Efrain`s PCR cheat sheet - 2nd School on Representational Analysis
advertisement
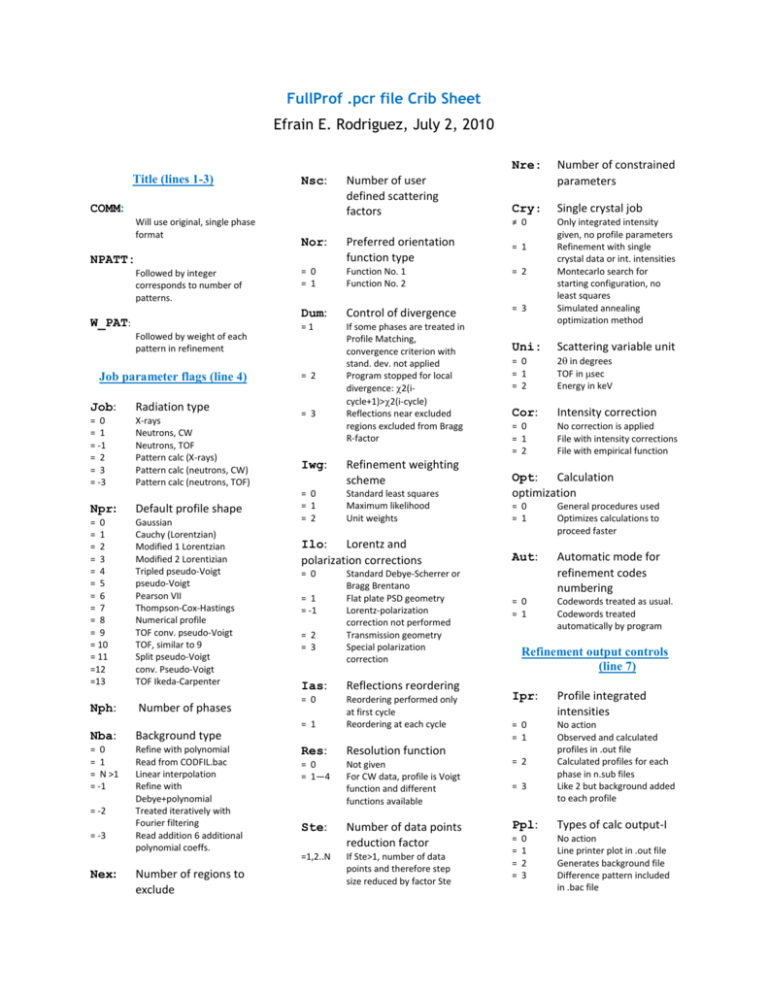
FullProf .pcr file Crib Sheet Efrain E. Rodriguez, July 2, 2010 Title (lines 1-3) Nsc: COMM: Will use original, single phase format W_PAT: Followed by weight of each pattern in refinement Job parameter flags (line 4) Job: Radiation type = 0 = 1 = -1 = 2 = 3 = -3 X-rays Neutrons, CW Neutrons, TOF Pattern calc (X-rays) Pattern calc (neutrons, CW) Pattern calc (neutrons, TOF) Npr: Default profile shape = 0 = 1 = 2 = 3 = 4 = 5 = 6 = 7 = 8 = 9 = 10 = 11 =12 =13 Gaussian Cauchy (Lorentzian) Modified 1 Lorentzian Modified 2 Lorentizian Tripled pseudo-Voigt pseudo-Voigt Pearson VII Thompson-Cox-Hastings Numerical profile TOF conv. pseudo-Voigt TOF, similar to 9 Split pseudo-Voigt conv. Pseudo-Voigt TOF Ikeda-Carpenter Nph: Number of phases Nba: Background type = 0 = 1 = N >1 = -1 Refine with polynomial Read from CODFIL.bac Linear interpolation Refine with Debye+polynomial Treated iteratively with Fourier filtering Read addition 6 additional polynomial coeffs. = -2 = -3 Nex: Number of regions to exclude Nre: Number of constrained parameters Cry: Single crystal job ≠ 0 Only integrated intensity given, no profile parameters Refinement with single crystal data or int. intensities Montecarlo search for starting configuration, no least squares Simulated annealing optimization method Nor: Preferred orientation function type = 0 = 1 Function No. 1 Function No. 2 = 2 Dum: Control of divergence = 3 =1 If some phases are treated in Profile Matching, convergence criterion with stand. dev. not applied Program stopped for local divergence: 2(icycle+1)>2(i-cycle) Reflections near excluded regions excluded from Bragg R-factor NPATT: Followed by integer corresponds to number of patterns. Number of user defined scattering factors = 2 = 3 Iwg: Refinement weighting scheme = 0 = 1 = 2 Standard least squares Maximum likelihood Unit weights Ilo: Lorentz and polarization corrections = 0 = 1 = -1 = 2 = 3 Standard Debye-Scherrer or Bragg Brentano Flat plate PSD geometry Lorentz-polarization correction not performed Transmission geometry Special polarization correction = 1 Uni: Scattering variable unit = 0 = 1 = 2 2 in degrees TOF in sec Energy in keV Cor: Intensity correction = 0 = 1 = 2 No correction is applied File with intensity corrections File with empirical function Opt: Calculation optimization = 0 = 1 General procedures used Optimizes calculations to proceed faster Aut: Automatic mode for refinement codes numbering = 0 = 1 Codewords treated as usual. Codewords treated automatically by program Refinement output controls (line 7) Ias: Reflections reordering = 0 = 1 Reordering performed only at first cycle Reordering at each cycle Res: Resolution function = 0 = 1—4 Not given For CW data, profile is Voigt function and different functions available = 2 Ste: Number of data points reduction factor Ppl: Types of calc output-I = = = = No action Line printer plot in .out file Generates background file Difference pattern included in .bac file =1,2..N If Ste>1, number of data points and therefore step size reduced by factor Ste Ipr: Profile integrated intensities = 0 = 1 No action Observed and calculated profiles in .out file Calculated profiles for each phase in n.sub files Like 2 