Rocks and Minerals Study Guide
advertisement

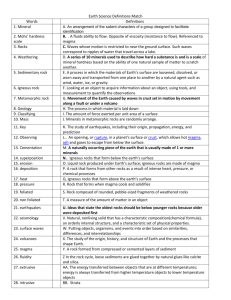
Science: Chapter 2, Unit C Study guide Rocks and Minerals ASSESSMENT DATE:_____________________ STUDENTS SHOULD USE THIS STUDY GUIDE IN ADDITION TO THEIR TEXTBOOKS, INTERACTIVE NOTEBOOKS AND ONLINE FLASHCARDS. ONLINE FLASHCARDS ARE AVAILABLE AT HTTP://QUIZLET.COM/15420063/ROCKSAND-MINERALS-FLASH-CARDS/ KEY VOCABULARY: Rock: Material made up of one or more minerals. Have properties that can be observed, tested and described. Can be classified into three categories: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock: Rocks that have been melted by Earth’s heat and then cooled (or hardened) over a long period of time. New rock. Examples include: basalt, obsidian and pumice. Metamorphic rock: A rock that has been changed by high heat and great pressure. Changed Rock. Examples include: marble, gneiss and slate. Sedimentary rock: Forms when rock pieces and layers are deposited over time and pressed together. Fossils are most commonly found in this type of rock. Examples include: sandstone, limestone and shale. Rock Cycle: The pattern of slow changes in rocks from one kind to another. Rocks are formed, changed and reformed over long periods of time. This process involves heat, pressure, compaction, cementing, melting, erosion, weathering and deposition. Students should be able to draw and label this cycle. Mineral: A natural solid that has its particles arranged in a crystal pattern. Formed in the mantle or deep in the crust. Made from particles that were never alive. Example uses: graphite pencils, musical instruments, coins, jewelry, cars, appliances and salt. Properties of Minerals: Color, Luster, Hardness, and Streak. Luster: Describes how a mineral’s surface looks when light reflects from it. Hardness: Describes to what extent a mineral can resist being scratched. This is shown using a scratch test. Harder minerals scratch softer minerals. Moh’s Hardness Scale is a scratch test where 1(talc) is the softest and 10 (diamond) is the hardest. Streak: The color of the dust, or powder, left behind by a mineral when rubbed against a tile. Science: Chapter 2, Unit C Study guide Rocks and Minerals KEY CONCEPTS THAT STUDENTS SHOULD UNDERSTAND: The difference between rocks and minerals Model and explain how igneous rocks could be changed into sedimentary rock Model and explain how metamorphic rocks form Explain why fossils can be present in sedimentary rocks but can never be found in metamorphic and igneous rocks. Students should be able to determine which minerals could scratch eachother using Moh’s hardness scale below. For example, Quartz can scratch Apatite. Moh’s Hardness Scale 1 is the softest. 10 is the hardest 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Talc Gypsum Calcite Fluorite Apatite Orthoclase Quartz Topaz Corundum Diamond ROCK CYCLE Rocks move and change over time due to heat and pressure within Earth and due to weathering, erosion, and deposition at the surface. These and other processes constantly change rock from one type to another. Science: Chapter 2, Unit C Study guide Rocks and Minerals Depending on how rocks are formed, they are classified as sedimentary (layers of sediment cemented together) igneous (melted and cooled, e.g., lava and magma) metamorphic (changed by heat and pressure) ROCK IDENTIFICATION Rocks have properties that can be observed, tested, and described. Composition, grain size and textural features, color, and the presence of fossils help with identification. Science: Chapter 2, Unit C Study guide Rocks and Minerals ANCIENT EARTH - FOSSILS Scientific evidence indicates Earth is ancient — approximately 4.6 billion years old. The age of many rocks can be determined very reliably. Fossils provide information about life and conditions of the past. Study Tips: Reread the work in your notebook Reread Chapter 2 , Unit C in your Science textbook Quiz yourself on vocabulary Ask a friend or family member to quiz you on key terms and key concepts Highlight terms or concepts that you don’t understand and find the answers in your book and notebook Take a practice test Use flashcards and play games on Quizlet Remember, knowing the vocabulary will only get you a 2! You will need to study your notes and classwork to get a 3 or a 4!