Study Guide
advertisement

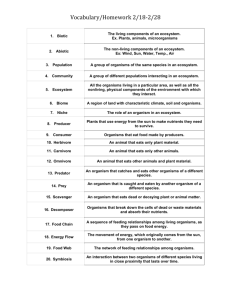
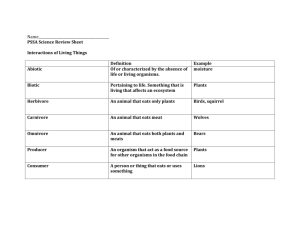
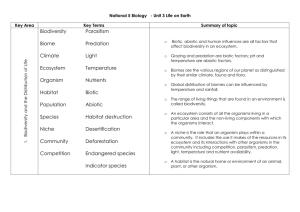
Study Guide Ecology Quiz Ecology - The study of the interactions between living and non-living factors in an environment. biotic - all living factors in an environment; animals, plants, bacteria abiotic - all the non-living factors in an environment; weather, sun, water, temperature Population –same group or species living in the same place at the same time. Community- groups of different organisms sharing the same environment (all biotic factors within an environment). Ecosystem- all of the organisms within a biotic community and the abiotic factors living together. Symbiosis - a close long-term association between two or more species. 3 types of symbiotic relationships: mutualism - symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit ex: the clownfish and sea anemone. Sea anemone provides protection for the fish and the fish provides scrapes of food for anemone. parasitism – symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed ex: heartworms in dogs, fleas and ticks on animals. commensalism – symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected ex: shark and remora. Remora benefits from feeding off sharks scrapes, protection and transportation, the shark is not affected. Food chain – a diagram that shows the flow of energy from one organism to the next. Energy from sun producer herbivore carnivore Producer Herbivore Carnivore scavenger Scavenger Food web - a complex diagram showing the many energy pathways in a real ecosystem; many food chains together Producers: grass and trees Primary consumers or herbivores: a type of consumer that eats plants ex: rabbit, deer, grasshopper, chipmunk Primary consumer or carnivores: a type of consumer that eats animals ex: fox, owl, eagle Secondary consumer or Omnivore: a type of consumer that eats plants and animals ex: humans Scavenger: a type of consumer that eats remains of dead organisms ex: vulture (not shown in picture) Decomposers: will break down the remains of dead organisms for energy. Energy Pyramid: Energy Pyramid - is a diagram shaped like a triangle that shows the loss of energy at each level of the food chain. -Producers are the plants that convert sunlight energy into chemical energy in sugar -Primary Consumers or herbivores eat the producers -Secondary consumers or carnivores eat the primary consumers. -Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. If there were as many tertiary consumers as the number of producers then there would not be enough food for all the higher level consumers. Key Vocabulary: Habitat – the environment where an organism lives. Niche – an organisms way of life and its relationships with its abiotic (nonliving) and biotic (living) environments. Carrying Capacity and Limiting Factors: All organisms need food, shelter, living space, and water to survive. These resources are called limiting factors. The availability of these limiting factors have an affect on the number of organisms that can live in an area at the same time. The carrying capacity is the largest population that an environment can support. > > Limiting factors > > Competition – two or more species or individuals trying to use the same limited resource. Example of Competition between Species: Example of Competition within a Species: