LT #1 Genetic Characteristics and Attributes
advertisement

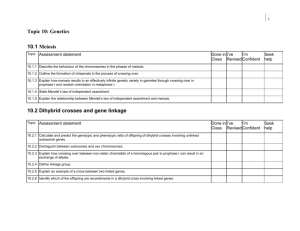
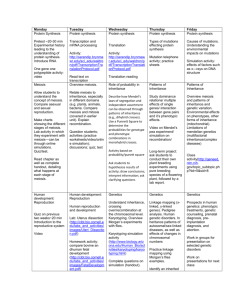
LT #1 Genetic Characteristics and Attributes I can differentiate and interpret how the various physical attributes of a human are the phenotypic expression of the genetic blueprint. LT. 1.1 I can differentiate between a genotype and phenotype in terms of genetic expression and inheritance. Highly Proficient LT 1.1 LT 1.2 LT 1.3 1.2 I can distinguish between genetic characteristics or traits to infer the genotypic relationship. 1.3 I can relate how alleles represent the genetic diversity of genes. GENETICIST Score 4 Student can demonstrate in-depth inferences, analysis or synthesis—with little to no errors. I can compare and contrast the connection between heredity and genetics. I can apply my understanding of a genotype and a phenotype. I can distinguish the difference between a hybrid and pure trait. I can differentiate between homozygous recessive, heterozygous, and homozygous dominant genotypes. I can classify dominant and recessive alleles. I can apply my understanding of autosomal and sex linked traits. I can illustrate the difference between a gene, trait, locus and allele. I can analyze patterns of genetic linkage. I can interpret and show how genes have multiple phenotypic effects (pleiotropy). RESEARCHER Proficient Score 3 Student can demonstrate their understanding and apply their knowledge in multiple ways—with some minor errors. I can provide examples to explain the difference between heredity and genetics. LT 1.1 I can explain the difference between a genotype and a phenotype. I can describe the difference between hybrid and pure trait. I can distinguish the difference between homozygous recessive, heterozygous, and homozygous dominant genotypes. LT 1.2 I can explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. I can explain the difference between autosomal and sex linked traits. I can explain the difference between a gene, trait, locus and allele. LT 1.3 I can describe examples of genetic linkage. I can describe how genes have multiple phenotypic effects (pleiotropy). Developing Proficient LAB TECHNICIAN Score 2 Student can demonstrate evidence of understanding and comprehension—errors exists but do not impede understanding. LT 1.1 LT 1.2 LT 1.3 I can identify the difference between heredity and genetics. I can identify the difference between a genotype and a phenotype. I can identify the difference between hybrid and pure trait. I can identify the difference between homozygous recessive, heterozygous, and homozygous dominant genotypes. I can identify the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. I can identify the difference between autosomal and sex linked traits. I can identify the difference between a gene, trait, locus and allele. I can identify examples of genetic linkage. I can identify examples of how genes have multiple phenotypic effects (pleiotropy). Beginning Proficient Score 1 Student can demonstrate a partial understanding of some of the knowledge—however major errors or misconceptions exist. Not Proficient Score 0 Lack or insufficient evidence to determine proficiency. LT #2 Structure and Function of DNA I can apply and analyze DNA based on its structure, function and ability to replicate either to produce a diploid or haploid cell. 2.1 I can apply my understanding of DNA to demonstrate its unique characteristics, structure and ability to encode information that can be transcribed and translated into a blueprint for life. LT 2.2 LT 2.3 2.3 I can analyze the products of protein synthesis and apply my understanding of mutation to analyze the effects mutation will have on the organism. GENETICIST Highly Proficient LT 2.1 2.2 I can transcribe and translate a sequence of DNA into a protein (protein synthesis). Score 4 Student can demonstrate in-depth inferences, analysis or synthesis—with little to no errors. I can construct a sequence of DNA to show correctly paired nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds, in an anti-parallel orientation. I can analyze and infer the percent of nitrogen bases in a genome based on Chargaff’s Rules. I can synthesize a cipher to demonstrate my understanding of how information can be encoded. I can model the process of transcription within the cell. I can model the process of translation within the cell. I can integrate the role of tRNA, mRNA and rRNA in the process of protein synthesis. I can analyze multiple strands of DNA and their subsequent peptides to infer and predict which mutations will lead to a more deleterious