Prelab Review
advertisement

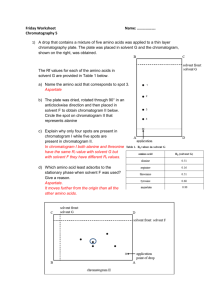
CHEM 1030L Fundamentals of Chemistry Laboratory Pre-lab Review – Paper Chromatography of Amino Acids Prepare for Laboratory 1. Review the following textbook section(s) 9.1 – Solutions 16.1 – Proteins and Amino Acids 16.2 – Amino acids as acids and bases 2. Review the background and procedure for this lab that are posted online. 3. Be able to work the following textbook problems. 9.5, 16.3, 16.5, 16.7 4. Be able to summarize the purpose of the experiment. Two or three sentences summarizing what you will do, what you expect to learn, and what chemical or scientific principles you expect to understand better. Imagine what you would tell your roommate over a breakfast of Pop-Tarts about what you will be doing in lab that day. 5. Know and be able to do the following. a. Calculate Rf from spot height data b. Determine the identity of spots based on data similar to the problem in #6, below. c. Know the safety and waste disposal considerations for the experiment. d. Define or briefly explain the following terms mobile phase eluent stationary phase visualization chromatography like dissolves like solute solvent 6. Example questions a. What is the stationary phase used in this experiment? b. Name two materials used in this experiment that are health hazards. c. Name two ways that acetic acid is hazardous to health. d. Name two items that must be kept in the fume hood at all times in order to prevent exposure to acetic acid fumes. e. Why must gloves be used when handling the chromatogram? f. What kind of writing instrument must be used to mark the chromatogram? g. Compounds that are very soluble in the mobile phase will not travel far up the chromatogram. True or False? h. Nonpolar solutes are soluble in polar solvents. True or False? i. During elution, the mobile phase must climb to the very top of the chromatogram. True or False? j. Name two things that can cause the chromatogram to elute improperly. Page 1 of 3 k. Sucrose is a polar compound. Is it more likely to be soluble in carbon tetrachloride (a nonpolar solvent) or water (a polar solvent)? l. What part of the amino acid determines whether it is polar, non-polar, acidic, or basic. m. Write the formula used to calculate Rf. n. Distances are to be measured to how many decimal places of cm? o. The measurements made on the chromatogram pictured at right resulted in the data in the following table. i. Calculate the Rf for each spot. (Answers are at bottom.) ii. Use the Rf and Observations to identify the two spots in the Unknown Sample. Sample ID Name Spot Height (cm) Solvent Height (cm) Observations Include spot color(s) and other observations A Compound A 2.5 8.4 Light gray spot with dark gray center B Compound B 1.5 8.2 Light gray spot with darkest area slightly above the center of the spot C Compound C 5.3 8.1 Uniform light gray spot 2.2 8.0 Light gray spot with dark gray center 5.1 8.0 Uniform light gray spot Unk1 Unk2 Unknown Sample spot #1 Unknown Sample spot #2 Answers 6.o.i. 0.30, 0.18, 0.65, 0.28, 0.64 Page 2 of 3 6.o.ii. A, C Page 3 of 3