Wien`s Law Note & Questions
advertisement

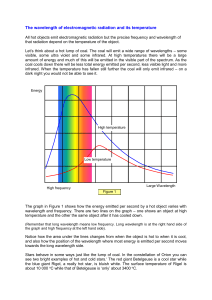
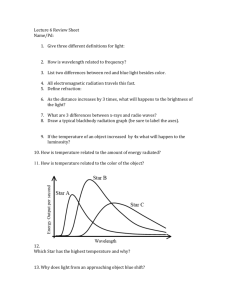
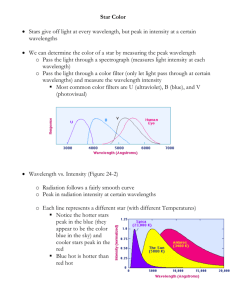
SES4U Grade 12 Earth and Space Science – University Unit: Astronomy Temperature of a Star (Wien’s Law) A black body in any object that is completely opaque. It absorbs and emits Electromagnetic Radiation. We can be considered a black body since we emit infrared radiation. Stars are another example of a black body. By measuring the intensity of radiation being emitted by a star we can determine at what wavelength they have their greatest or peak wavelength in which they emit the most energy. Wilhem Wien found that the maximum wavelength emitted by a black body radiator is inversely proportional to the temperature of the object. By using spectroscopy, the peak wavelength can be determined and then Wien’s Law can be used to determine the temperature. Wiens Law: 𝜆𝑚𝑎𝑥 = 𝑏 𝑇 where: b = 2,897,768.5nmK T is the temperature measured in Kelvin 𝜆𝑚𝑎𝑥 is the maximum wavelength of emitted energy measured in nanometers (nm) Example: The Sun emits energy over a wide range of wavelengths. Calculate the surface temperature of the Sun when the maximum wavelength is 500nm. G: R: A: S: S: SES4U Grade 12 Earth and Space Science – University Unit: Astronomy Wien’s Law Practice with Graphs Determine the temperature of the following blackbodies. Wien’s Law Practice Questions 1. A star has a surface temperature of 10000 K. At what wavelength will this star emit most of its light? 2. What is the temperature of a star which has maximum energy emitted at the wavelength of 550 nm? 3. If a star has a surface temperature of 6174 K, determine the wavelength at which it emits its maximum amount of energy. 4. What is the wavelength at which the human body radiates maximum energy (hint K = C + 273.15)?