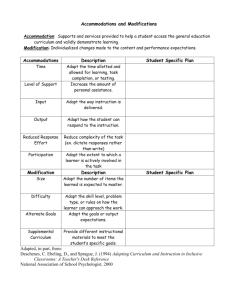
CHART: Freshwater Ecosystems, C.7.1 TEACHER COPY
advertisement

Name _______TEACHER COPY ________ Period ______ Date _________________ Chapter 7.1 Freshwater Aquatic Ecosystems CHART - Use the classroom or online chart to fill in the empty spaces. FRESHWATER AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS Characteristics Plants and Some of Their Adaptations Ecosystem Freshwater (F) or Saltwater (S) Lakes and Ponds Mainly F Some S In Littoral Zone: shallow shore and upper layer in deeper water both are nutrient rich with full sunlight and diverse plants and animals In Benthic Zone: bottom has dead and decaying organisms Marsh Wetlands Mainly F Some S Swamp Wetlands Mainly F Some S Rivers, Creeks, and Streams Mainly F Few S Animals and Some of Their Adaptations Threats Phytoplankton, cattail reeds, pond lilies Zooplankton; water beetles use hairs to trap surface air for underwater dives; catfish whiskers can sense food on bottom from vibrations; amphibians burrow into Littoral mud when temperatures are freezing Eutrophication accelerated by runoff containing sewage, fertilizers, and animal wastes; Recreational users leave garbage and oil products Land covered with water part of the year; Brackish marshes have slightly saline water; Function as habitat, feeding and spawning sites for fish; flood control; and purifies waste water On flat, poorly drained land, have little water movement, often near streams; Breeding grounds for many insects needed for larger animals to live Non woody plants: reeds, rushes, cattails rooted in rich bottom sediments with leaves above water Waterfowl: grebes and ducks adapt to eat marsh plants with flat bills; nesting birds like blackbirds and herons feed on frogs and fish; animals adapt to changes in water salinity Amphibians such as green frogs and salamanders; Reptiles such as alligators and crocodiles; Birds such as wood ducks Drained for urban development, farms, residential building, or commercial factories Usually starts in mountains from rain and melted snow; runs down into oceans; usually cold at head of river and warm where it spreads out; constantly moving Mosses and plants that can adapt to the cold water at the head; Water plants that can survive the currents Fish such as trout, catfish, and carp live in calmer waters Industries dump wastes from manufacturing; Businesses use water in making products; People use rivers to dispose of wastes such as sewage and garbage - All these dump toxin which filter to the animals and stay in the bottom sediments Plants adapt to changes in water salinity Woody plants or shrubs; water-tolerant trees like red maple, cedar, oak, cypress Drained for urban development, farms, residential building, or commercial factories