but background added to each profile = 3 0 1 2 3 Wdt: Cut off for peak profile tails in FWHM units = 7 = 8 = 10 = 11 = 12 GENERAL FORMAT for TWO AXIS D1A/D2B format prepared by SUM, ADDET or MPDSUM From D4 or D20L DMC at Paul-Scherrer Inst. X, Y, sigma fromat Variable time XRD GSAS ~4 ~20-30 ~4—5 for Gaussian for Lorentzian for TOF Output .rpa/.sav file muR: = 5 Ioc: Types of calc output-II = 0 = 1 No action List of observed and calculated integrated intensities in .out file Reflection from 2nd wavelength if different = 2 = 6 Mat: Correlation matrix Rpa: = 0 = 1 No action Correlation matrix written in .out file Diagonal of LS matrix printed before inversion at every cycle = 0 = 1 = 2 Pcr: = 0 = 1 = 2 Update of .pcr after refinement .pcr re-written with updated parameters New input file generated called .new = 2 Prepares output file CODFIL.rpa Prepares file CODFIL.sav Sym: Output .sym file = 0 = 1 Prepares CODFIL.sym Hkl: Output of reflection list =0 = 1 No action Code, h, k, l, mult, d_hkl, 2, FWHM, I_obs, I_calc, I_obscalc h, k, l, mult, sinq/l, 2, FWHM, F2, s(F2) Real and imaginary parts of structure factors, h, k, l, mult, F_real, F_imag, 2, intensity h, k, l, F2, (F2) h, k, l, mult, F_calc, T_hkl, d_hkl, Q_hkl = 2 Ls1: Types of calc output-III = 0 = 1 No action Reflection list before starting cycles written in .out file = 3 Ls2: Types of calc output-IV = 0 = 1 No action Corrected data list written in .out file Plot of diffraction pattern displayed on the screen at each cycle = 4 = 5 = 4 LS3: Types of calc output-V = 0 = 1 No action Merged reflection list written in .out file Prf: Output format of Rietveld plot file = = = = 0 1 2 3 = 4 For WinPLOTR For IGOR For KaleidaGraph and WinPLOTR For Picsure, Xvgr Ins: Data file format First 3 real values are Ti, step, Tf = = = = = Free format, 7 comments ok D1A/D2B, original Rietveld D1B old format ILL instruments D1B, D20 Brookhaven, pairs of lines with 10 items DBWS program 0 1 2 3 4 = -4 Cthm: Monochromator polarization correction Absorption correction m = effective absorption coeff. R= radius or thickness of sample AsyLim: Limit angle for asymmetry correction Rpolarz: Polarization factor Iabscor: Absorption correction for TOF data = 1 = 2 = 3 Flat plate perp. to inc. beam Cylindrical Exponential, Abs = exp(-c2) Refinement controls (line 9) Fou: Output of CODEFIL.fou NCY: = = = = = No action Cambridge format SHELXS format FOURIER format GFOURIER Number of refinement cycles Eps: Control of convergence precision 0 1 2 3 4 Sho: = 0 = 1 Reduced output during refinement Forced termination when shifts < EPS x e.s.d R_at shifts of atomic parameters: coordinates, moments, occupancies, Uiso’s Suppress out from each cycle, only last printed Experimental set up controls (line 8) Lamda1:wavelength 1 Lamda2:wavelength 2 Ratio: I2/I1 If <0, parameters U,V,W for l2 read separately Bkpos:Origin of polynomial for background Relaxation factor of R_an Relaxation factor for shifts of anisotropic displacement parameters R_pr: Relaxation factor of profile parameters, asymmetry, overall displacement, cell constants, strains, size, propagation vectors, user-supplied parameters R_gl: Relaxation factor of Global parameters, zeroshift, background, displacement and transparency Thmin: Starting scattering variable value (2/TOF/Energy) Step: Step