File
advertisement

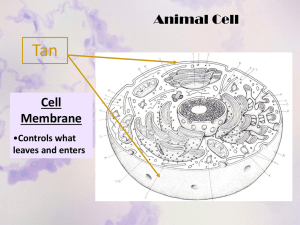
Number: Science: Nucleus, Ribosomes, ER Name: #6.3 Date: HR: Objective: I can compare and contrast the function of the nucleus, ribosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum. DO NOW 1. A rock is pushed deep underground in an area where mountain building is occurring and undergoes the following processes. First, the rock experiences high pressure that causes its minerals to align themselves in bands. Second, the rock is pushed further underground and completely melts, then erupts from a volcano and hardens. Third, the rock is broken down by wind and water into small particles, which flow into a river and get compressed into rock. Which order correctly shows this progression of rock types? A. igneous metamorphic sedimentary B. metamorphic igneous sedimentary C. metamorphic sedimentary igneous D. sedimentary igneous metamorphic 2. Which of the following provides evidence for plate tectonics? A. Coriolis effect B. ocean currents C. atmospheric temperature variations D. sea-floor spreading HOMEWORK REVIEW 1. Which type of rock is formed from weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, and cementation? ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 2. What are two differences between Earth’s inner and outer core? ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 3. What happens to lithospheric plates at a convergent boundary? ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 4. Newton’s third law of motion states that every action force is accompanied by what? 2 ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ REVIEW FROM YESTERDAY What is the function for each of the following cell parts? Cell Membrane ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ Cytoplasm ____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ Organelle ____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ DNA ______________________________________________________________________________ _____ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 3 Objective: I can compare and contrast the function of the nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Two Kinds of Cells All cells have ________________________________, ___________________________, _____________________, and ________________. But there are two basic types of cells— cells without a nucleus and cells with a nucleus. Cells with no nucleus are prokaryotic (proh KAR ee AHT ik) cells. Cells that have a nucleus are eukaryotic (yoo KAR ee AHT ik) cells. Prokaryotic cells are further classified into two groups: bacteria (bak TIR ee uh) and archaea (AHR kee uh). Eukaryotic Cells and Eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells are the largest cells. Most eukaryotic cells are still microscopic, but they are about 10 times larger than most bacterial cells. A typical eukaryotic cell is shown below. All living things that are not bacteria or archaea are made of one or more eukaryotic cells. Organisms made of eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes. Many eukaryotes are multicellular. Multicellular means “many cells.” Multicellular organisms are usually larger than single-cell organisms. So, most organisms you see with your naked eye are eukaryotes. There are many types of eukaryotes. Animals, including humans, are eukaryotes. So are plants. 1. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms? 4 ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ Eukaryotic Cells Even though most cells are small, cells are still complex. A eukaryotic cell has many parts that help the cell stay alive. Similarities: Plant cells and animal cells are two types of eukaryotic cells. These two types of cells have many cell parts in common. But plant cells and animal cells also have cell parts that are different. Look at the diagrams below. List similarities and differences you see between plant and animal cells. Differences: 5 Nucleus The nucleus is a large organelle in a eukaryotic cell that directs all cell activities and is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane. Materials enter and leave the nucleus through openings in this membrane. The nucleus contains the instructions for everything the cell does. These instructions are found on DNA, the chemical structure that contains the code for the cell’s structure and activities. The nucleus of many cells contains a dark area called the nucleolus, where a cell begins to make its ribosomes. 1. What is the function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell? ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 6 ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 2. What is the nucleolus and what does it do? ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ Ribosomes One substance that takes part in nearly every cell activity is protein. Proteins are part of cell membranes, and other proteins are needed for chemical reactions that take place in the cytoplasm. Organelles that make proteins are called ribosomes. Ribosomes are some of the smallest of all organelles, and there are more ribosomes in a cell that there are any other organelles. Some ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm. Others are attached to membranes. Unlike most organelles, ribosomes are not covered by a membrane. 3. What is unique about ribosomes and what is their function? ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ Endoplasmic Reticulum Many chemical reactions take place in a cell. Many of these reactions happen on or in the endoplasmic reticulum (EN doh PLAZ mik ri TIK yuh luhm). The endoplasmic reticulum, or ER, is a system of folded membranes in which proteins and other materials are processed and transported inside the cell. The ER is shown below. 7 The ER is part of the internal delivery system of the cell. Its folded membrane contains many tubes and passageways. Substances move through the ER to different places in the cell. Endoplasmic reticulum is either rough ER or smooth ER. The part of the ER covered in ribosomes is rough ER. Rough ER is usually found near the nucleus. Ribosomes on rough ER make many of the cell’s proteins. The ER delivers these proteins throughout the cell. ER that lacks ribosomes is smooth ER. The functions of smooth ER include making lipids and breaking down toxic materials that could damage the cell. 3. Describe the function of the endoplasmic reticulum. ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 4. Compare and contrast the function of the nucleus and ribosomes. ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 8 ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 5. Describe how the nucleus, ribosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum work together to help a cell function. ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ____________ 9 10