Syllabus
advertisement

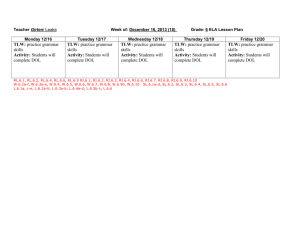
Syllabus First Nine Weeks Unit 1 - Scientific Method and Processes Unit Goal: TLW (The Learner Will) identify and describe basic principles of science and demonstrate the approach used by scientists to investigate the natural world. Textbook References: Chapter 1 Objectives: TLW Identify general and specific topics studied in biology. TLW Identify and describe characteristics of living things. TLW Define homeostasis and describe why it is important to organisms. TLW Identify, list, and describe the steps of the scientific method. TLW Design and conduct controlled, inquiry-based experiments. TLW Collect, organize, analyze, and interpret quantitative and qualitative data. Unit 2 – Biodiversity Taxonomy and Classification Unit Goal: The Learner Will (TLW) identify criteria used for classifying organisms into different taxonomic kingdoms. Textbook References: Chapter 18 Objectives: TLW Describe the contributions of Carolus Linneaus to the science of taxonomy. TLW Use rules of binomial nomenclature to identify and write the scientific names of organisms. TLW Identify criteria used in the classification of organisms into taxonomic groups. TLW List and describe the major characteristics of the three domains and six kingdoms of organisms. TLW Construct, interpret, and use dichotomous keys to classify objects and unknown species of organisms. Microorganisms Unit Goal: TLW analyze the diversity of living organisms that are neither plants nor animals; viruses*, bacteria, and protists. (*Denotes a nonliving microscopic particle.) Textbook References: Chapters 19 and 20 Objectives: TLW examine the structure of various types of viruses emphasizing viral characteristics and viral reproduction via the lytic and lysogenic cycles. TLW analyze reasons why viruses are such effective agents of infection. TLW compare and contrast members of Kingdoms Archaebacteria and Eubacteria with special emphasis placed on their adaptations to different environments, classification, roles as nutrient recyclers, and roles as agents of disease. TLW compare and contrast members of Kingdom Protista with special emphasis placed on their adaptations to different environments, classification, roles in ecosystems, and roles as agents of disease. Fungi Unit Goal: TLW describe the classification, morphology, and ecological importance of fungi. Textbook References: Chapter 21 Objectives: TLW compare and contrast members of Kingdom Fungi with special emphasis placed on their adaptations to different environments, roles in ecosystems, economic importance, and roles as agents of disease. TLW identify and describe the major phyla of fungi and representative examples from each phyla. Second Nine Weeks Plants Unit Goal: The Learner Will (TLW) compare and contrast the different classifications of plants by analyzing plant structures and their functions. Textbook References: Chapters 22, 23, 24, and 25 Objectives: TLW list and describe general characteristics of members of Kingdom Plantae. TLW compare and contrast the four major groups of plants: mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and sngiosperms. TLW describe the structure and function of roots, stems, leaves, and vascular tissues. TLW relate the advantages of seeds and cones to the evolution and adaptation of gymnosperms. TLW relate the advantages of flowers, fruits, and covered seeds to the evolution and adaptation of angiosperms. Animals Unit Goal: TLW compare and contrast major anatomical structures and features of invertebrates and vertebrates. Textbook References: Chapters 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, and 32 Objectives: TLW compare and contrast methods of locomotion, feeding, respiration, circulation, and reproduction in common invertebrates. TLW analyze structural adaptations that enabled common invertebrates to adapt to their environments. TLW describe the ecological importance of common invertebrates. TLW compare and contrast methods of locomotion, feeding, respiration, circulation, and reproduction in common vertebrates. TLW compare and contrast anatomical structures and basic physiology among representative members of the five vertebrate classes. TLW analyze structural adaptations that enabled common vertebrates to adapt to their environments. Unit 2 - The Cell Structure and Function Unit Goal: TLW analyze how cell structures carry out specific cell functions. Textbook References: Chapter 7 Objectives: TLW Demonstrate knowledge of the structure and proper use of a microscope. TLW Identify components of the cell theory. TLW Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellular organization. TLW Identify and describe the functions of cellular organelles. TLW Compare and contrast plant and animal cells. TLW Differentiate between unicellular