Supplemental Combustion Analysis WS
advertisement

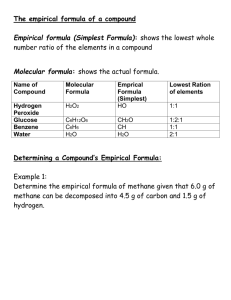
Supplemental Combustion Analysis Problems AP Chemistry Hart 1415 Review 1. Isobutylene is a hydrocarbon (contains carbon and hydrogen, no oxygen) used in the manufacture of synthetic rubber. Its molar mass is 56 g/mol. When 0.847 g isobutylene was analyzed by combustion, the amount of CO2 produced was 2.657 g and that of H2O was 1.089 g. a) What is the empirical formula of isobutylene? b) The molar mass of isobutylene is 56 g/mol. What is its molecular formula? (Silberberg, p. 125, #42) 2. Oleic acid is the major constituent of olive oil, its unsaturated structure providing olive oil’s positive health effects. When 0.988 g of oleic acid was analyzed by combustion, the amount of CO2 produced was 2.77 g and that of H2O was 1.07 g. It also contains oxygen. a) What is the empirical formula of oleic acid? b) The molar mass of oleic acid is 283 g/mol. What is its molecular formula? 3. Butyl butyrate, which contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, is one of a number of components that is used to create the smell of pineapple. When 0.858 g of butyl butyrate was analyzed by combustion, the amount of CO2 produced was 2.16 g and that of H2O was 0.663 g. a) What is the empirical formula of butyl butyrate? b) The molar mass of butyl butyrate is 140 g/mol. What is its molecular formula? 4. 2.500 g of a white powder known to contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is burned in a furnace. The resulting carbon dioxide (3.668 g) and water (1.502 g) are captured. a) What is the empirical formula of this substance? c) Mass spectrometer analysis reveals its molar mass to be 180 g/mol. What is its molecular formula? Recommended for everybody 5. Nicotine, a component of tobacco, is composed of C, H and N. A 5.250 g ample of nicotine was combusted, producing 14.242 g CO2 and 4.083 g H2O. a) What is the empirical formula of nicotine? b) If nicotine has a molar mass of 160 g/mol, what is its molecular formula? (Brown and LeMay, 11e, p. 112, #52b) Extension 6. A sample (1.37 g) of an organic compound containing C, H and O only, was burned in an excess of oxygen to yield water (1.64 g) and carbon dioxide (1.26 L), measured at 25oC and 1.33 atm. What is the empirical formula of the compound? (derived from University of Sydney Chemistry I Practice Problems p. 2-7, #2.42) 7. When 0.210 g of a gaseous compound containing only hydrogen and carbon was burned, 0.660 g of CO2 was recovered. a) What is the empirical formula of the compound? b) A determination of the density of this hydrocarbon gave a value of 1.87 g/L at 273 K and 1.00 atm. What is the molecular formula of the substance? (derived from University of Sydney Chemistry I Practice Problems p. 2-7, #2.41)