Levels of Organization Worksheet: Cells to Organisms
advertisement

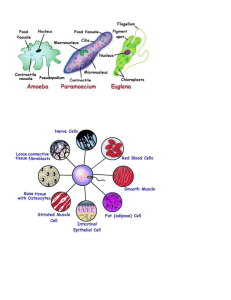
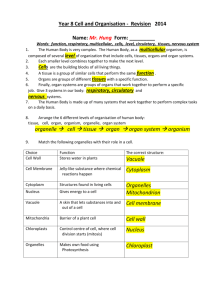
Name Date Content Practice A Class LESSON 2 Levels of Organization Directions: On the line before each definition, write the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Each term is used only once. B 1. a cell that can become many different cell types A. cell differentiation C 2. a group of similar cells that work together to B. stem cell carry out a specific task E 3. a group of different organs that work together to complete a series of tasks A 4. the process by which cells becomes different types of cells F 5. a group of organ systems that carry out all the jobs needed for their survival D 6. a group of different tissues working together to perform a particular job C. tissue D. organ E. organ system F. organism Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that correctly completes each sentence. 7. Cells work together in a (multicellular/unicellular) organism. 8. A cell in a (multicellular/unicellular) organism must carry out all the activities that are necessary to survive. 9. Different types of cells in a multicellular organism have (different/the same) chromosomes. 10. Multicellular organisms are (eukaryotes/prokaryotes). Name Date Content Practice B Class LESSON 2 Levels of Organization Directions: Answer each question or respond to each statement on the lines provided. 1. How are unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms the same? They both have the six characteristics shared by all living things 2. How are a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism different? Multicellular organisms have many cells which work together to keep the organism alive. Unicellular organisms have to rely on their one cell for all life functions. 3. What is cell differentiation? Why is it important? Differentiation is the process in which stem cells become specialized. This is important because it allows for an embryo to develop into a multicellular organism with specialized parts. 4. Explain how stem cells are necessary for cell differentiation. Stem cells are what differentiate to become specialized cells that eventually form tissues and organs. 5. Compare what makes up cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Cells are composed of organelles and molecules, tissues are composed of cells, organs are composed of tissues, and organ systems are composed of organs. 34 From a Cell to an Organism