present States
and Actions
Structure and Usage
Use the present perfect to express a state or repeated action that began in the past and continues
into the moment of speaking. The present perfect or the present perfect continuous can often be
interchanged. The main difference between these two forms is that the present perfect continuous
is generally used to express the length of the current activity up to the present moment in time.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... for + amount of time
... since + specific point in time
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + have / has + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
I have lived in Portland for four years.
Negative
Subject + have / has not (haven't, hasn't) + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
Max hasn't played tennis since 1999.
Question
(Question Word) + have / has + subject + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
Where have you worked since 2002?
Present Perfect to Express Recent Events
Structure and Usage
The present perfect is often used to express recent events that affect the present moment. These
sentences generally use the time expressions 'just', 'yet', 'already', or 'recently' to express this
connection. Remember that if you give a specific time in the past, the past simple is required.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
just
yet
already
recently
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + have / has + just / recently + past participle + object(s)
Henry has just gone to the bank.
Negative
Subject + have / has not (haven't, hasn't) + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
Peter hasn't finished his homework yet.
Question
(Question Word) + have / has + subject + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
Have you spoken to Andy yet?
Present Perfect for Unspecified Past Events
Structure and Usage
The present perfect is often used to express events that occurred in the past at an unspecified
moment. This form is often used to express cumulative life experiences up to the present
moment. Remember that if you use a specific past time expression, choose the past simple.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
twice, three times, four times, etc.
ever
never
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + have / has + past participle + object(s)
Peter has visited Europe three times in his life.
Negative
Subject + have / has not (haven't, hasn't) + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
I haven't played golf many times.
Question
(Question Word) + have / has + subject + (ever) + past participle + object(s)
Have you ever been to France?
Present Perfect Continuous
Structure and Usage
The present perfect continuous is used to express how long a current activity has been going on.
It is often used in context to provide a reason for a present result. Remember that continuous
forms can only be used with action verbs.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
...since + specific point in time
... for + amount of time
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + has / have + been + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
He's been cleaning house for two hours.
Negative
Subject + has / have not (hasn't / haven't) + been + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
Janice hasn't been studying for too long.
Question
(Question Word) + has / have + subject + been + verb + ing + object(s) + (time Expression)
How long have you been working in the garden?
Future Perfect
Structure and Usage
Use the future perfect tense to express what will happened by a certain time in the future. The
future perfect tense is often used to express achievements or work done by a future point in time.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... by Monday, Tuesday, etc.
... by the time ...
... by five o'clock, two-thirty, etc.
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + will + have + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
They will have finished the report by tomorrow afternoon.
Negative
Subject + will not (won't) + have + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
Mary won't have answered all the questions by the end of this hour.
Question
(Question Word) + will + subject + have + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
What will you have done by the end of this month?
Future Perfect Continuous
Structure and Usage
The future perfect continuous is used to express the duration of an action up to a future point in
time. This tense is not commonly used in English.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... by / ... by the time ...
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + will + have + been + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
We will have been studying for two hours by the time he arrives.
Negative
Subject + will not (won't) + have + been + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
He won't have been working long by two o'clock.
Question
(Question Word) + will + subject + have + been + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
How long will you have been working on that project by the time he arrives?
Past Perfect Continuous
Structure and Usage
The past perfect continuous is used to describe how long an activity had been going on before
something else happened. It is often used to provide context, or a reason for a specific action.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... for X hours, days, months, etc
... since Monday, Tuesday, etc.
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + had + been + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
She had been waiting for two hours when he finally arrived.
Negative
Subject + had not (hadn't) + been + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
They hadn't been working long when the boss asked them to change their focus.
Question
(Question Word) + had + subject + been + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
How long had Tom been working on that project when they decided to give it to Pete?
Past Perfect
Structure and Usage
The past perfect is used to express something that happened before another point in time. It is
often used to provide context, or an explanation for a specific action or result.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
... before
already
once, twice, three times, etc.
... by the time
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + had + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
She had already eaten by the time the children came home.
Negative
Subject + had not (hadn't) + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
They hadn't finished their homework before the teacher asked them to hand it in.
Question
(Question Word) + had + subject + past participle + object(s) + time Expression
Where had you gone before the class began?
Future Continuous
Usage and Construction
The future continuous is used to talk about an activity that will be in progress at a specific point
in time in the future. For example, We'll be having lunch on the beach this time next week.
This tense is often used with the following time expressions:
...this time tomorrow / next week, month, year
...tomorrow / Monday, Tuesday, etc. / at X o'clock
... in two, three, four, etc. / weeks, months, years time
Basic Construction
Positive
Subject + will + be + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
Peter will be doing his homework this time tomorrow.
Negative
Subject + will not (won't) + be + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
Sharon won't be working in New York in three weeks time.
Question
(Question Word) + will + subject + be + verb + ing + object(s) + time Expression
What will you be doing this time next year?