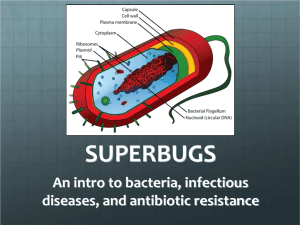
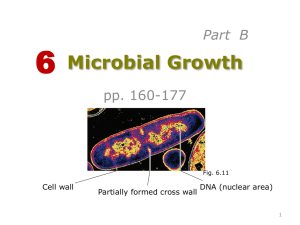
Which of the following statements about anaerobic respiration is
advertisement

Microbiology Exam #2-Fall 2010 Name________________________ Multiple choice. Choose the best answer (2 points each) 1._____The generation time of a bacterial population: a) is the same for all bacterial species; b) is “n” in the formula Nf=(ni)2n ; c) is the amount of time it takes a bacterial population to double; d) averages 24 hours for bacteria; e) b and c are both correct. 2. _____Bacterial cells are most sensitive to chemical inhibitors in this phase of the bacterial growth curve: a) lag phase; b) stationary phase; c) log phase; d) phase of positive acceleration; e) death phase. 3. _____ A Coulter counter is an example of this bacterial counting method: a) standard plat count; b) 50% end point analysis; c) measuring oxygen consumption; d) a direct cell count; e) counting by measuring turbidity. 4. _____ To relate turbidity levels to actual cell numbers using a spectrophotometer, an investigator must first: a) make a standard curve for the species you are counting; b) construct a growth curve; c) determine the 50% end point dilution; d) determine the phenol coefficient. e) use the formula Nf=(ni)2n 5._____ A measure of the relative number of infectious organisms in a sample is called the: a) phenol coefficient; b) infectious dose 50; c) titer; d) 50% end point dilution. 6. _____Use of this counting method requires doing serial dilutions and assumes that one bacterial colony arises from one cell in the original sample: a) Petroff-Hauser chamber; b) standard plate count; c) Coulter counter; d) 50% end point analysis; e) b and d 7._____An organism that requires supplements (such as vitamins) being added to minimal media before they will grow are said to be: a) psychrophiles; b) fastidious; c) halophiles; d) chemolithotrophs. 8. _____The source of carbon and nitrogen in minimal media such as nutrient broth is: a) peptones; b) beef extract; c) glucose; d) phenol red; e) sodium chloride. 9._____Most human pathogens are: a) halophils; b) saccrophils; c) psychrophils; d) mesophils; e) thermophils. 10. _____Singlet oxygen: a) is broken down by catalase; b) is produced routinely by phagocytic white blood cells; c) is produced only during anaerobic respiration; d) is a common byproduct of ferementation; e) kills bacteria that are obligate aerobes. 11. _____ Which of these types of organisms lack the enzyme superoxide dismutase? a) obligate aerobes; b) obligate anaerobes; c) facultative anaerobes; d) aerotolerant anaerobes; e) microaerophils 12. _____This type of organism would grow better in a normal incubator than in a Gas Pak, but it would grow in the Gas Pak. a) obligate aerobes; b) obligate anaerobes; c) facultative anaerobes; e) aerotolerant anaerobes; e) microaerophils. 13._____A term used to describe a bacterium whose carbon source was glucose and which obtained its energy through the oxidation of inorganic molecules: a) photoautotroph; b) photoheterotroph; c) chemoautotroph; d) chemoheterotroph. 14._____A carbon source is essential for microbial growth because, in addition to serving as an energy source carbon compounds are also needed to: a) provide carbon skeletons for biosynthesis; b) supply the material for catabolic reactions; c) keep the environment isotonic; d) release excess energy from the electron transport system; e) produce the energy needed for chemiosmotic ATP synthesis. 15. _____If an organism gives you a positive oxidase test, you know that: a) it produces acid during fermentation; b) it produces gas in fermentation; c) it is a microaerophil; d) it has cytochrome A3 in its electron transport system; e) it has the enzyme nitrogenase 16. _____Fermentation: a) must produce gas; b) must produce acid; c) reduces nitrate into nitrite; d) recycles NADH into NAD; e) always produces harmless byproducts. 17. _____Methanogens, which convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas into methane, water and ATP are characterized as this type of organism: a) chemoheterotroph; b) chemoautotroph; c) photoautotroph; d) photoheterotroph;. 