Earth Science Reference Table pg. 6
advertisement

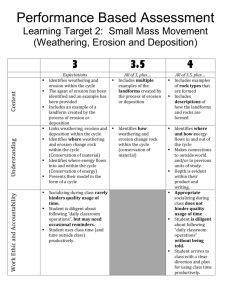
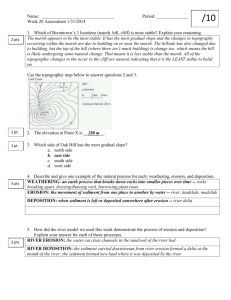
CURRICULUM TOOL: CHANGING THE EARTH’S SURFACE WEATHERING, EROSION, & DEPOSITION NYS Earth Science Core Curriculum Performance Indicator 2.1 Use the concepts of density and heat energy to explain observations of weather patterns, seasonal changes, and the movements of Earth’s plates. 2.1s Weathering is the physical and chemical breakdown of rocks at or near Earth’s surface. Soils are the result of weathering and biological activity over long periods of time. 2.1t Natural agents of erosion, generally driven by gravity, remove, transport, and deposit weathered rock particles. Each agent of erosion produces distinctive changes in the material that it transports and creates characteristic surface features and landscapes. In certain erosional situations, loss of property, personal injury, and loss of life can be reduced by effective emergency preparedness. 2.1u The natural agents of erosion include: • Streams (running water): Gradient, discharge, and channel shape influence a stream’s velocity and the erosion and deposition of sediments. Sediments transported by streams tend to become rounded as a result of abrasion. Stream features include V-shaped valleys, deltas, flood plains, and meanders. A watershed is the area drained by a steam and its tributaries. • Glaciers (moving ice): Glacial erosional processes include the formation of U-shaped valleys, parallel scratches, and grooves in bedrock. Glacial features include moraines, drumlins, kettle lakes, finger lakes, and outwash plains. • Wave Action: Erosion and deposition cause changes in shoreline features, including beaches, sandbars, and barrier islands. Wave action rounds sediments as a result of abrasion. Waves approaching a shoreline move sand parallel to the shore within the zone of breaking waves. • Wind: Erosion of sediments by wind is most common in arid climates and along shorelines. Wind-generated features include dunes and sand-blasted bedrock. • Mass Movement: Earth materials move downslope under the influence of gravity. 2.1v Patterns of deposition result from a loss of energy within the transporting systems and are influence by the size, shape, and density of the transported particles. Sediment deposits may be sorted or unsorted. 2.1w Sediments of inorganic and organic origin often accumulate in depositional environments. Sedimentary rocks form when sediments are compacted and/or cemented after burial or as the result of chemical precipitation from seawater. High School of Language and Innovation 2012 (draft) Curriculum-Based Questions What affects the rate of weathering of a rock? How does gravity affect erosion? What are the natural agents of erosion? What are the different factors affecting the deposition of sediments? How are weathering, erosion, and deposition related? Complete one activity from the green Changing Earth’s Surface binder. Earth Science Reference Table pg. 6 (related pages: 1, 7, 16) CURRICULUM TOOL: CHANGING THE EARTH’S SURFACE WEATHERING, EROSION, & DEPOSITION Some Past Part A Questions 1. Which agent of erosion most likely formed the drumlins and finger lakes in New York State? (1) running water (3) wave action (2) moving ice (4) mass movement 2. Which sediment is most easily picked up and transported by the wind? (1) cobbles (3) sand (2) pebbles (4) silt 3. A river’s current carries sediments into the ocean. Which sediment size will most likely be deposited in deeper water farthest from the shore? (3) pebble (3) silt (4) sand (4) clay 4. The map shows a meandering stream as it enters a lake. The arrow shows the direction of stream flow. Points A through D represent locations on the surface of the stream. The greatest stream velocities are found closest to points (1) A and B (2) B and C (3) C and D (4) D and A High School of Language and Innovation 2012 (draft) Some Past Part B-1, B-2, C Questions August 2012 Question 57 June 2012 Questions 42-45 January 2012 Questions 46-48, 72-73 August 2011 Questions 83-84 *Released Regents Tests: http://www.nysedregents.org/earthscience/ CURRICULUM TOOL: CHANGING THE EARTH’S SURFACE WEATHERING, EROSION, & DEPOSITION Readings Holt (yellow book) Weathering: pg. 343-348 (types), 349-352 (rates), 353-356 (soil) Erosion: pg. 357-360 (soil), 361-362 (gravity), 379-382 (streams), 423-425 (glaciers), 445 (wind), 451-453 (waves) Deposition: pg. 383-386 (streams), 426-430 (glaciers), 447-449 (wind), 453 (waves) Glencoe (big blue book) Weathering: pg. 153-158 (types) 158-161 (rates), 191203 Erosion: pg. 123, 162-165 (gravity and water), 165-166 (glaciers, wind), 167 (soil), 181188 (mass movement), 191-193 (wind), 201-202 (glaciers) Deposition: pg. 123-124, 226 McGuire (little blue book) Weathering: pg. 165-174 (types and rates), 175-177 (soil) Erosion: pg. 185-192, 275-276 (glaciers). 373-374 (mass movements) Deposition pg. 193-198, 277-281 (glaciers) Unison Reading Binder: Changing the Earth’s Surface Resources for Learning Websites Regents Exam Prep Center: Earth Science http://regentsprep.org/Regents/earthsci/earthsci.cf m Geology: Surface Processes http://www.hmxearthscience.com/surface_process es.html Weathering http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/geology/s ed_weathering.html&edu=high Erosion and Transport http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/geology/s ed_erosion.html&edu=high Deposition http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/geology/s ed_deposition.html&edu=high Water Erosion and Deposition http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/High_School_Earth_Sci ence/Water_Erosion_and_Deposition Regents Review Materials http://reviewearthscience.com/ http://regentsearth.com/ Foreign Language: Desgaste http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/geology/s ed_weathering.html&edu=high&lang=sp Deposición http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/geology/s ed_deposition.html&edu=high&lang=sp High School of Language and Innovation 2012 (draft) Videos Weathering and Erosion http://www.unitedstreaming.com/videos/dsc/extern alApplications/interactiveVideos/index.html?vid=32 Weathering and Erosion http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/scie nce/rocks-minerals-landforms/weathering-anderosion.htm Weathering and Erosion http://schoolmediainteractive.com/view/object/clip/ 6EF46CAA2D38E0EABB11A57BAFFB1753 Deposition and Erosion http://www.unitedstreaming.com/videos/dsc/extern alApplications/simulationses/Explorations/Content/Resources/ES_1_2_3_Erosio n_Deposition/flash/ES_1_2_3_Erosion_Deposition.ht ml At home: Erosion Characteristics www.youtube.com/watch?v=R21W6El_vv4 Weathering and Erosion www.youtube.com/watch?v=L5ozKOBBUcY Physical Weathering www.youtube.com/watch?v=u_WN2ICRb2M Chemical Weathering www.youtube.com/watch?v=6VnVRHIV6j4 Deposition www.youtube.com/watch?v=yqxelEQMNaU Water Velocity Chart www.youtube.com/watch?v=UHAtv5J76FM In-Class Activities Changing Earth’s Surface Binder Weathering and Erosion Vocabulary Weathering and Erosion Memory Deposition Vocabulary Deposition Memory