Density Stations - Boone County Schools
advertisement

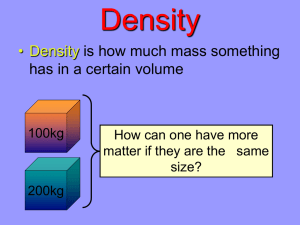
Density Stations NAME:__________________________________ Instructions: You will have 12 minutes to complete each of the seven stations. If you finish at your station before the timer goes off you are to work with your group to complete the last page of the packet entitled “A Matter of Density” – on this sheet you will calculate the density of four different liquids and then color in the order in which the liquids will settle out in the barrel on the back of the page. Cool fact about density: The density of Saturn is so low that if you were to put it in a giant glass of water it would float. STATION 1: Internet Assignment – The website is already on the computer for you. Do not close it out when you are finished. http://www.edathlon.com/science_challenges/density.htm If each ball has the same mass, which box would weigh more? Why? What is the formula for calculating density? Density of block 1Density of block 2Block 1 is made of – Block 2 is made of – Open a new tab and go to Google. Research which floats and which sinks – Coke or Diet Coke – Explain your findings STATION 2: Calculating the Density of Irregular Objects Density = Mass/Volume Mass – weigh on the digital scale – units (grams) Volume of an Irregular Object – displacement in a graduated cylinder (how much water is pushed up in the g.c.) – units (ml) 1. Find the density of the Lego Man Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 2. Find the density of the Marble Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 3. Find the density of the Aluminum Cylinder Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 4. Find the density of Buzz Lightyear Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 5. Find the density of the Monopoly car Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 6. Find the density of the Copper Cylinder Mass= Volume= Density Calculations= If you were to place all of the objects in a graduated cylinder, explain what order the objects would be in- you can illustrate if you would like. Test your hypothesis to see if you are correct STATION 3: Calculating the Density of Regular Shaped Objects Density= Mass/Volume Mass- weigh on digital scale – units (grams) Volume – L X W X H – units (cm3) 1. Find the density of the wood block Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 2. Find the density of the chalk board eraser Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 3. Find the density of the pack of index cards Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 4. Find the density of the Lego Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 5. Find the density of die Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = 6. Find the density of a domino Mass= Volume= Density Calculations = If you were to place these items in a tub of water, in what order would you find them? Explain. You may use an illustration if you would like. STATION 4: Calculating the Density of Liquids Calculate the density of each of the four liquids: Density = Mass/Volume Mass- Weigh the beaker on the balance (subtract the mass of an empty beaker) units (grams) Volume – read the line on the beaker – units (ml) Liquid 1: Mass________________,Volume___________________,Density______________ Liquid 2 Mass________________,Volume___________________,Density______________ Liquid 3: Mass________________,Volume___________________,Density______________ Liquid 4: Mass________________,Volume___________________,Density______________ Using the pipette found in each beaker of colored liquid, put 10ml of each liquid in the graduated cylinder. Draw what you see below: ****Empty your graduated cylinder in the middle sink and put it back on your desk. Based on your density calculations, which solution has the highest density? Which solution is the least dense? A raw egg will sink in fresh water, but will float in salt water. Explain why. STATION 5: Group Density Questions 1. 100 grams of a liquid completely fill a 200 mL bottle. What is the density of the liquid? 2. A solution has a density of 1.50 g/mL. How many grams are needed to obtain 10.0 mL of solution? 3. If a block of copper measures 2.00 cm x 4.00 cm x 5.00 cm and weighs 356 grams, what is its density? 4. A piece of silver has a mass of 2800 grams and occupies a volume of 266 cm 3. What is the density of silver? 5. Calculate the mass of a liquid with a density of 3.2 g/mL and a volume of 25 mL. 6. Calculate the density of a 500 g rectangular block with the following dimensions: length = 8 cm, width = 6 cm, height = 5 cm. 7. What determines if something will sink or float in water? a) Objects and substances less dense than the water will sink. b) Objects and substances less dense than the water will float. c) Objects and substances more dense than the water will float. d) Objects more dense that water will sink and substances more dense than the water will float. CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE Use the table below to answer the following question: 8. Which has the highest density? a) Beeswax b) Rock Salt c) Olive Oil Substance Mass Volume Density Beeswax 672 g 700ml Rock Salt 1853 g 850ml Olive Oil 550.8g 600ml Put a check by all the true statements. ____ a) Density is the relationship between the mass and volume of an object. ____ b) Density is the amount of stuff in a given amount of space. ____ c) The more salt you add to water, the less dense it becomes. ____ d) Mass is the amount of space taken up by an object. STATION 6: Candy bar Density Density = Mass/Volume Mass – digital scale– units (grams) Volume = L X W X H units (cm3) Problem: How do you find the density of candy bars? Materials: 2 “fun size” candy bars (Snickers or 3 Musketeers) Balance Metric Ruler 1. Measure the mass bar Snickers Mass= __________g. 3 Musketeers Mass =__________________g. 2. Measure the length, width and height of each candy bar in centimeters. Record the data in the space below. (No, it doesn’t really matter which way the candy bar is positioned- as long as you measure all 3 dimensions.) Length=____________ cm Length = _______________cm Width=_____________ cm Width = _______________cm Height=____________cm Height=_______________cm 3. Calculate the volume of each bar. Use the formula Volume= L x W x H a. Volume = _________________ cm3 b. Volume=_________________cm3 4. Calculate the density of each candy bar. Use the formula D=M÷V D= density M= mass V= volume a. Density = _________________ g/ cm3 b.Density = ________________ g/cm3 5. Considering that the volume of water is 1.0 g/ml, predict if the candy bar would float in water- or will it sink? Prediction: ______________________ What happened? ____________________ Which candy bar is the least dense? STATION 7: Dunkin’ for Density Objectives: • to determine the density at which an object will float, suspend or sink in water. • to use the formula density = mass/volume Materials: • Digital Scale • 3 empty film canisters per group • Aquarium filled with water • small objects of various masses (marbles, figures, etc.) • large beaker Procedure Part 1: 1. Using the materials at your desk, modify three film canisters so that they will float, sink, or remain suspended in the middle of a tub of tap water. 2. One canister should float (1) 3. Another should remain suspended (2) 4. And another should sink to the bottom (3) 5. Have your teacher check your canisters before you proceed to the next part. Procedure Part 2: 1. Once you have completed Part 1, use the equipment provided to find the mass and volume of each canister. 2. Record the information in Table 1. 3. Calculate the density for each canister using the formula D=M/V Data: Table 1: Mass, Volume and Density of film canisters Canister Mass (g) Volume (cm3) Density (g/cm3) Analysis and Results: 1. What is the mass of an empty film canister? ______________________________ 2. Did the mass of the canister change at all? Explain. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. Did the volume of the film canister change at all? Explain. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 4. What caused each canister to stay at their level in the water? Explain what caused the canisters to float, sink, or suspend using the term density. _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________