Water & the Fitness of the Environment
advertisement

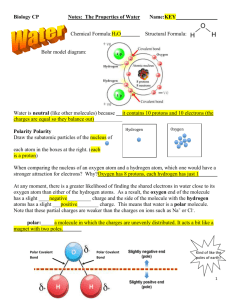
Water & the Fitness of the Environment Name_________________________ Date__________________________ Student Objectives: 1. Explain how water supports all life 2. Explain why water is polar and how it affects its properties 3. List and describe the four properties of water Notes: Water Supports All Life Most cells are surrounded by water, and cells consist of about ______________ water. Three-quarters of the ________________________ is submerged in water. The abundance of water is the main reason the Earth is _____________________________. Properties of Water The polarity of water molecules results in ________________________________. The water molecule is a ______________________________ due to uneven distribution of ___________________________. The ________________________________ of a water molecule have ___________________________________. Place the correct charges on the polar water molecule below (-) and (+) showing the positive and negative poles : Polarity of Water The ____________________ of water molecules allows them to form _____________________________ with each other and contributes to various properties water exhibits. Four Properties of Water The four properties of water that contribute to Earth’s fitness for life: 1) ________________________________________________________ 2) ________________________________________________________ 3) ________________________________________________________ 4) ________________________________________________________ Water & the Fitness of the Environment Name_________________________ Date__________________________ 1) Cohesive Behavior: Water molecules exhibit cohesion; cohesion is the ___________________ of a high percentage of water molecules to neighboring ___________________. Cohesion is due to ___________________________________. Adhesion is the hydrogen bonding between water and other ______________________________. Surface Tension is related to _____________________; it is a measurement of how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid. 2) Moderation of temperature: Water moderates air temperature by ____________________ heat from warmer air and ____________________ the stored heat from cooler air. Water can absorb or release a large amount of heat with only a slight change in its own temperature. Heat & Temperature a. __________________________ is the energy of motion b. __________________________ is a measure of the total amount of kinetic energy due to molecular motion c. __________________________ is the measures the intensity of heat due to average kinetic energy of molecules d. __________________________ is the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 gram of that substance to change its temperature by 1° C. Water has a high ______________________ relative to other compounds. 3) Expansion upon Freezing: The hydrogen bonds in ice are more “______________” than in liquid water, making ice less ________________ and able to float. 4) Versatility as a Solvent: Water is a versatile solvent due to its _____________________. The different regions of the polar water molecules can interact with ionic compounds called solutes and dissolve them. An __________________ solution has water as the solvent. Water & the Fitness of the Environment Name_________________________ Date__________________________ Skill Building & Application of concepts: 1. In a single molecule of water, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by a. Hydrogen bonds b. Nonpolar covalent bonds c. Polar covalent bonds d. Ionic bonds e. Van der Waals interactions 2. The slight negative charge at one end of one water molecule is attracted to the slight positive charge of another water molecule. What is this attraction called? a. A covalent bond b. A hydrogen bond c. An ionic bond d. A hydrophilic bond e. A hydrophobic bond 3. What determines the cohesiveness of water molecules? a. Hydrophobic interactions b. Nonpolar covalent bonds c. Ionic bonds d. Hydrogen bonds e. Both A and C 4. Which of the following is possible due to the high surface tension of water? a. Lakes don’t freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures b. A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond c. Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions d. Water can act as a solvent e. The ph of water remains exactly neutral 5. What do cohesion, surface tension, and adhesion have in common with reference to water? a. All increase when temperature increases b. All are produced by ionic bonding c. All are properties related to hydrogen bonding d. All have to do with nonpolar covalent bonds e. c and d only Water & the Fitness of the Environment Name_________________________ Date__________________________ 6. Water’s high specific heat is mainly a consequence of the a. Small size of the water molecules b. High specific heat of oxygen and hydrogen atoms c. Absorption and release of heat when hydrogen bonds break and form d. The fact that water is a poor heat conductor e. Inability of water to dissipate heat into dry air 7. Ice is lighter and floats in water because it is a crystalline structure in which each water molecule is bonded to a maximum of four other water molecules by which kind of bond? a. Ionic b. Hydrogen c. Covalent d. A and C only e. A, B and C 8. Explain how water supports all life 9. Explain why water is polar and how it affects its properties 10. List and describe the four properties of water