File - Just Remember the Past
advertisement

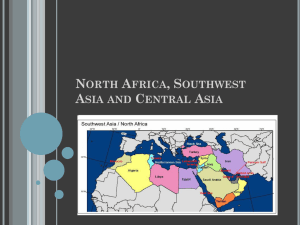
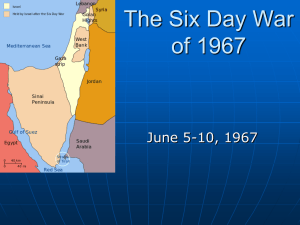
Middle East Glossary General OPEC- Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries. Founded in 1960, its aim to coordinate petroleum policies of its members, who include Iraq, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Venezuela and Nigeria. GCC (Gulf Co-operation Council)- political and economic union which consists of Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, UAE and Bahrain. Ba’ath Party- pan-Arab socialist movement. Has been in power in Syria since 1966 and dominated Iraq from 1968 to 2003. Pan-Arabism- Political ideology based on Arab nationalism and unity. Shi’a- branch of Islam dominant in Iraq, Iran and parts of Lebanon, although there are Shi’a minorities in Kuwait, Qatar, UAE and Saudi Arabia. There is a Shi’a majority in Bahrain although it is a Sunni kingdom. Iran is held up as the leader of Shi’a nations. Sunni- dominant branch of Islam in the rest of the Middle East, with Saudi Arabia the self-styled leader of Sunni countries. Scorched Earth- destructive policy sometimes pursued in war times when one side is retreating. In the Gulf War, the retreating Iraqi Army set fire to Kuwaiti oil wells. Iran-Iraq War- war fought between 1980 and 1988 with an estimated 2 million casualties on both sides. Very futile war fought in the manner of WWI and was a result of the Islamic Revolution in Iran. OPEC oil embargo (1974)- oil sanctions passed by OPEC members in response to Western support for Israel 1980’s oil glut- occurred when many OPEC members broke their own oil production quotas to flood the global markets with cheap oil and restore Western dependence on Middle Eastern oil, which had declined following the OPEC oil embargo. United Arab Republic (UAR)- political union of Egypt and Syria between 1958 and 1961. Sykes-Picot Agreement- secret British and French agreement which broke promises made to Arabs in return for revolting against the Ottoman Empire during World War One and divided the Middle East between them instead. Treaty of Sevres (1923)- Paris Peace Treaty that dealt with the Ottoman Empire and handed control of Iraq, Transjordan and Palestine to Britain and Lebanon and Syria to France. Kuwait Al Sabah- Kuwaiti royal family. Operation Desert Storm- UN military operation to liberate Kuwait from Iraqi control in 1991. Operation Desert Shield- UN military build-up in 1990 to protect Saudi Arabia from potential Iraqi invasion. Iraq Saddam Hussein- Ba’athist leader of Iraq between 1979 and 2003. Abd al-Karim al Qasim- Prime Minister of Iraq between 1958 and 1963. Leader of the July Revolution that overthrew the Iraqi monarchy. Assassinated during the 1963 Ramadan Revolution. Abdul Salam Arif- Deputy Prime Minister under Qasim and who overthrew him in the Ramadan revolution. President of Iraq between 1963 and 1966. Died of natural causes in 1966. July Revolution (1958)- Military coup d’état that removed the Iraqi monarchy in 1958. Ramadan Revolution (1963)- coup d’état that removed Qasim from power in 1963. Republican Guard- Saddam’s elite forces and bodyguard. Shatt al-Arab Waterway- river that connects the Southern Iraqi port of Basra to the Arabian Gulf. One of only two Iraqi points of access to the sea and lies along the Iran-Iraq border. It has frequently been a source of dispute between both countries. Halabja- Kurdish town in northern Iraq which was attacked by the Iraqi Army in 1988. Approximately 20,000 innocent civilians were killed used chemical weapons such as mustard gas and sarin nerve gas. This war crime was reported by western journalists. Baghdad- capital of Iraq. Rumailah oil field- Iraqi oil field that lies close to the border of Iraq. Iraq accused Kuwait of slant-drilling into the oil field. Iran Shah- Persian word for king. Mohammad Reza Pahlavi- the Shah of Iran who ruled from 1941 to 1979, when he was deposed during the Islamic Revolution. Mohammad Mossadegh- democratically elected nationalist and secular prime minister of Iran who was removed from power by coup d’état organized by the CIA and MI6 in 1953. He was deposed because he threatened to nationalise the oil holdings of the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company. Operation Ajax- joint CIA-MI6 operation to remove Mohammad Mossadegh from power. White Revolution- the Shah’s modernisation program that was launched in the 1960’s SAVAK- the Shah’s secret police, trained by Mossad (Israeli special forces) Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini- Shi’a Islamic cleric who was an opponent of the Shah and the White Revolution and chased into exile as a result. Lived in Iraq between 1964 and 1978, when he was told to leave by Saddam