-Water In The Air Water Cycle - continuous process/movement from

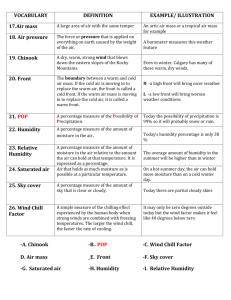
-Water In The Air
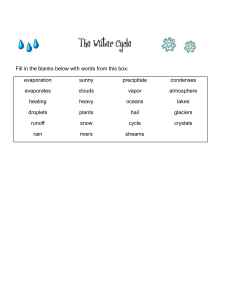
Water Cycle - continuous process/movement from water sources
Dew Point – when air can’t hold any more water/moisture, cools to saturation
Condensation – process water vapor/gas becomes water droplets/liquid
Evaporation -
Weather – condition in atmosphere particular time/place
Precipitation
Psychrometer - Measures relative humidity
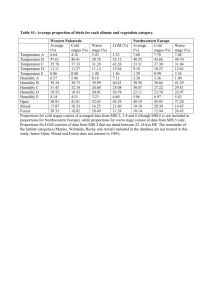
Relative Humidity – amnt of moisture in atmosphere compared to max it can hold
Humidity – water/moisture in air (more water vapor in air = higher % humidity)
-Clouds (collection of millions of water droplets/ice crystals)
Stratus – covers large areas, form in layers, water droplets (lowest)
Cumulous – warm air rises, when large, produce storms, flat bottoms, water droplets and ice crystals (middle)
Sirius – thin/feathery, form in strong wind, ice crystals (high)
Precipitation – when droplets become to heavy, they fall as precip
Hail- usually formed in cumulonimbus clouds
Rain guage- measures precip
-Air Masses and Fronts – large body of air w/ similar temps/moisture
Fronts – boundry between two air masses, leading edge of new air mass
Cold Front – violent storms, warm up, cold air down (followed by cooler weather)
Warm Front – drizzle, become clear warm warm air mass meets and uplifts cold
Occluded Front – cool temps, light precip,
Stationary Front – cold air meets warm air, little movement, continuous rain
Severe Weather
Cause property damage
Thunder Storm - small intense storm, strong winds heavy rain, lightning/thunder
Tornado – small rotating column of air, high wind speeds, touches ground
Hurricane – large rotating tropical storm, <119 Km/h winds, most powerful storms on earth
Forcasting the Weather
Thermometer – measures air temp
Barometer – measures air pressure
Forcast – prediction of weather 3-5 days, effects how you dress, know the forcast!
Wind Vane/Windsock – measures wind direction
Anemometer – measures wind speed
Isobars – lines connecting equal air pressure
Weather Balloon – measures air pressure, temperature, humidity
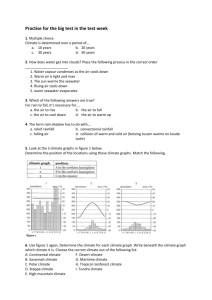
Climate – ave weather conditions in area long period of time
Seasons – 4 seasons
Latitude – distance North or South of equator, lower latitudes receive more energy, higher latitudes receive less energy
Altitude – Higher altitudes colder. Lower altitudes warmer
Prevailing winds – mainly blow in 1 direction
Elevation – height above sea level
Surface Currents – warm currents start at equator
Ice Age – period ice collects in high latitudes moving towards low latitudes
Earth’s Orbit – 100,000 years changes from circular shape to elliptical
Global Warming -
Greenhouse Effect – earth’s natural heating process
Volcanoes – ash in atmosphere, reflecting radiation back into space
Tectonic Plates – plates move across the world