effect. RESEARCHER Proficient Score 3 Student can demonstrate their understanding and apply their knowledge in multiple ways—with some minor errors. I can describe the structure of DNA to account for its’ overall shape, antiparallel orientation and nucleotide classifications (purines and pyrimidines). LT 2.1 I can construct a complimentary strand of DNA according to Chargaff’s Rule. I can decipher a message to apply my knowledge of encryption. I can transcribe a sequence of DNA into mRNA. LT 2.2 I can translate a sequence of mRNA into a peptide. I can describe the function of tRNA, mRNA and rRNA. I can explain how the following types of mutations: substitution, deletion, insertion, inversion LT 2.3 and translocation can affect the genotypic and phenotypic expression of an organism. LAB TECHNICIAN Developing Proficient Score 2 Student can demonstrate evidence of understanding and comprehension—errors exists but do not impede understanding. LT 2.1 LT 2.2 LT 2.3 I can label a strand of DNA to show location of sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base. I can identify correctly paired nitrogen bases according to Chargaff’s Rule. I understand how information can be encrypted. I can explain the process and purpose of transcription. I can explain the process and purpose of translation. I identify the function of tRNA, mRNA and rRNA. I can identify the following types of mutations: substitution, deletion, insertion, inversion and translocation. Beginning Proficient Score 1 Student can demonstrate a partial understanding of some of the knowledge—however major errors or misconceptions exist. Not Proficient Score 0 Lack or insufficient evidence to determine proficiency. LT #3 Meiosis and Genetic Recombination I can evaluate the complexity of the human genome to explain how variation arises through mutation and sexual reproduction. 3.1 I can illustrate the process of meiosis to demonstrate how it leads to the formation of a haploid cell. 3.2 I can breakdown how the process of meiosis increases variation within a sexually reproducing population. 3.3 I can apply my understanding of meiosis to describe the events that lead to non-disjunction and how that affects the organism. Highly Proficient LT 3.1 LT 3.2 LT 3.3 GENETICIST Score 4 Student can demonstrate in-depth inferences, analysis or synthesis—with little to no errors. I can draw and model the phases of meiosis in the correct order. I can draw and label the important components necessary for gamete formation. I can draw the correct number of chromosomes for each phase of meiosis—increasing and reducing their numbers when appropriate. I can illustrate the difference between a sister and homologous chromosome. I can differentiate the difference between a haploid and diploid cell. I can analyze how the process of crossing over leads to genetic variation. I can analyze how independent assortment leads to genetic variation. I can analyze a karyotype to interpret to evaluate the effect non-disjunction has on an organisms genotype and phenotype. RESEARCHER Proficient Score 3 Student can demonstrate their understanding and apply their knowledge in multiple ways—with some minor errors. I can explain why the phases of meiosis need to occur in a specific sequence. LT 3.1 I can explain the major events of meiosis that lead to gamete formation. I can explain how chromosomes change during Interphase through each phase of meiosis. I can explain the difference between a sister and homologous chromosome. I can explain the difference between a haploid and diploid cell. LT 3.2 I can explain how the process of crossing over leads to genetic recombination. I can explain how independent assortment leads to genetic variation. I can explain how the different types of non-disjunction affect an organisms genotype and LT 3.3 phenotype. Developing Proficient LAB TECHNICIAN Score 2 Student can demonstrate evidence of understanding and comprehension—errors exists but do not impede understanding. LT 3.1 LT 3.2 LT 3.3 I can identify the major phases of meiosis in order. I can identify the major events of meiosis in order. I can identify the correct number of chromosomes in each phase of meiosis, which leads to the formation of human sex cells. I can identify the difference between a sister and homologous chromosome. I can identify the difference between a haploid and diploid cell. I can identify the process of crossing over that leads to genetic recombination. I can identify the process of independent assortment. I can identify different types of non-disjunction to their chromosomal anomaly. Beginning Proficient Score 1 Student can demonstrate a partial understanding of some of the knowledge—however major errors or misconceptions exist. Not Proficient Score 0 Lack or insufficient evidence to determine proficiency. LT #4 Inheritance Patterns I can apply and analyze inheritance patterns to interpret hereditary relationships and traits. 