18._____A test tube containing sucrose, nutrient broth, phenol red, and Durham tube would be used to: a) determine whether an organism was oxidase positive; b) do a catalase tes; b) do a fermentation test; d) determine whether an organism was an obligate anaerobe; e) do a nitrate utilization test. 19. _____Which of the following the following terms refers to lowering the number of microorganisms so that public health standards are met? a) sepsis; b) disinfection; c) antisepsis; d) sanitization; e) sterilize. 20._____Which of the following processes would take the longest amount of time to achieve the desired results? a) ultrapasteurization; b) autoclaving; c) oven sterilization at 160 C; d) boiling to kill vegetative cells (not spores). 21._____ Lyophillization is the name of a process that: a) pasteurizes food at ultra high temperatures for a very short time period; b) sterilizes foods using ionizing radiation; c) preserves bacterial cultures by rapid freezing in liquid nitrogen under a vacuum; d) involves the use of a hot air oven; e) kills bacteria using a "gas" autoclave. 22._____ This process of moist heat treatment of solutions utilizes conditions of time and temperature designed to only kill certain types of organisms: a) boiling; b) autoclaving; c) pasteurization; d) incineration; e) Tyndallization. 23._____ Thymine-thymine dimers are most likely to form in a cell following its exposure to: a) gamma irridation; b) phenol; c) halogens; d) ultraviolet light; e) low temperatures. 24. _____A bisphenol that has been shown to cause neurological damage in infants: a) hexachlorophene; b) tincture of iodine; c) betadine; d) formalin e) triclosan. 25._____Bacteria like Mycoplasms which lack cell walls would be least likely to be killed by this method: a) UV light; b) ionizing radiation; c) sonication (ultrasound); d) ethylene oxide treatment; e) pasteurization. 26._____ HEPA filters are most associated with: a) filtration of virus from bacteriological media; b) helping to create a contaminant free work area for jobs like culture transfers; c) removing bacteria from liquid materials used to make media; d) bottling of draft beer; e) device that protects you from UV radiation. 27._____ A halogen compound complexed with a detergent which kills microorganisms but does not irritate the nerve endings of skin tissue: a) phenols; b) chlorhexidine; c) iodophore; d) chloramines; e) iodine. 28._____ Substances that add ethyl or methyl groups to molecules (especially nucleic acids and proteins) and cause them to become nonfunctional by cross linking them are called: a) phenolics; b) alkylating agents; c) halogens; d) heavy metals; e) disinfectants. 29._____ A compound that discourages bacterial growth by altering the pH of the environment and is often used as a food preservative: a) merthiolate; b) benzylalkonium chloride; c) silver nitrate; d) ethylene oxide ; e) benzoic acid. 30.____This substance, which used to be formulated from a mixture of cresols, was once used widely for birth control until it was deemed unsafe and ineffective: a) Chlorox; b) formaldehyde; c) Lysol; d) ammonium hydroxide; e) silver nitrate. 31. (4 points each). Agree or disagree with the following statements. In either case, fully defend your position. A. The microbial counting methods of using turbidity, oxygen consumption, or carbon dioxide production of a bacterial culture all share something in common. B. Organisms should not just be categorized using their metabolic strategies using just the terms autotroph and heterotroph. C. Both antiseptics and disinfectants are used in the process of degermination. D. If you were looking for an emergency antiseptic to put on a cut, you’d be better off going to a drug store to buy rubbing alcohol than a liquor store to buy 100% (grain) alcohol. 32. (8 points) Compare the microbial counting methods of 50% end point analysis and a Petroff-Hauser chamber in regards to the following aspects: a) how the counting method works, b) situations where you should use the method, c) advantages of the method, and d) limitations of the method. 33. (8 points) Using the following terms, chemoautotrophic metabolism, anaerobic respiration, nitrogen fixation, and deamination, describe the nitrogen cycle and the role that bacterial metabolism plays in this cycle. Why is the nitrogen cycle (and therefore bacteria) so important? 34. (8 points) Compare gamma irradiation and UV irradiation addressing the following points: 1) how they kill microorganisms (mechanism of action) 2) applications they are used for, 3) advantages of the method over other methods that are routinely used for the same purpose, and 4) limitations of the method.