and multicellular organisms. TLW Describe the hierarchy of cellular organization. TLW Describe the structure and functions of the plasma membrane. TLW Identify and describe different cellular transport processes. TLW Analyze factors that affect cellular activities: molecular factors and environmental factors. The Cell: Growth and Division Unit Goal: The Learner Will (TLW) describe why somatic (body) cells divide and how cell division takes place. Textbook References: Chapter 10 Objectives: TLW Analyze why cells divide by relating surface area to volume. TLW Describe the importance of the cell cycle emphasizing the role of mitosis. TLW Identify and describe the major events taking place during each of the four phases of mitosis. TLW Compare and contrast mitosis in plant and animal cells. Third Nine Weeks Unit 3 – Interdependence Photosynthesis and Respiration Unit Goal: TLW analyze the production, release, and utilization of energy involved in photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Textbook References: Chapters 8, 9, and 3 Objectives: TLW Define ATP and describe how energy is stored and released from ATP molecules. TLW Explain the relationships between matter and energy shown by food chains and food webs. TLW Compare and contrast the ways matter (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and water) cycle through biotic and abiotic components of ecosystems. TLW Summarize the process of photosynthesis emphasizing reactants, products, role of chloroplasts, and chlorophyll. TLW Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration processes emphasizing the roles of oxygen, mitochondria, and ATP molecules. Ecology Unit Goal: TLW describe the interdependence between organisms and their environment. Textbook References: Chapters 4 and 5 Objectives: TLW Compare and contrast major biomes of the earth, paying particular attention to the adaptations of plants and animals living in each biome. TLW Identify three forms of community interactions that affect ecosystems. TLW Compare and contrast primary and secondary forms of ecological succession. TLW Explore factors that contribute to changes in population growth. Fourth Nine Weeks Unit 4 - Genetics: Heredity and Reproduction Unit Goal: TLW recognize how cells store, transmit, and express genetically encoded information and how these processes are important in understanding inheritance patterns. Textbook References: Chapters 11, 12, and 14 Objectives: TLW TLW Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis in terms of purpose, chromosome number, variation, and cellular occurrence. TLW Categorize different types of mutations that occur in DNA as chromosomal or gene. TLW Identify common sources of genetic mutations in the environment; radiation, chemical, and chance. TLW Create and interpret information from genetic pedigrees. TLW Identify Mendel's three laws of genetic inheritance. TLW Apply Mendel's laws to determine possible allele combinations in offspring by completing monohybrid and dihybrid crosses. TLW Predict and analyze statistical data from monohybrid and dihybrid genetic crosses. TLW Identify human genetic disorders that are caused by autosomal dominant alleles, recessive alleles, and sex-linked alleles. TLW Identify common polygenic traits and describe their transmission among populations. TLW List and describe the phases of meiosis and how this process transfers genetic information. TLW Analyze the structure, function, and importance of DNA. TLW Construct a model of DNA and describe how the structure of DNA facilitates replication. TLW Identify and sequence the steps in protein synthesis; replication, transcription, and translation. Unit 5 - Evolution Unit Goal: TLW describe the role that natural selection plays in producing the great diversity among living things. Textbook References: Chapters 15, 16, 17, and 32.3 Objectives: TLW Describe the importance of fossil evidence, anatomical studies, embryological studies, and genetic comparisons in substantiating the theory of evolution. TLW Identify and describe theoretical mechanisms for evolution by natural selection; genetic drift, isolation, and acquired characteristics. TLW Describe the conditions needed for the process of fossil formation. TLW Demonstrate how fossils are dated using radioisotopes and half-life calculations. TLW Summarize Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. TLW Examine why natural selection and genetic drift affect populations rather than individuals. TLW Summarize the effects of different types of natural selection on a gene pool. TLW Describe the process of speciation and identify factors that affect speciation. TLW Compare and contrast convergent and divergent evolutionary processes. TLW Analyze environmental changes and adaptations associated with the evolution of primates and hominids