in scattering variable Thmax: Last value of scattering variable PSD: Incident beam angle Sent0: Maximum angle at which primary beam completely enlightens sample Number of refined parameters Maxs: Number of refined parameters (one integer, one line) Refinement controls II (line 14, refinable) Zero: Zero point for T Sycos: Systematic shift with cos dependence Zerot: Zero shift for thermal neutrons = -2 Dtt1t: Coeff. #1 for d-spacing calc = -3 Dtt2t: Coeff. #2 for d-spacing calculation x-cross: Position of the center of the crossover region Lambda: Wavelength to be refined More: Flag to read microabsorption coefficients ≠ 0 Line 15 is read to define microabsorption Jason-Hodges formulation for TOF data (line 16) = 4 = 5 = 10 = 15 Width: Width of crossover region Background parameters (line 17) Nba = 0, = -1 = -3 = N>1 6 coefficient polynomial, 6 reals-6 codes 6 coefficient polynomial + Debye, 6 reals-6 codes-6 reals-6 codes-6 reals-6 codes 12 coefficient, 6 reals-6 codes-6 reals-6codes interpolation with N values for 2, background, and codes Pr1, Pr2, Pr3: Preferred orientation in reciprocal space for all three directions Irf: = 0 = 1 = 2 = 3 = 4 Refinement parameters for each phase (line 19) Nat: Number of atoms in asymmetric unit Dis: Number of distance constraints Mom: Number of angle constraints or number of magnetic moment constraints Jbt: = 0 = 1 = -1 = 2 Structure factor model and refinement method Rietveld Method Rietveld Method but purely magnetic phases Like 1 but with extra parameters in spherical coordinates Profile matching mode with constant scale factor Method of reflection generation List of reflections for the phase generated by space group h, k, l, mult read from .hkl file h, k, l, mult, intensity read from .hkl file h,k,l, mult, F_real, F_imag read from .hkl file list of integrated intensities given as observations Isy: Symmetry operators reading control code = 0 Operators automatically generated from Space Group Symmetry operators read below (use for magnetism) Basis functions of irreducible representations of propagation vector group instead of symmetry operators = 1 Sysin: Systematic 2 shift with sin2 dependence = 3 Like 2 but modulus instead of intensity given in .hkl file Profile matching with constant relative intensities Like 3 but modulus instead of intensity given in .hkl file Intensities of nuclear reflections are calculated from Rigid body groups Intensities of magnetic reflections calculated from conical magnetic structures in real space Phase can contain nuclear and magnetic contributions Phase is treated as commensurate modulated crystal structure = 2 Str: Size-strain reading control = 0 Strain/size parameters correspond to selected models Generalized formulation of strain used Generalized formulation of size used Options 1 and 2 simultaneously, size read before strain Generalized formulation of size and strain parameters = 1 = 2 = -1 = 3 Furth:Number of user defined parameters (only when Jbt=4) ATZ: Z: Mw: f: t: Quantitative phase analysis coefficient ATZ = ZMwf2/t Formula units per cell Molecular weight Site multiplicity Brindley coefficient for microabsorption Nvk: Npr Number of propagation vectors Specific profile function for the phase Scale: Scale factor = 1 to 14 One of the 14 Laue classes as represented by an integer Shape 1: