AP Psychology Sensation & Perception Spring 2015 Sensation
advertisement

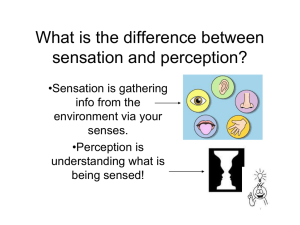
AP Psychology Sensation & Perception Spring 2015 Barron’s Book Chapter 4 (97-117) Wavelength Hue Intensity Pupil Iris Lens Retina *Cornea* Rods Sensation & Perception (6-8% of Test) Chapter 6 (229-285) Basic Principles Sensation Subliminal Stimulation Perception Priming Bottom-Up Processing Difference Thresholds Top-Down Processing Weber’s Law Psychophysics Sensory Adaptation Absolute Threshold Transduction Signal Detection Theory Vision Cones Optic Nerve Blind Spot Fovea Feature Detectors Parallel Processing Trichromatic Theory Afterimages Opp.-Process Theory Gestalt Figure-Ground Grouping Principles -Proximity -Similarity -Continuity -Connectedness -Closure Sensation Hearing Audition Frequency Pitch Middle Ear Cochlea Inner Ear Place Theory Frequency Theory Conduction hearing loss Sensorineural hearing loss Cochlear implant Touch Kinesthesis Vestibular Sense Pain Gate-Control theory Perception Depth Perception Motion Taste Sensory Interaction Perceptual Constancies Stroboscopic Movement Shape Constancy Phi Phenomenon Size Constancy Brightness Constancy Color Constancy Visual cliff Binocular cues -Retinal Disparity -*Convergence* Monocular Cues -Relative Height -Relative Size -Interposition -Linear Perspective -Relative Motion -Light & Shadow -*Texture Gradient* -*Relative Clarity* Other Perceptual Adaptation Extrasensory Perception Concepts Perceptual Set Parapsychology Smell Sensation Vision: What type of energy is being transduced? What are the parts of the eye (and the types of receptor cells) & how does it all function? Where in the brain are visual stimuli processed? What role do feature detectors & parallel processing play? Understand the two theories of color vision (Trichromatic & Opponent Process) & what causes colorblindness? Hearing: What type of energy is being transduced? What are the parts off the ear & how does it function? Where in the brain are auditory signals processed? How do we perceive loudness & how do we perceive pitch (place theory & frequency theory)? What allows us to locate sounds? What are the different causes of hearing loss? Touch: What are the 4 types of nerve endings for touch? What is the Kinesthetic Sense and the Vestibular Sense? How is pain valuable to us? Understand gate-control theory. How to psychological influences and social-cultural influences affect our perception of pain? Taste: What is the sense of taste detecting? Know the five different types of receptor cells (taste buds). What is the evolutionary function of each of them? Understand the role of sensory interaction in perceiving flavor. What is Synesthesia? Smell/Olfaction: What is an olfactory bulb & what do its receptor cells detect? What is the relationship between the sense of smell & memory? Wrap up Question Which of the 5 senses are energy senses, chemical senses, & body position senses? Perception: Understand Gestalt organizational concepts (Figure-Ground & Grouping Principles) What is the purpose of the visual cliff test? Understand how depth perception works & the different binocular cues and monocular cues. Understand the different ways our brain perceives motion. How do perceptual constancies create a stable awareness of the external world? What is perceptual adaptation? Understand how perceptual sets and context effects can influence perception. What role do Emotion & Motivation play in Perception? Extrasensory Perception: What does the scientific community think about Extrasensory Perception? Be able to challenge common beliefs in parapsychological phenomenon.