Hussein. He spent some time in Paris before returning to Iran in early 1979, leading the Islamic Revolution to remove the Shah’s government and create an Islamic republic. Islamic Revolution (1979)- population movement, supported by devout Muslims and opponents of the Shah, which deposed the Shah’s government and created an Islamic Republic in Iran. Khuzestan- Oil-rich coastal region of Iran with an Arab population of largely Iraqi origin. Claimed by Saddam Hussein and the disputes over the territory were a cause of the Iran-Iraq War between 1980 and 1988. Tehran- Capital of Iran Egypt Gamal Abdul Nasser- Pan-Arabian leader of Egypt between 1952 and 1970. He was extremely popular within the Arab world and was a leader of the non-aligned movement during the Cold War. Nasserism- Nasser’s vision of pan-Arabism, or Arab Nationalism. Aswan Dam- project proposed to assist with water distribution in the Nile Valley in the 1950’s. When US-Egyptian negotiations collapsed in 1956, the Soviet Union agreed to fund its construction, which was completed in 1958. Suez Canal- manmade waterway which connected the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea (and therefore the Western hemisphere to Asia). Originally co-owned by the UK and France, it was nationalised by Nasser in 1956 and led to the Suez Canal Crisis. Anwar Sadat- Leader of Egypt between 1970 and 1981, when he was assassinated by the Muslim Brotherhood. He managed to win back the Sinai Peninsula from Israeli control and signed the Camp David Peace Accords. Camp David Peace Accords (1979)- Peace treaty between Egypt and Israel. Egypt became the first Arab state to formally recognise Israel. ‘Shuttle’ Diplomacy- name given for the ‘back and forth’ diplomatic negotiations between Israel and Egypt and overseen by US Secretary of State Henry Kissinger between 1974 and 1977. Kissinger often travelled between Jerusalem and Cairo to negotiate an agreement. Muslim Brotherhood- Islamist organization in Egypt who were responsible for the assassination of Egyptian president Anwar Sadat in 1981. They recently won the Egyptian elections in 2011 but were subsequently removed by power by the Egyptian military in 2013. Arab-Israeli conflicts Balfour Declaration- 1908 declaration by British Foreign Secretary Balfour to create a Jewish state. Partition of Palestine (1948)- UN plan to divide Palestine in to Arab and Jewish areas. The Jewish community in Palestine accepted the plan and founded the state of Israel. The plan was rejected by the Arab League on behalf od the Palestinians Arabs. To this day, there is no formal recognition of a Palestinian state. Arab-Israel War of 1948- following the Partition of Palestine and creation of Israel, a number of Arab countries attacked Israel, although mostly to seize areas of land rather than to assist the Palestinian people. Eilat- southern Red Sea port in Israel. Blockaded by Egypt in the build-up to the Six Days War in 1967. Sinai Peninsula- Egyptian peninsula that connects North Africa to the Middle East (and Asia). The Suez Canal is located on the western side of the peninsula and it was in Israeli hands between the Six Days War and the Yom Kippur War. Golan Heights- Area of southern Lebanon that has often been occupied by Israeli forces in response to insurgent attacks in northern Israel. West Bank- Palestinian part of Jerusalem that lies on the western bank of the River Jordan. Gaza Strip- narrow strip of Palestinian land located on the Mediterranean coast of southern Israel on the border with Egypt. Six Day War (1967)- pre-emptive war by an Arab coalition against Israel. The Israeli defeated the Arab forces in six days and seized the Sinai Peninsula, the Golan Heights and the West Bank. Effectively destroyed Nasser’s credibility in the Arab world. Yom Kippur War (1973)- Arab attack on Israel launched during the Jewish holiday of Yom Kippur. Although largely an Arab failure, the Egyptians took back the Sinai Peninsula from Israel. David Ben-Gurion- considered the founding father of Israel and the first Prime Minister. Zionists- Jews committed to establishing a Jewish state in the Middle East. Chaim Weizmann- another important Zionist founder of Israel and the second prime minister. Golda Meir- female prime minister of Israel during the Munich Olympic massacre and the Yom Kippur War. Yasser Arafat- leader of the PLO PLO- Palestine Liberation Organisation. A loose coalition of Palestinian nationalist insurgency and political organisations that wanted to achieve Palestinian statehood. IDF- Israel Defence Forces Hamas- Sunni Islamist insurgency/paramilitary group responsible for terrorist attacks on Israel. Now in control of the Gaza Strip. Hezbollah- Lebanese Shi’a Islamist insurgency/paramilitary group funded by Iran.