Chemistry -- Gas Laws ACT Questions [USE TO STUDY
advertisement

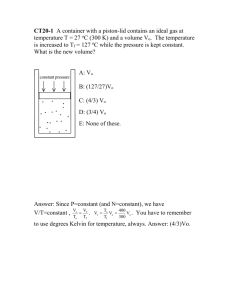
Chemistry -- Gas Laws ACT Questions [USE TO STUDY FOR YOUR TEST] Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. At 22°C, the air pressure in a car tire is 1293 torr. c. 755 Convert this pressure to atmospheres (atm). d. 877 a. 12.76 5. At 1.00 atm, a sealed weather balloon contains 20.0 b. 5.262 L of helium (He) gas at 25.0°C. Assume that none c. 1.701 of the He escapes and the pressure is constant. d. 1.293 What is the volume, in liters, of He in the weather 2. This diagram shows a closed-end mercury (Hg) balloon at 35.0°C? a. 40.0 b. 28.0 c. 20.7 d. 14.3 barometer. When atmospheric pressure is 1.30 atm, what is the height (h), in millimeters, of the Hg in the barometer? a. 132 b. 585 c. 760 d. 988 3. A chemist compresses a 1.5 L sample of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas at 1.2 atm to a final volume of 0.75 L. Assuming the temperature is constant, what is the final pressure, in atm, exerted by the CO2 gas? a. 0.60 b. 0.94 c. 1.7 d. 2.4 6. At 1254 m above sea level, the city of Helena, Montana, has an average atmospheric pressure of 0.859 atm. A chemistry student in Helena finds that pure distilled water boils at 95.9°C. Which statement explains the student’s results at this high elevation? a. The boiling point of water increases due to lower atmospheric pressure. b. The boiling point of water increases due to higher atmospheric pressure. c. The boiling point of water decreases due to lower atmospheric pressure. d. The boiling point of water decreases due to higher atmospheric pressure. 4. A vessel connected to an open-end mercury (Hg) manometer contains nitrogen (N2) gas. The atmospheric pressure is 0.993 atm. The height difference between the two arms of the manometer 7. For a chemistry homework assignment, Beth must consider the effusion rates of methane (CH4) gas and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) gas at 25°C. Effusion occurs as gas particles escape from a container through a small hole. Which statement accurately compares the effusion rates of CH4 and NF3 at 25°C? a. CH4 effuses 2 times faster than NF3. b. CH4 effuses 4 times faster than NF3. c. NF3 effuses 2 times faster than CH4. d. NF3 effuses 4 times faster than CH4. is 122 mm. What is the pressure, in mm Hg, of the N2 gas? a. 355 b. 633 8. At standard temperature and pessure, a chemist burns 3.50 L of pentane (C5H12) in excess oxygen (O2) gas. C5H12(l) + 8 O2(g) -> 5 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) What is the maximum number of liters of carbon dioxide (CO2) that the reaction can produce? a. 17.5 b. 8.50 c. 5.60 d. 0.700 9. At high temperatures, chlorine (Cl2) reacts wiht flourine (F2) to produce chlorine triflouride (ClF3) Cl2 (g) + 3 F2 (g) --> 2 ClF3 (g) A chemist carries out the reaction of 0.250 mol of F_2 wit excess Cl2. At 250.0°c and 1.00 atm, what is the maximum volume of ClF3 in liters, that the reaction can produce? a. b. c. d. 3.42 3.73 7.16 10.7 10. Real gases best imitate the behavior of ideal gases under what conditions? a. Low temperatures and low pressure b. low temperature and high pressure c. high temperatures and low pressure d. high temperatures and high pressure 11. A chemist purchases a 43.7 L cylinder of methane ( ) gas. At 295 K, the pressure inside the cylinder is 1.88 atm. How many grams of are in the cylinder? a. 3.39 b. 12.2 c. 23.2 d. 54.4 12. At 83.7 kPa and 35.0°C, what is the density, in g/L, of phosphorous hydride ( )? a. 0.528 b. 1.11 c. 1.52 d. 2.39 13. At 15°C, 0.252 mol of argon (Ar) gas occupies 174 ml. What is the pressure, in atm, of the Ar gas? a. 1.78 b. 2.92 c. 12.6 d. 34.2 14. Sylvia heats 2.28g of a liquid until it completely vaporizes. The boiling point of the liquid is 56.3°C. She collects all of the gas in a 750.0 ml vessel. The pressure of the gas is 1.41 atm at 56.3°C. What is the molar mass, in g/mol, of the liquid? a. 9.97 b. 22.3 c. 58.3 d. 121 15. The boiling point of chlorine ( ) is -34.6°C. What is this temperature in Kelvin? a. 307.6 K b. 238.4 K c. -238.4 d. -307.6 K 16. Which statement correctly describes the melting point of a solid? a. The particles in the solid lose enough kinetic energy to overcome the interactions preventing them from approaching one another. b. The particles in the solid lose enough kinetic enrgy to overcome the interactions holding them in an organized pattern. c. The particles in the solid gain enough kinetic enrgy to overcome the interactions preventing them from approaching one another. d. The particles in the solid gain enough kinetic energy to overcome the interactiong holding them in an organized pattern. 17. At constant temperature, Kelly increases the volume of a fixed amount of gas. Use the kineticmolecular theory to explain how increasing the volume affects the pressure of a gas. a. The pressure decreases because there are fewer collisions between gas molecules and the container walls. b. The pressure decreses because there are more collisions between gas molecuyles and the container walls. c. The pressure increases becuase there are fewer collisions between gas molecules and the container walls. d. The pressure increses because there are more collisions between gas molecuyles and the container walls.