Unit 1: Science Process, Kintetic Molecular Theory, Phase Change
advertisement

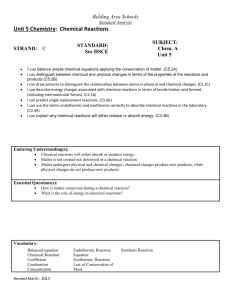
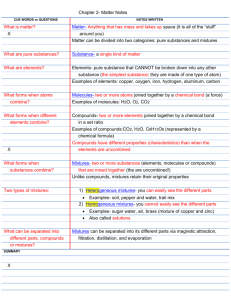
Belding Area Schools Standard Analysis Unit 1 Chemistry: Science Process, Measurement, Changes and types of matter, Element/Compounds/Mixtures STRAND: C STANDARD: See HSCE SUBJECT: Chem. A Unit 1 I CAN Statements: I CAN critique whether specific questions can be answered through scientific investigations. (C1.2A) I CAN review the steps in the scientific method and analyze the steps in given examples. (C1.1A, C1.1B, C1.1C, C1.1D, C1.1E, 1.1f, C1.1g, C1.1h, C1.1i) I CAN review the proper use of tools and techniques used for measurement in scientific investigations. (C.1.1B, C1.1C) I CAN determine what degree of accuracy is reasonable for measurements in a given situation and express accuracy through the use of significant digits or percent error. (C1.1B, C1.1C) I CAN explain the difference in physical and chemical properties of substances and describe energy changes in states of matter. (C2.2A, C2.2B, C4.3A, C4.3B,C5.2B)) I CAN recognize that solids have a more ordered, regular arrangement of their properties than liquids and that liquids are more ordered than gases. (C4.3B) I CAN explain the impact of heating on substances. (C3.3A, C3.3B) I CAN illustrate changes in state through phase change diagrams. (C5.4B) I CAN use the terms endothermic and exothermic correctly to describe chemical reactions in the laboratory. (C3.4A) I CAN explain why freezing is an exothermic change of state (C5.4d) Explain the impact of heating on substances (C2.1c, C2.2A, C2.2d, C2.2f, C3.3A, C3.3B) The learner will explain why chemical reactions will release or absorb energy. (C3.4B) I CAN explain the difference between elements, compounds and mixtures. (P4.p2) I CAN identify different types of mixtures. (P4.p2) I CAN compare the density of pure water to that of a sugar solution. (C4.7b) Revised March, 2014 Belding Area Schools Standard Analysis Enduring Understanding(s): A chemical change does not always occur when substances are combined. Accuracy in measurement can be expressed through the use of significant digits and percent error. Chemical changes occur when matter reacts and produces new substances; physical changes yield different forms of the same substance rather than a new substance. Every experiment provides useful results, whether or not the results match the hypothesis. Evidence of chemical change includes color change, gas formation, solid formation and temperature change. Mathematical and scientific solutions should be accurate, reasonable and use appropriate notation. Scientific investigations follow processes that require systematic and logical development, observation, and careful analysis. Scientific investigations generally lead to new questions. Substances may be classified by their physical and/or chemical properties. The foundation of scientific theory is replicable investigations. Through repeated inquiry, patterns emerge and theories are proposed. Boiling and Evaporation are not the same Energy is absorbed or released as a substance changes from one phase to another. Energy may be transferred from one object to another. Heat and temperature are not the same. Heating is the transfer of energy from one substance to another. As temperature increases, average kinetic energy increases. Molecules that comprise matter are constantly in motion. Essential Questions(s): How are accuracy and reasonable precision of measurements determined? How can substances be classified? How does science help us answer questions about the world around us? What does it mean to question? What happens to substances during a chemical change? What is scientific inquiry? Why do scientists conduct investigations? How is heat energy transferred from one substance to another? What happens to energy as a substance changes from one phase to another? What happens to the molecules of a substance as the substance is heated? What is the difference between boiling and evaporation? What is the difference between heat and temperature? Revised March, 2014 Belding Area Schools Standard Analysis Vocabulary: Science Process: Chemistry Matter Observation Inference Hypothesis Data Analyze Conclusion Dependent variable Independent variable Scientific method Scientific experiment Measurement: Qualitative measurement Quantitative measurement Accuracy Precision Significant figure Metric measurement Measurement tools Dimensional analysis Density Percent error HSCE (High School Content Expectations) See above Changes in Matter: Physical property` Chemical property Extensive property Intensive property Chemical change Physical change Conservation of mass Conservation of energy Phase (s, l, g) Phase changes Melting Freezing Vaporization Condensation Sublimation Deposition Boiling point Melting point Endothermic Exothermic Element/Compounds/Mixtures: Element Compound Mixture Periodic table Atom Molecule Symbol Formula Heterogeneous Homogeneous Solution colloid Information/Rules/Procedures/Resources/Assessments Instructional Strategies for all students: See instructors Moodle page for daily lesson plans, activities, labs, power points, homework, and tutorials. Differentiated Instruction for at-risk students: After school study sessions. Review Guides Tutorials on Moodle Retesting opportunity on all assessments Co-taught classes available Assessments: On staff share drive. Revised March, 2014