Teacher
advertisement

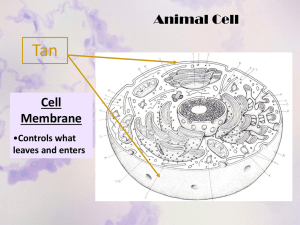
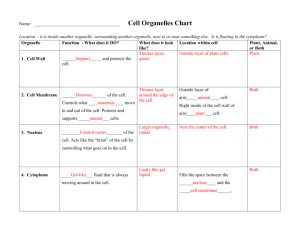
Station 4 1A Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane in maintaining homeostasis Structure Function Plant, Animal, or Both Vacuole Membrane-bound sac that acts as a storage area Both Chloroplast Converts light energy into carbohydrates Plant Mitochondria Converts energy from food molecules to energy in the form of ATP Both Cytoplasm Fluid material inside the cell membrane, not including the nucleus Both Nucleus Golgi Apparatus Lysosome Control center of a cell; contains genetic information Modifies and packages substances such as proteins, sugars, and enzymes Contains enzymes to digest and recycle materials found in the cytoplasm Both Both Animals Cell Wall Structure in plants and fungi that protects and supports the organism Plants Ribosome Responsible for protein synthesis Both Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Cell Membrane Moves molecules from one part of the cell to another; involved in synthesis of lipids; has not ribosomes Moves molecules from one part of the cell to another including proteins; covered with ribosomes Thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. Regulates what materials enter and leave the cell Both Both Both Centrioles Groups of microtubules important for cell division Animals Cytoskeleton A framework for the cell within the cytoplasm Both Nucleolus The site of ribosome production within the nucleus of Eukaryotic cells Both Structure Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondria Cytoplasm Function Plant, Animal, or Both Nucleus Golgi Apparatus Lysosome Cell Wall Ribosome Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Cell Membrane Centrioles Cytoskeleton Nucleolus Function Plant, Animal, or Both Membrane-bound sac that acts as a storage area Both Converts light energy into carbohydrates Plant Converts energy from food molecules to energy in the form of ATP Both Fluid material inside the cell membrane, not including the nucleus Both Control center of a cell; contains genetic information Modifies and packages substances such as proteins, sugars, and enzymes Contains enzymes to digest and recycle materials found in the cytoplasm Both Both Animals Structure in plants and fungi that protects and supports the organism Plants Responsible for protein synthesis Both Moves molecules from one part of the cell to another; involved in synthesis of lipids; has not ribosomes Moves molecules from one part of the cell to another including proteins; covered with ribosomes Thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. Regulates what materials enter and leave the cell Groups of microtubules important for cell division Both Both Both Animals A framework for the cell within the cytoplasm Both The site of ribosome production within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells Both