Biology Name______________________ Block_____ CHiNOPS
advertisement

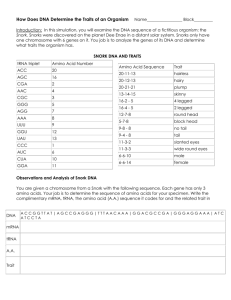
Biology Name______________________ CHiNOPS : Block_____ A Model of Protein Synthesis Objectives: Students will be able to 1. Apply the processes of transcription and translation to a DNA sequence. 2. Explain the one gene produces one protein concept in living organisms. 3. Create a functional DNA sequence from the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Background: How does DNA code produce traits that can be observed in an organism? DNA contains the information for all the diversity of life on the planet from a firefly’s glow produced by luciferase enzyme activity to the intense blue color of a gentian flower made by another enzyme. DNA is a polymer with millions of nucleotides in the strands of the chromosomes. DNA is the source of information to operate a cell. Sections of the DNA code for proteins. Some 20,000 genes (estimated) code for proteins. Other segments of DNA code for RNA that regulates the production of proteins (1,000’s more). Each portion of DNA coding for a protein is a gene. Genes control the traits that we can observe in an organism. Using the DNA to build an RNA molecule is transcription The sequence of base pairs in DNA is read in triplets of nucleotides. A triplet specifies a single amino acid. Each triplet is a codon. Each codon will bond with a specific anticodon on a transfer RNA (tRNA). tRNA are carriers of the amino acids that will be used to build a protein. When the messenger RNA (mRNA) binds with a ribosome, the construction of a specific protein can begin. tRNA deliver amino acids to be assembled at the ribosome. The process of assembling amino acids into a polypeptide, a protein, is called translation. The sequence of nucleotides determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein. The finished structure of the protein determines what it can do: an enzyme, a pigment, a structural protein in muscle, and many other functions. In this investigation, you will simulate the process of protein synthesis and thereby determine the traits inherited by fictitious organisms called CHiNOPS. CHiNOPS are members of the kingdom Animalia, and their cells contain one chromosome. A CHiNOPS chromosome is made up of only six genes (A, B, C, D, E, and F), each of which is responsible for one specific trait. Biology Name______________________ Block_____ Prelab Questions: 1. Where will transcription take place (Hint: where is the DNA located?) Why?____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 2. Which molecule is used as a template to build proteins? Circle one. DNA tRNA mRNA rRNA Protein Enzyme Transcription >Takes place in the nucleus. >mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are made from the DNA strand . Translation Procedure: >Takes place at the ribosome (rRNA) in the cytoplasm. >mRNA codons are read and the matching. >Transfer RNA (tRNA) carries the amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain. 1. To determine the trait for Gene A of your CHiNOPS, fill in the information in the box labeled Gene A in the Data Table. First, simulate transcription by using the DNA sequence to write a complementary sequence of mRNA. Then, simulate translation by using the charts provided to translate the mRNA codons into an amino acid sequence. Biology Name______________________ Block_____ 2. Using the charts provided, find the trait that matches the amino acid sequence for Gene A. Record this information in the appropriate place in the Data Table. 3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for the remaining genes (B through F) 4. Using all the inherited traits, sketch your CHiNOPS in the space provided below the Data Table – in color. Label the traits mRNA UGG UCG GCU UUG AUU CCC UGU UUU AAA AAC AGA GGG CAC GAU GAG Amino Acid Tryptophan Serine Alanine Leucine Isoleucine Proline Cysteine Phenylalanine Lysine Asparagine Arginine Glycine Histidine Aspartic Acid Glutamic Acid Amino Acid Sequence Trait Tryp-GluA-Arg Hairless Tryp-Asp-Arg Hairy Tryp-Iso-Pro Plump Arg-Iso-Leu Skinny Ser-Ala Four-legged Asp-Cys-Phe-Gly Long nose Pro-Cys-Phe-Gly Short nose Lys-Phe No freckles Lys-Leu Freckles GluA-AspA-Ala Blue skin GluA-AspA-AspA Orange skin His-His-AspA Male His-His-Thr Female Gene A DNA ACC TTG TCT mRNA _______________ Amino acid Sequence _____________ Trait _________________ Gene B DNA AGC CGA mRNA _______________ Amino acid Sequence _____________ Trait _________________ Gene C DNA TTT AAC mRNA _______________ Amino acid Sequence _____________ Trait _________________ Gene D DNA CTC CTA CGA mRNA _______________ Amino acid Sequence _____________ Trait _________________ Gene E DNA GGG ACA AAA CCC mRNA ________________ Amino acid Sequence ______________ Trait __________________ Gene F DNA GTG GTG CTA mRNA _______________ Amino acid Sequence _____________ Trait _________________ Biology Name______________________ Block_____ Finally, answer the questions provided. 3. What is the function of a codon? (Hint: which molecule is it found on?) _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Name of your CHiNOPS____________________________________ Give a scientific name with genus and species. Biology Name______________________ Block_____ 4. Name two traits your CHiNOPS has that are NOT coded for by the six genes (A-F). Example: curved back, 2 eyes, 8 eyes, tail, or other physical trait. Use the table below to record your trait. Use what you know about translation to use the process in reverse order. Create a sequence of 2 to 4 amino acids for the protein responsible for your trait. Make a mRNA sequence, and from the mRNA make a DNA sequence. Gene W DNA mRNA ____________________________3 Amino acid Sequence __________________________2 Trait ______________________________1 Gene Z DNA mRNA ____________________________3 Amino acid Sequence __________________________2 Trait ______________________________1 5. You have reverse engineered a DNA sequence for your traits. When transcribing DNA to RNA and translating RNA to protein, there is one possible outcome without errors. How many DNA sequences are possible for your proteins when going through the reverse process? One, two, or more than two? Why? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Resources: Department Staff, 2014, Talking Glossary of Genetic Terms, National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health, http://www.genome.gov/Glossary/ Department Staff, 2014, What’s a Gene? Interviews, National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health, http://www.genome.gov/27554026 Department Staff, 2014, Transcription and Translation, PBS LearningMedia adapted from Institute of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Nebraska, http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/lsps07.sci.life.stru.celltrans/celltranscription-and-translation/ Biology Name______________________ Block_____