Unit 4 Key Terms: Sickle Cell Anemia
advertisement
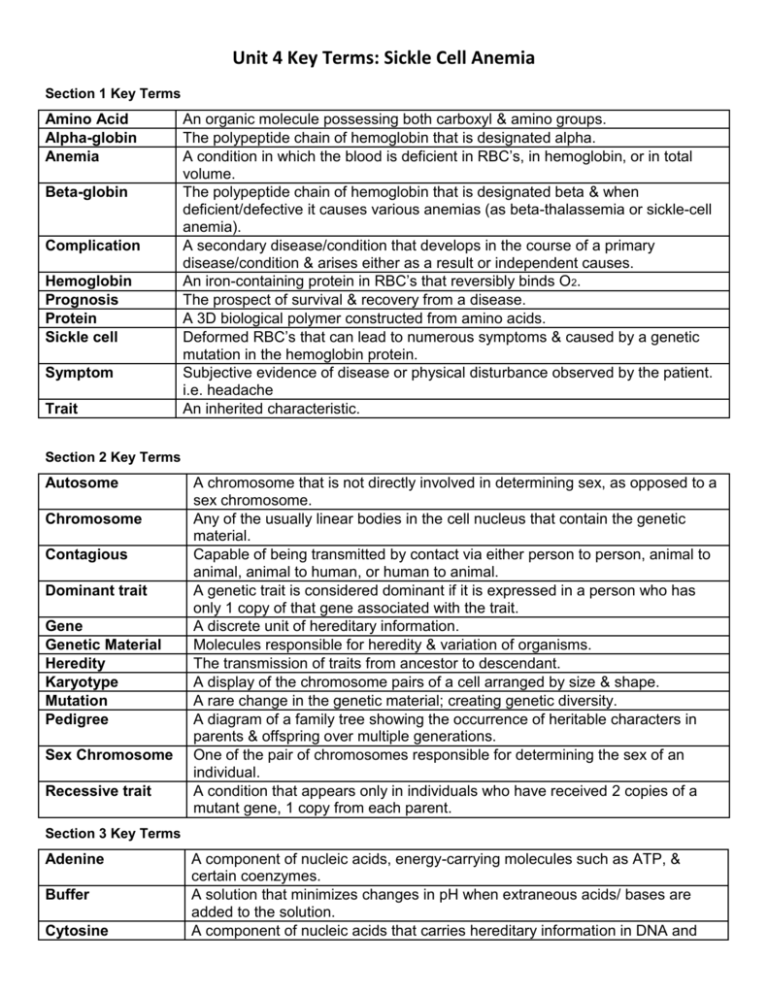
Unit 4 Key Terms: Sickle Cell Anemia Section 1 Key Terms Amino Acid Alpha-globin Anemia Beta-globin Complication Hemoglobin Prognosis Protein Sickle cell Symptom Trait An organic molecule possessing both carboxyl & amino groups. The polypeptide chain of hemoglobin that is designated alpha. A condition in which the blood is deficient in RBC’s, in hemoglobin, or in total volume. The polypeptide chain of hemoglobin that is designated beta & when deficient/defective it causes various anemias (as beta-thalassemia or sickle-cell anemia). A secondary disease/condition that develops in the course of a primary disease/condition & arises either as a result or independent causes. An iron-containing protein in RBC’s that reversibly binds O2. The prospect of survival & recovery from a disease. A 3D biological polymer constructed from amino acids. Deformed RBC’s that can lead to numerous symptoms & caused by a genetic mutation in the hemoglobin protein. Subjective evidence of disease or physical disturbance observed by the patient. i.e. headache An inherited characteristic. Section 2 Key Terms Autosome Chromosome Contagious Dominant trait Gene Genetic Material Heredity Karyotype Mutation Pedigree Sex Chromosome Recessive trait A chromosome that is not directly involved in determining sex, as opposed to a sex chromosome. Any of the usually linear bodies in the cell nucleus that contain the genetic material. Capable of being transmitted by contact via either person to person, animal to animal, animal to human, or human to animal. A genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only 1 copy of that gene associated with the trait. A discrete unit of hereditary information. Molecules responsible for heredity & variation of organisms. The transmission of traits from ancestor to descendant. A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size & shape. A rare change in the genetic material; creating genetic diversity. A diagram of a family tree showing the occurrence of heritable characters in parents & offspring over multiple generations. One of the pair of chromosomes responsible for determining the sex of an individual. A condition that appears only in individuals who have received 2 copies of a mutant gene, 1 copy from each parent. Section 3 Key Terms Adenine Buffer Cytosine A component of nucleic acids, energy-carrying molecules such as ATP, & certain coenzymes. A solution that minimizes changes in pH when extraneous acids/ bases are added to the solution. A component of nucleic acids that carries hereditary information in DNA and Guanine Helix Hydrogen bond Lysis Nucleotide Thymine Supernatant RNA in cells. A component of nucleic acids that carries hereditary information in DNA and RNA in cells. Something spiral in form. A type of weak chemical bond formed with H atom. A process of disintegration/dissolution; cell death. A building block of DNA, consisting of a 5-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base & a phosphate group. A component of nucleic acid that carries hereditary information in DNA in cells. The liquid on top of material deposited by settling or centrifugation. Section 4 Key Terms Codon Exon Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Hydroxyl group Messenger RNA (mRNA) Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Ribosome Transcription Transfer RNA (tRNA) Translation A 3-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code. A coding region of a eukaryotic gene. Having an affinity for water (love). Having an aversion to water (fear). A functional group consisting of an H atom joined to an O atom by a polar covalent bond. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water & are called alcohols. A type of RNA, synthesized from DNA & attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm; it specifies the primary structure of a protein. A type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers with a ribose sugar & the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); functions in protein synthesis. A cell organelle that fxns as the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. The synthesis of RNA on a DNA template. An RNA molecule that fxns as an interpreter btw nucleic acid & protein language by picking up specific amino acids & recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA. The synthesis of a polypeptide using the genetic information encoded in an mRNA molecule. Language changes from nucleotides to amino acids. Section 5 Key Terms Polymerize To undergo a chem rxn in which 2 or more small molecules combine to form larger molecules that contain repeating structural units of the original molecules.