Highs Lows Fronts
advertisement

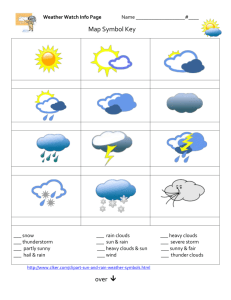
15.2 Highs, Lows, and Fronts Front a zone between air masses Cold Front a colder (polar) air mass that overtakes and moves past a warmer (tropical) air mass The warm air rises rapidly (updraft) because it is less dense than the cold air mass. The water vapour in the warm air cools quickly and condenses to form clouds. Cumulus clouds form due to the updraft. see Figure 15.12 p 497 Cumulonimbus (storm clouds) result from a fast moving cold front and a hot, humid (mT) air mass. Intense rain or snow that lasts a short time - Lightning, hail, and tornadoes may result in extreme cases. Warm Front a warmer (T) air mass moves over a slower cold (P) air mass. The water vapour in the warm air cools slowly and condenses to form clouds. Stratus clouds are common, but altostratus and cirrus clouds may also form. see Figure 15.13 p 497 Nimbostratus (rain clouds) result from a fast moving warm, humid (mT) air mass overtaking a cold air mass. Gentle rain or snow that lasts several hours or days. Stationary Front a front (cold or warm) that does not move; the warm air continues to slowly rise. see Figure 15.14 p 498 Stratus clouds remain for several days and may bring gentle rains (nimbostratus clouds) Highs and Lows Air pressure the force of the air exerted per square meter The air applies the same pressure on you from every direction. affected by: Air Temperature warm air rises (less pressure L) Humidity (%H2O) water molecules (H2O) have less mass than nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) molecules humid air weighs less than dry air moist air (less mass L) Normal Air Pressure cool air falls down (more pressure H) dry air (more mass H) 101.3 kPa (kilopascals) = 1 atm (atmosphere) Low Pressure (mT) air rising less than 101.3 kPa High Pressure (cP) air falling more than 101.3 kPa warm moist cool dry tropical depression = low pressure storm system resulting from a maritime tropical (mT) air mass cloudy, storms clear