MagMat: Bov: Atom: Atom name Typ: Atom type X, Y, Z: Coordinates Biso: Isotropic B factor Occ: Occupancy In/Fin: Ordinal number of first and last symmetry operator applied to the atom (when users supply own list of reflections) N_t: Atom type = 0 = 2 = 4 Isotropic atom Anisotropic atom Form-factor of atom is calculated Spc: Number of chemical species (For bond valence calcs.) betaij: 6 numbers (i,j =1,2) for anisotropic factors (line 25b) Profile shape parameters Overall isotropic B factor DepMat: Number of atomic displacement rotation matrices (not really magnetism) Str1, Str2, Str3: Strain parameters Strain Model: Ireps: Number of irreducible representations U,V,W: Half-width parameters X: Lorentzian isotropic strain param. More: If not 0, then line 19-1 read Atomic parameters (line 25) Number of magnetic rotation matrices Profile shape parameter Y: Lorentzian isotropic size param. GauSiz: Isotropic size parameter of Gaussian character LorSiz: Anisotropic Lorentzian contribution of particle size Size-Model: Size model selector N_Bas: Number of atomic basis functions User-defined symmetry operators or basis functions (line 24) Sij: Symmetries relating atomic positions (integers). There are 9 along with 3 real numbers (Ti) Mij: Matrix relating Fourier components of magnetic moment. They are 9 integers followed by the phase, Ph written as real numer. Dij: Matrix relating Fourier components of the displacement parameters They are 9 integers followed by the phase, Ph written as real numer. (not really for magnetism) Data range parameters (last line) 2Th1/TOF1: First value for x-axis 2Th2/TOF2: Last value for x-axis SYMM: (For Isy = -1) Magnetic refinement job type (line 23) Coordinates of the atom site DSYM: (For Isy = -1) Nsym: Fourier components of the displacement vector along x,y,z and given in symbols u,v,w. Real numerical value at end is the phase in units of 2pi. Number of symmetry operators Cen: =1 =2 Laue: Non-centrosymmetric Centrosymmetric MSYM: Occupancy of the site (For Isy = -1) Fourier components of the magnetic vector along x,y,z and given in symbols u,v,w. Real numerical value at end is the phase in units of 2pi SYMM: RX,RY,RZ: Components along the crystallographic axis of the moments RM, Rphi, Rthet: (For Isy = -2) Components given in spherical coordinates Coordinates of the atom site IX,IY,IZ: BASR: Imaginary components along the crystallographic axis of the moments (For Isy = -2) The numbers corresponding the real part of the basis vectors for a particular site. Im, Iphi, Ithet: Imaginary components given in spherical coordinates BASI: (For Isy = -2) The numbers corresponding the imaginary part of the basis vectors for a particular site C1 to C9: Coefficients of the basis functions MagPh: Atomic parameters for magnetic phase (line 23) ATOM: Identification name Typ: Atom type used for getting actual scattering power of the site Mag: Magnetic rotation matrix identifier. Ordinal number of the matrix applied to moment of the atom site Vek: =0 <0 Propagation vector identifier. Ordinal number of the vector applied to moment of atom site atom contributes to all the propagation vectors atom contributes to two vectors: Vek and (Vek + NvK/2) X,Y,Z: Fractional atomic coordinates Biso: Isotropic displacement parameter Occ: Magnetic phase. Given in units of 2pi