Assignment Title
advertisement
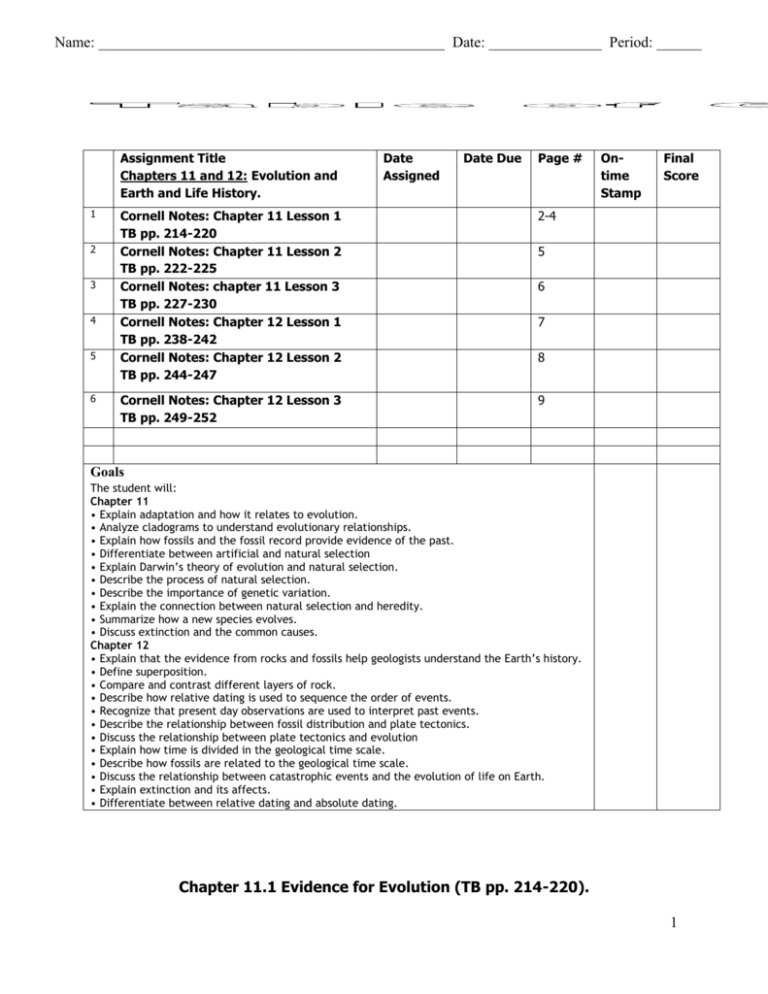
Name: ______________________________________________ Date: _______________ Period: ______ Assignment Title Chapters 11 and 12: Evolution and Earth and Life History. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Date Assigned Date Due Page # Cornell Notes: Chapter 11 Lesson 1 TB pp. 214-220 Cornell Notes: Chapter 11 Lesson 2 TB pp. 222-225 Cornell Notes: chapter 11 Lesson 3 TB pp. 227-230 Cornell Notes: Chapter 12 Lesson 1 TB pp. 238-242 Cornell Notes: Chapter 12 Lesson 2 TB pp. 244-247 2-4 Cornell Notes: Chapter 12 Lesson 3 TB pp. 249-252 9 Ontime Stamp Final Score 5 6 7 8 Goals The student will: Chapter 11 • Explain adaptation and how it relates to evolution. • Analyze cladograms to understand evolutionary relationships. • Explain how fossils and the fossil record provide evidence of the past. • Differentiate between artificial and natural selection • Explain Darwin’s theory of evolution and natural selection. • Describe the process of natural selection. • Describe the importance of genetic variation. • Explain the connection between natural selection and heredity. • Summarize how a new species evolves. • Discuss extinction and the common causes. Chapter 12 • Explain that the evidence from rocks and fossils help geologists understand the Earth’s history. • Define superposition. • Compare and contrast different layers of rock. • Describe how relative dating is used to sequence the order of events. • Recognize that present day observations are used to interpret past events. • Describe the relationship between fossil distribution and plate tectonics. • Discuss the relationship between plate tectonics and evolution • Explain how time is divided in the geological time scale. • Describe how fossils are related to the geological time scale. • Discuss the relationship between catastrophic events and the evolution of life on Earth. • Explain extinction and its affects. • Differentiate between relative dating and absolute dating. Chapter 11.1 Evidence for Evolution (TB pp. 214-220). 1 What is Evolution Define: Adaptation Evolution Q1. For each organism list an adaptation and its function: a. spider b. turtle c. crab Evolution is a branching process Define: Ancestor Cladogram Q. Use the diagram below to make a cladogram with the following organisms; human, snake, chimpanzee, and mouse. Explain the reasoning for your placement. 2 Chapter 11.1 Evidence for Evolution (TB pp. 214-220). An Evolutionary Timeline Questions: 1. How old do scientists believe the earth is? 2. When did life first appear on earth? What type of cells? 3. When did the first humans appear? 4. When did the first multicelluar organisms appear? 5. List one other important event from the timeline. 3 Chapter 11.1 Evidence for Evolution (TB pp. 214-220) Lines of Evidence Define: Homologous Structures Analogous Structures Vertebrates Question: 1. How do similarities in the bones of humans, porpoises, birds, and elephants provide evidence for evolution? Fossils Define: Fossil Fossil record Questions: 1. Why are there gaps in the fossil record? 2. In which layer in the diagram at right will you find the youngest fossils? The oldest? 4 Chapter 11.2 How Evolution Works (TB pp. 222-225) The finches of the Galapagos Q. 1. What was Darwin’s hypothesis about the finches on the islands? Darwin’s theory of evolution and natural selection Define: Natural selection Q. 1. What are 3 variables that affect the size of a population? The process of natural selection Q. 1. List the four steps of natural selection. 5 Chapter 11.3 Natural Selection (TB pp. 227-230) Mutations Q. 1. What do random mutations produce? The importance of genetic variation Define: Genetic variation Q. 1. Why is genetic variation necessary for natural selection to occur? How a new species evolves Know the steps shown here. Extinction of a species Define: Extinction Q. 1. List 3 causes of extinction. 6 Chapter 12.1 Evidence form Rocks (TB pp. 238-242) Fossil formation Define: Geology Q. 1. What does evidence from rocks and fossils allow us to understand? The formation of sedimentary rock Define: Rock cycle Superposition Q. 1. Which fossil is the oldest in figure 12.2? How do you know? Which term does it represent? 2. What is an inclusion? 7 Chapter 12.2 How Earth Changes (TB pp. 244-247) Pangaea Define: Uniformitarianism Pangaea Pangaea Plate Tectonics Define: Plate tectonics Lithospheric plates 8 Chapter 12.3 Life History (TB pp. 249-252) The geologic time scale Define: Geologic time scale Q. 1. List one significant event from each geologic era (there are 3 of them). Mass extinctions Define: Mass extinctions Q. 1. Name at least 2 possible causes for mass extinctions? 1. What is the cause of the “sixth” mass extinction? Absolute dating Define: Absolute dating Half-life 9