Exercise 31 & 32: Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear
advertisement

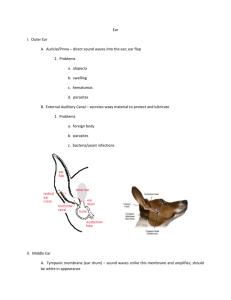
2401 A&P-I Laboratory Exercises Exercise 31 & 32: Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear Identifying Structures of the Ear 1. Identify the following ear structures on various ear models, the labyrinth model, & the cochlea model, and the cochlea histology slide, and state the function of each. a. External ear i. auricle (pinna) ii. external acoustic meatus (external auditory canal) contain ceruminous glands iii. tympanic membrane b. Middle ear i. tympanic cavity ii. ear ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) iii. pharyngotympanic (auditory or Eustachian) tube c. Internal ear i. osseous labyrinth filled with perilymph ii. membranous labyrinth filled with endolymph d. The 3 subdivisions of the inner ear found within the temporal bone i. cochlea – contain sensory receptors for hearing ii. vestibule – contain sensory receptors for static equilibrium iii. semicircular canals – contain sensory receptors for dynamic equilibrium e. Cochlea [structures with an (*) can be seen on some models but not in the slides] i. scala vestibule vi. vestibular membrane vii. spiral organ (organ of has perilymph Corti) ii. scala tympani viii. hair cells has perilymph ix. supporting cells* iii. cochlear duct x. cochlear nerve* has endolymph xi. oval window* iv. tectorial membrane xii. round window* v. basilar membrane f. Vestibular apparatus [structures with an (*) cannot be seen on the models] i. vestibule – static equilibrium (linear acceleration, otoliths respond to gravity) utricle saccule hair cells* ii. semicircular canals – dynamic equilibrium (angular/rotational acceleration) ampulla crista hair cells* 1 2401 A&P-I Laboratory Exercises Activity 1: Equilibrium 1. Perform the equilibrium test described in your lab manual. 2. Indicate that a person requires at least 2 of the following 3 senses to maintain balance while standing: a. Proprioception (sense of one’s body’s position in space) b. Vestibular function (sense of one’s head’s position in space) c. Vision (sense that monitors and aids in adjustment of the body’s position) 3. Indicate that balance tests are used to detect alcohol- and drug-induced driving impairment. Activity 2: Nystagmus 1. Define nystagmus 2. Perform the test for nystagmus described in your lab manual. Activity 3: Conduct ing Laboratory Tests of Hearing 1. Conduct the following tests for conduction and nerve (sensorineural) deafness and interpret the results by following instructions outlined in the lab manual. a. Weber test b. Rinne test 2. Define the difference between conduction and nerve deafness. 2