4.1 I can complete a Punnett square and pedigree to analyze a dominant/recessive genetic trait, using simple dominant, codominant and incomplete dominance inheritance patterns. 4.2 I can complete a Punnett square and pedigree to analyze polygenic and multi-allelic inheritance patterns. 4.3 I can research and analyze a genetic disorder to demonstrate my understanding of how the disorder was created, how the disorder will affect the person genotypically, phenotypically and support my research with Punnett Squares, karyotypes and pedigrees when necessary. GENETICIST Highly Proficient LT 4.1 LT 4.2 LT 4.3 Score 4 Student can demonstrate in-depth inferences, analysis or synthesis—with little to no errors. I can complete a Punnett square for a monohybrid cross and/or dihybrid cross—calculating the genotypic and phenotypic ratio and determine the type of inheritance pattern that is being analyzed. (Simple, Codominant, Incomplete) I can analyze a pedigree to determine if it has characteristics of a simple dominant, codominant or incomplete dominant inheritance pattern. I can complete a Punnett square for a monohybrid cross and/or dihybrid cross—calculating the genotypic and phenotypic ratio and determine the type of inheritance pattern that is being analyzed. (Polygenic, Multiallelic) I can analyze a pedigree to determine if it has characteristics of polygenic and multi-allelic inheritance pattern. Student has received an average score of 3.5 to 4.0 on the Genetic Disorder Research Project RESEARCHER Proficient Score 3 Student can demonstrate their understanding and apply their knowledge in multiple ways—with some minor errors. I can complete a Punnett square for a monohybrid cross for simple dominance, codominance and incomplete dominance inheritance patterns—calculating the genotypic and phenotypic LT 4.1 ratio. I can apply my understanding of simple dominant, codominant and incomplete dominant inheritance patterns to pedigree analysis. I can complete a Punnett square for a monohybrid cross for polygenic and multi-allelic inheritance patterns.—calculating the genotypic and phenotypic ratio. LT 4.2 I can apply my understanding of polygenic and multi-allelic inheritance patterns to pedigree analysis. Student has received an average score of 3.0 to 3.5 on the Genetic Disorder Research Project LT 4.3 LAB TECHNICIAN Developing Proficient Score 2 Student can demonstrate evidence of understanding and comprehension—errors exists but do not impede understanding. LT 4.1 LT 4.2 LT 4.3 I can determine the parental genotypes and complete a Punnett square for a monohybrid cross for simple dominance, codominance and incomplete dominance inheritance patterns. I can identify the basic characteristics of a simple dominant, codominant and incomplete dominant pedigree. I can determine the parental genotypes and complete a Punnett square for a monohybrid cross for polygenic and multi-allelic inheritance patterns. I can identify the basic characteristics of polygenic and multi-allelic inheritance patterns. Student has received an average score of 2.5 to 3.0 on the Genetic Disorder Research Project Beginning Proficient Score 1 Student can demonstrate a partial understanding of some of the knowledge—however major errors or misconceptions exist. Not Proficient Score 0 Lack or insufficient evidence to determine proficiency. Molecular Genetics Name: Evidence of Learning Evidence #1 Bullseye Quizzes Learning Target 1.1 Learning Target 1.2 Learning Target 1.3 Learning Target 2.1 Evidence #2 Alternative* Evidence #3 Project/Portfolio X X X Evidence #4 Summative Tests Evidence #5 Cumulative Final Learning Target 2.2 Learning Target 2.3 Learning Target 3.1 Learning Target 3.2 Learning Target 3.3 X X X Learning Target 4.1 Learning Target 4.2 Learning Target 4.3 *Alternative: Assessment through group work, discussions, teaching and/or mentoring other students, oral assessments/questioning. The evidence collected for each short term learning target will be used to determine a student’s overall proficiency in each long term learning target. Students cannot demonstrate proficiency if they receive a 0 or 1 on any short term learning target. Students must provide all multiple sources of evidence to provide sufficient examples of their proficiency—insufficient evidence will result in the student receiving a NYP