The Six Day War of 1967Dominic,Charlotte, Taylor,Isabelle
advertisement
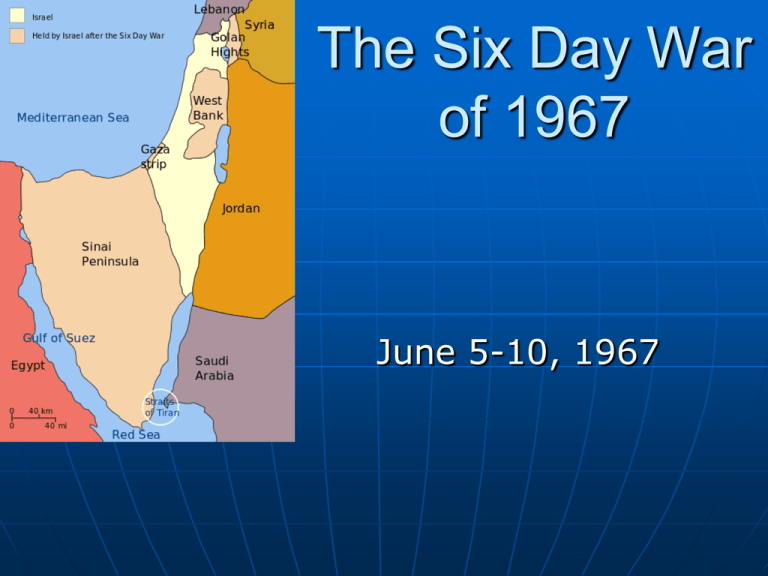
The Six Day War of 1967 June 5-10, 1967 Arab Points of Contention Syrian and Israeli tensions rise with Nasser’s pact with Syria Israel attacks Jordan in response to the Egyptian-Syrian pact Soviets release false report that Israel planned to attack Syria Arab Points of Contention Inter Arab struggle for influence and power- Nasser and Hussein insult each other and encourage the conflict to escalate. Inter Arab conflict for power rose between Syria, Egypt, Jordan, and Iraq, creating tension Israeli Points of Contention The al-Fatah terror group, with Syrian support, attack Israel New Syrian Baathist regime made the destruction of Israel their primary goal Syria shells Israel in July of 1966only one of numerous Arab-Israeli attacks leading up to the war Israeli Points of Contention Egypt mobilizes tens of thousands of troops into Sinai Egypt closes straits of Tiran- cuts off Israel’s supply of oil from Iran Jordan, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Syria, and Lebanon deploy over 230,000 troops to the Israeli border Key Players Gamal Nasser- President of Egypt during conflict. Did not intend to go to war but his aims of gaining power gave him the primary blame for starting the Six Day War- Gave Israel no alternative but to fight. Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO)- provided military and economic assistance to Palestinian resistance groups King Hussein of Jordan- had personal conflict with Nasser that rose tension but ended up signing a mutual defense pact with Nasser Key Battles Day 1: June 5th, Israel destroys most of the Egyptian air force in raids. Jordan, Syria, and Iraq attack Israel. Day 3: June 7th, Israel gains control over Jerusalem and breaks the blockade on the Straits of Tiran Day 6: June 10th, Israel takes control of the Golan Heights and a ceasefire is declared. Outcome of the Conflict Israel came out ahead after the six day war. They controlled East Jerusalem, the West Bank, the Sinai Desert, and the Golan Heights. Also enjoyed the support of Western powers. After suffering great loses, the Arabs were motivated to continue to struggle against the Israelis. Resolution 242 resulted from the aftermath of the war. This resolution proposed ideas of how to execute peace between Arabs and Israelis. Works Cited The Arab-Israeli Conflict By T.G Fraser The Arab-Israeli Conflict By Kirsten E. Schulze A PowerPoint by Charlotte Larson, Taylor Schlichting, Isabelle Cetas, Dominic Galen, Isabel Dammann