Schedule, Vocabulary List and Objectives

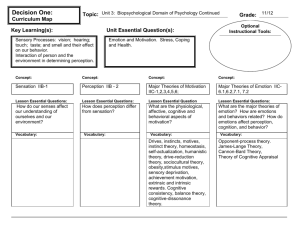
Unit 4: Sensation & Perception, Motivation & Emotion
11/4-11/5 Sensation and Perception: Principles 115-124
11/6-11/9 Perception: Vision & Visual Perception
11/10-11/12 S & P: Auditory & Other Senses
124-133
133-150
11/13-11/16 S & P: Perceptual Organization & ESP 150-169 4D
11/17-11/18 Motivation: Theories & Hunger Vocab. Quiz 327-348 4E
4A
4B
4C
11/19-11/20 Motivation: Sex & Belongingness
11/23-11/24 Emotion: Theories & Expression
348-362
367-384
4F
4G
11/25-11/30 Emotion: Experienced & Stress and Health 384-406 4H
12/1-12/2 Unit 4 Exam: Sensation & Perception, Motivation &
Emotion
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION (6-8%)
AP Learning Objectives:
Discuss basic principles of sensory transduction, including absolute threshold, difference threshold, signal detection, and sensory adaptation.
Describe sensory processes (e.g., hearing, vision, touch, taste, smell, vestibular, kinesthesis, pain),
Explain common sensory disorders (e.g., visual and hearing impairments).
including the specific nature of energy transduction, relevant anatomical structures, and specialized pathways in the brain for each of the senses.
Describe general principles of organizing and integrating sensation to promote stable awareness of the external world (e.g., Gestalt principles, depth perception).
Discuss how experience and culture can influence perceptual processes (e.g., perceptual set, context effects).
Explain the role of top-down processing in producing vulnerability to illusion.
Discuss the role of attention in behavior.
Challenge common beliefs in parapsychological phenomena.
Identify the major historical figures in sensation and perception, (e.g., Gustav Fechner, David Hubel,
Ernst Weber, Torsten Wiesel).
MOTIVATION AND EMOTION (6-8%)
AP Learning Objectives:
Identify and apply basic motivational concepts to understand the behavior of humans and other
animals (e.g., instincts, incentives, intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation).
Discuss the biological underpinnings of motivation, including needs, drives, and homeostasis.
Compare and contrast motivational theories (e.g., drive reduction theory, arousal theory, general adaptation theory), including the strengths and weaknesses of each.
Describe classic research findings in specific motivation systems (e.g., eating, sex, social).
Discuss theories of stress and the effects of stress on psychological and physical well-being.
Compare and contrast major theories of emotion (e.g., James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, Schachter twofactor theory).
Describe how cultural influences shape emotional expression, including variations in body language.
Identify key contributors in the psychology of motivation and emotion (e.g., William James, Alfred
Kinsey, Abraham Maslow, Stanley Schachter, Hans Selye).
BASIC PRINCIPLES
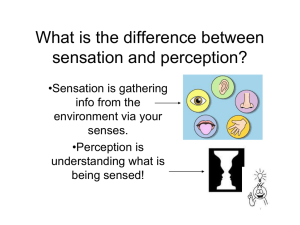
Sensation perception bottom-up processing top-down processing
psychophysics
Selective attention (Cocktail party effect) absolute threshold
difference threshold signal detection theory sensory adaptation selective attention
Weber’s law
Gustav Fechner
David Hubel
Ernst Weber
Torsten Wiesel
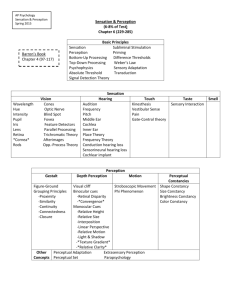
HEARING
Audition frequency pitch cochlea
Hair cells place theory frequency theory conduction hearing loss
loss cochlear implant
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION VOCAB LIST
VISION cornea iris pupil lens retina receptor cells rods cones optic nerve blind spot accommodation trichromatic theory opponent-processing theory parallel processing
Young-Helmholtz
Auditory nerve
Kinesthetic sense
Vestibular sense gate-control theory sensory interaction gestalt principles figure-ground grouping depth perception visual cliff (experiment) binocular (depth) cues monocular cues retinal disparity
Gestalt:
Perceptual constancy
Perceptual set
Telekinesis
Clairvoyance
Precognition
Prophetic dreams
Extrasensory perception
(ESP) parapsychology
Motivation
Instinct
Drive reduction theory
Yerkes-Dodson law
Homeostasis
Extrinsic motivation
Intrinsic motivation
Hierarchy of needs
Self-actualization
Achievement motivation
Abraham Maslow
Henry Murray
Alfred Kinsey
James-Lange Theory
Cannon-Bard Theory
Autonomic response system
Display rules
MOTIVATION AND EMOTION VOCABULARY LIST
Set point
Basal metabolic rate
Anorexia nervosa
Bulimia nervosa
Willima James
Carl Lange
Walter Cannon
Stanley Schachter
Robert Zajonc
Richard Lazarus
Hans Selye