Creative thinking - Assuring Graduate Capabilities
advertisement

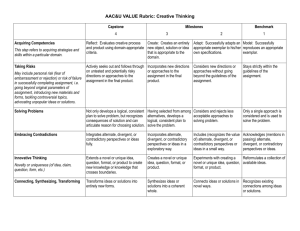
CREATIVE THINKING STANDARDS — MARKETING — UNISA Adapted from the AAC&U VALUE Rubrics and acknowledged with thanks. See Assuring Graduate Capabilities Definition: Creative thinking is the capacity to combine or synthesize existing ideas, images, or expertise in original ways and the experience of thinking, reacting, and working in an imaginative way characterized by a high degree of innovation. Novice to Competent categories Acquiring Competencies Refers to acquiring knowledge and skills within a particular field of study. Curiosity and Risk taking May include personal risk (fear of embarrassment or rejection) or risk of failure in completing assignment. Beginner Students after their first year can … List and describe: Successfully reproduce an appropriate exemplar by listing relevant independent aspects and describing their effects. Novice Students after their second year can … Relate and adapt: Successfully adapt appropriate exemplars by integrating one or more related independent aspects into an original structure. Competent Graduates can … Reflect, explain and hypothesise: Reflect on what has been discovered and generate hypotheses that explain the causes of relevant aspects in a particular field of study. Stay strictly within the guidelines of the assignment. Include some new directions or approaches but stay Explore new directions or approaches to the within the guidelines of the assignment. assignment, which may differ from those suggested in the course. Formulate and logically defend an informed opinion supported by relevant facts or experience that has been generated by themselves or by others. Embracing Contradictions Acknowledge (mention in passing) alternate, divergent or contradictory perspectives or ideas. Include (recognize the value of) alternate, Incorporate alternate, divergent or contradictory divergent, or contradictory perspectives or ideas in perspectives or ideas in an exploratory way and a small way. debate their benefits and shortfalls. Innovative Thinking Reformulate a collection of available ideas. Experiment with creating a novel or unique idea, question, format or product. Create a novel or unique idea, question, format, or product. Compare and contrast different ideas or solutions and connect them in novel ways. Synthesize new concepts by assembling existing ideas or solutions into a coherent and unique whole. Novelty or uniqueness (of idea, claim, question, form, etc.) Connecting, Synthesizing, Recognize existing connections among ideas or Transforming solutions. Exemplars Suggest different ways in which a firm could take advantage of an identified marketing opportunity, but not necessarily be able to evaluate those options through appropriate application of relevant theory. Generate original ideas, examples, personal Complete a task given an incomplete or experiences or observations, and explain how those rudimentary outline of what is required, such as support or contradict the content of an academic developing an advertising brief for an agency based article or lecture. on a broad marketing strategy outline. Support for this resource has been provided by the Australian Learning and Teaching Council Ltd, an initiative of the Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations. The views expressed in this resource do not necessarily reflect the views of the Australian Learning and Teaching Council. Last updated May 2011.