Multicellular Organization
advertisement

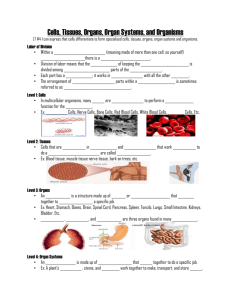
Structure and Function of The Cell Reference: Modern Biology CHAPTER 4 Multicellular Organization Modern Biology Chapter 4 - Sect. 3 Pgs. 86-88 BIG IDEAS **The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform one or a few functions **Cells of multicellular organisms depend on each other for the survival of the organism. MULTICELLULAR ORGANIZATION Multicellular Organisms • Contain many cells – Each cell has specific job • its structure fits its function or job • As multicellular organisms develop, their cells differentiate (change & separate) to form different types of cells. • The cells eventually group together to form tissues • Tissues come together to form organs • Organs form organ systems and organ system form the organism. Cells tissues organs organ systems ORGANISM 4 Levels of Organization 1. Cell -performs functions that work with other cells to keep organism alive -many different types of cells 2. Tissue -group of similar cells that carry out a common function – Ex: epithelial tissue made of sheets of closely packed cells that form surface coverings. 3. Organ -group of several types of tissues that interact to perform a function - Ex: Your heart is made up of muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Muscle tissue makes your heart pump, nerve tissue tells it when to pump and connective tissue holds the parts together. 4. Organ System -group of several organs working together to perform a series of related tasks Example: mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines work together to digest food. *All organ systems work together to carry out all the functions of life for the organism. MULTICELLULAR ORGANIZATION FYI: Plants also have cells, tissues, and organs. Plant cells form different kinds of tissues. For example, one tissue type covers the outside of a leaf. Another tissue transports water and nutrients. Special kinds of tissue form plant organs. Flowers, leaves, stems, and roots are all plant organs. MULTICELLULAR ORGANIZATION COLONIAL ORGANISMS Group of genetically identical cells that live in a closely connected group. Example: Volvox – Contains 500-6000 cells. – Cells maintain individual existence. » Some are specialized to carry out a specific task. Volvox Video Volvox Dances - Bing Videos STEM CELLS • Undifferentiated (“blank slate”) cells with the potential to become any cell in the body. – Found in embryos, umbilical cords, and adult bone marrow – Injected into patients to possibly treat degenerative diseases, burns, or other serious injuries – Controversial because obtaining embryonic stem cells requires the destruction of living embryos STEM CELLS http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-are-stem-cells-craig-a-kohn#watch Microscopic (10X) view of a colony of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells