EXPERIMENT 1: INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC DESIGN
advertisement
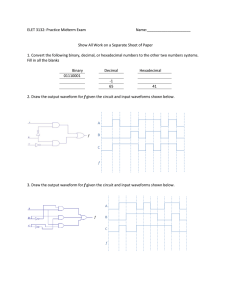
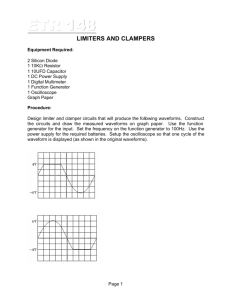
EXPERIMENT 1-- INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC DESIGN FINAL REPORT I. Turn in your Logic and Chip Layout Diagrams. II. Measurements a) Sketch the sine waveform observed in part B.3. VOLTS/DIV_________________ TIME/DIV_________________ b) What is the peak to peak voltage of the waveform? What is its period? What is its frequency? Indicate how you determined these values from the above sketch. 1.1 c) Record the waveforms observed in part B.4. DC Coupling AC Coupling 1.2 d) The waveforms observed using AC and DC coupling are different. Explain why. e) Sketch the waveforms observed on the oscilloscope in part B.5. DC Coupling 1.3 AC Coupling f) Why is the AC coupled trace distorted? g) From your observations in part B.6, explain how the TRIGGER LEVEL knob and the EDGE SLOPE softkeys determine where in the cycle of a periodic input signal the scope begins the trace. 1.4 III. Analysis of Logic Box and Breadboard a) Sketch the input and output waveforms obtained in part C.2 for the two different input frequencies. 1.5 b) Sketch the circuit you constructed showing the pin numbers on each gate. c) What are the frequencies of the input and output waveforms for the two input frequencies you selected? How do the input and output waveforms differ? Is this what was expected? d) Sketch the waveforms obtained in part C.3. Identify the waveforms, i.e., counter was free-running or single stepping and the vertical channel of the scope was in DC or AC mode. 1.6 1.7 1.8 e) Does the counter output behave as expected and what is its frequency? What voltages were obtained at the counter output for a logic 0 and logic 1? (Remember that we are using a positive logic convention.) 1.9 f) Explain how the counter output might be used to obtain the truth table for a combinational logic circuit. 1.10