File ontological and cosmological arguments
advertisement
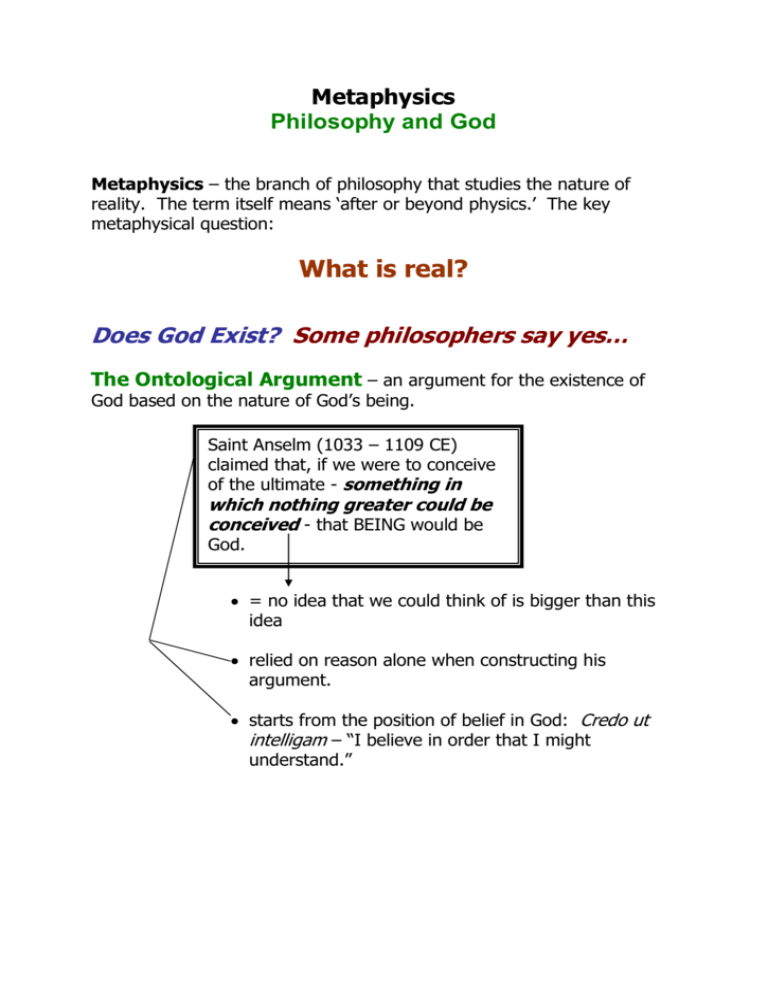
Metaphysics Philosophy and God Metaphysics – the branch of philosophy that studies the nature of reality. The term itself means ‘after or beyond physics.’ The key metaphysical question: What is real? Does God Exist? Some philosophers say yes… The Ontological Argument – an argument for the existence of God based on the nature of God’s being. Saint Anselm (1033 – 1109 CE) claimed that, if we were to conceive of the ultimate - something in which nothing greater could be conceived - that BEING would be God. = no idea that we could think of is bigger than this idea relied on reason alone when constructing his argument. starts from the position of belief in God: Credo ut intelligam – “I believe in order that I might understand.” The Cosmological Argument – an argument for the existence of God that claims that there must be an ultimate causal explanation for why the universe as a totality exists. Saint Thomas Aquinas (1225 – 1274 CE) claimed that there are five proofs for the existence of God. From the position of metaphysics, the two most important are: Motion – everything in the universe is in motion. For everything in the universe to moving there must be a MOVER. God = The First Mover Causal Order – everything in the universe has a cause. Stretching back through the chain of causes to the beginning leads one to God. God = The First Cause ST. THOMAS AQUINAS’ FIVE PROOFS FOR THE EXISTENCE OF GOD Teacher’s Copy ARGUMENT GOD AS 1. Motion / Change Unmoved Mover 2. Cause / Efficient Cause 3. Contingency / Necessity 4. Perfection / Excellence Uncaused Cause 5. Design / Order / Intelligence Intelligent Being – who directs/designs all things toward their respective ends Noncontingent / Necessary Being The Perfect CATEGORY / TYPE OF ARGUMENT Cosmological Argument - results from a study of the universe; there must be an ultimate causal explanation for the way things are Cosmological Argument Cosmological Argument Moral Argument - the perfect virtue(s) must exist for the partial virtues to exist. Design Argument - God is the supreme wise intelligence in whom all the order in the universe originates. - things could not exist by mere chance but are designed for a purpose by an Intelligent Being. Ontology and Cosmology go.grolier.com – Grolier online Encyclopedia Ontology, a branch of metaphysics that deals with reality itself, as apart from the subjective impressions and thoughts of the person who experiences it. The term was introduced by Christian von Wolff in the 18th century to designate a field of speculative thought lying between natural philosophy, which is concerned with the origins and the structure of the world, and mental philosophy, or psychology, dealing with the mind. Ontology, he asserted, should find the answers to questions more basic than those considered in either natural philosophy or psychology. There is a reality that gives rise to sensations. Obviously, the sensations are quite different from the "thing-in-itself" that stimulates them. Light waves, for example, are not the same as the colors that are experienced by the human observer. They are the "thing-in-itself," or an aspect of reality that gives rise to particular types of sensations. Cosmology, the study of the structure of the universe as a whole. The word derives from the Greek word, kosmos, for the order that is revealed in the beauty of the sky. Cosmology is distinct from cosmogony, which is concerned with the origin and evolution of individual objects in the universe, such as stars and galaxies. (These formation processes also are discussed in this article, although very little is understood about them as yet.) The study of the cosmos extends back to ancient times, but modern scientific cosmology may be said to have begun as recently as 1917, when Albert Einstein applied his general theory of relativity to the structure of the universe as a whole.