First Grade Science Standards Content Standard: Performance
advertisement

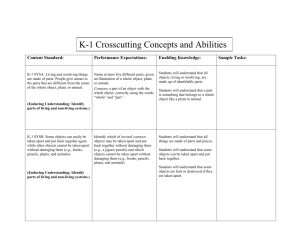
First Grade Science Standards Content Standard: Performance Expectations: Enabling Knowledge: K-1 PS2A Liquids take the shape of the part of the container they occupy. Predict the shape that water will take in a variety of different containers. Students will understand that a liquid is something that flows (pours out of a cup). Students will understand that when a liquid is poured (or flows) into another container, it will assume that containers shape. (Enduring Understanding: Different kinds of materials display different properties.) Students will understand that a liquids ability to flow is a physical property. K-1 PS2B Solids retain their shape regardless of the container they are in. (Enduring Understanding: Different kinds of materials display different properties.) Predict that frozen water (e.g., ice) will retain its shape when moved among containers of different shapes (e.g., ice cubes in a tray). Given several substances, sort them into those that are liquid and those that are solid. Students will understand that solids like to maintain a given shape. Students will understand that they can physically change the shape of a solid by cutting, breaking, tearing, etc, the object, but it is still a solid. Students will understand that an solids ability to maintain its shape is a physical property. Sample Tasks: K-1 ES1A Many things can be seen in the sky. Some change minute by minute, while others move in patterns that can be seen if they are observed day after day. Observe and communicate the many things that can be seen in the sky that change minute by minute (e.g., birds, airplanes, and clouds) and those that change their shape or position in observable patterns day after day (e.g., apparent shape of the moon).* (Enduring Understanding: The Sun and the Moon have patterns of movement that can be observed and recorded.) K-1 ES1B The position of the Sun in the sky appears to change during the day. (Enduring Understanding: The Sun and the Moon have patterns of movement that can be observed and recorded.) Students will understand that objects of all kinds are found in the day and night sky. Students will understand that some objects move very fast (like airplanes and birds) while others can take much longer to move (clouds). Students will understand that the earth is spinning on its axis, so some things stand almost still as we rotate by them, like the Sun, Moon, and Stars. Compare the position of the Sun in the sky in the morning with its position in the sky at midday and in the afternoon. Students will understand that the Sun sits in a stationary position in our Solar system (visual would be excellent here). Students will understand that the Earth spins on its axis (visual would be good here). Students will understand that the Sun’s position change is due to Earth’s rotation on its axis. K-1 ES1C The Moon can be seen sometimes during the day and sometimes during the night. The Moon appears to have different shapes on different days. Observe the Moon during different times of the day and month, and draw its apparent shape. Students will understand that Moon rotates on its axis once every 29 days and also orbits the Earth once every 29 days. Students will understand that the Moon, as it orbits the Earth, comes between the Earth and the Sun. (Enduring Understanding: The Sun and the Moon have patterns of movement that can be observed and recorded.) Students will understand that the Earth, as it orbits around the Sun, comes between the Moon and the Sun. Students will understand that these two occurrences cause the different shapes of the moon at different times of the month. K-1 LS2A There are different kinds of natural areas, or habitats, where many different plants and animals live together. (Enduring Understanding: Habitats are places that meet the daily needs of plants and animals.) Investigate an area near their home or school where many different plants and animals live together (e.g., a lawn, a vacant lot, a wooded park, a flower bed) and describe the different plants and animals found there. Students will understand that a habitat is an area where different organisms live together. Students will understand that habitats can be natural or manmade. Students will understand that all the living organisms in a habitat live, eat, move, multiply, and die within that habitat area. K-1 LS2B A habitat supports the growth of many different plants and animals by meeting their basic needs of food, water, and shelter. Identify the characteristics of a habitat that enable the habitat to support the growth of many different plants and animals (e.g., have trees to provide nesting places for birds and squirrels, pond water for tadpoles and frogs, blackberry bushes for rabbits to hide in). Students will understand that a habitat consists of many different living organisms (plants and animals). List two or more things that humans do that might harm plants and animals in a given habitat (e.g., throwing litter in a pond might cause difficulty for water birds and fish to find food or might poison the plants and animals that live there). Communicate ways that humans protect habitats and/or improve conditions for the growth of the plants and animals that live there (e.g., reuse or recycle products to avoid littering). Students will understand that humans will always affect any given habitat they come in contact with. Students will understand that a habitat provides all its living organisms with food, water, and shelter (a home). (Enduring Understanding: Habitats are places that meet the daily needs of plants and animals.) K-1 LS2C Humans can change natural habitats in ways that can be helpful or harmful for the plants and animals that live there. (Enduring Understanding: Habitats are places that meet the daily needs of plants and animals.) Students will understand that humans, through acts of littering, can cause major harm to a habitat. Students will understand that humans can also improve a habitat by helping to keep things clean and litter free and by carefully studying a habitat before attempting to fix or change something. K-1 LS3A Some things are alive and others are not. Use logical rules to sort objects into two groups, those that are alive and those that are not. Students will understand that living things require food, water and shelter in order to survive. Students will understand that nonliving things have no requirements. (Enduring Understanding: Both plants and animals have different characteristics that can be used to classify them.) K-1 LS3B There are many different types of living things on Earth. Many of them are classified as plants or animals. (Enduring Understanding: Both plants and animals have different characteristics that can be used to classify them.) Given a list, illustrations, or actual plants or animals, classify them as plants or animals. Students will understand that living organisms are classified into two basic groups: plants and animals. Students will understand that animals need oxygen to breath, are able to move from one place to another, and require food from other sources. Students will understand that a plant needs carbon dioxide to breath, stays in one place all its life, and gets its food and energy from the Sun and soil. K-1 LS3C External features of animals and plants are used to classify them into groups. (Enduring Understanding: Both plants and animals have different characteristics that can be used to classify them.) Describe several external features and behaviors of animals that can be used to classify them (e.g., size, color, shape of body parts). Describe several external features of plants that can be used to classify them (e.g., size, color, kinds of seeds, shapes, or texture of plant parts). Give examples to illustrate how pairs of plants and/or animals are similar to and different from each other (e.g., cats and dogs both have four legs, but many dogs have longer snouts than cats). Students will understand that plants and animals have different external features that distinguish them from one another. Students will understand that animals have legs, arms, fur, noses, mouths, ears, eyes, feathers, scales, etc. Students will understand that plants have roots, stems, leaves, flowers, bark, seeds, etc.