Ear I. Outer Ear A. Auricle/Pinna – direct sound waves into the ear
advertisement
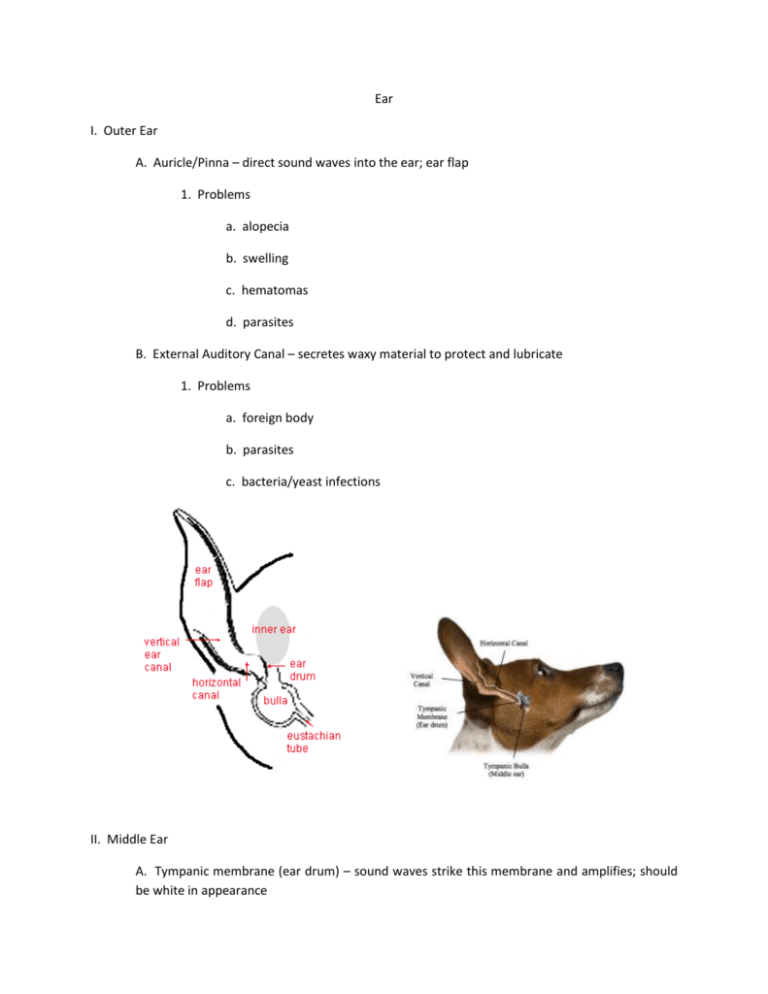
Ear I. Outer Ear A. Auricle/Pinna – direct sound waves into the ear; ear flap 1. Problems a. alopecia b. swelling c. hematomas d. parasites B. External Auditory Canal – secretes waxy material to protect and lubricate 1. Problems a. foreign body b. parasites c. bacteria/yeast infections II. Middle Ear A. Tympanic membrane (ear drum) – sound waves strike this membrane and amplifies; should be white in appearance B. Eustachian tube – establishes communication between the tympanic cavity and the nasal pharynx; adjusts the pressure of air in the cavity to the external pressure C. Ossicle (“small bone”) – amplify sound 40 times 1. malleus (hammer) 2. incus (anvil) 3. stapes (stirrup) III. Inner ear – transmits sound to the brain and provides equilibrium A. Bony labyrinth 1. Vestibule – contral portion 2. Semicircular canals – equilibrium B. Membranous labyrinth – fluids to provide a medium to conduct vibrations C. Cochlea (snail) – acoustic labyrinth; hairs vibrate and transform into electrical sensory impulses carried to the brain IV. Pathological Conditions A. Noninflammatory Alopecia – hair loss on the pinna without inflammation; hormone imbalance B. Pinnal Alopecia – hereditary predisposition in Dachshund, Chihuahuas, Whippet C. Actinic Dermatoses – most seen in white cats; chronic sun exposure to the ears cause’s hair loss and skin problems D. Contact Dermatitis – result of allergies, reaction to medication, or direct irritation E. Fly strike – fly dermatitis caused by stable flies; flies bite and tear open the skin on the ears F. Frost bite G. Aural hematomas – caused by scratching or head shaking; more common in the pendulous ears Treated aural hematoma H. Otitis Externa – most common disease in dogs and cats 1. Causes: abundance of hair in the canal, build-up of wax, foreign body, parasites, moisture in the canal, allergies 2. Clinical signs: head shaking, scratching at the ears, inflammation, head tilt, discharge, odor 3. Treatment: clean the ear and make sure it is dry; apply topical therapy I. Otitis Media – can result from otitis externa or ruptured ear drum (21 days to heal) 1. Clinical signs: facial nerves affected – drooping lips, drooling, drooping face on one side, head tilt V. Ceruminolytic Agents – breaks down wax Cerumene, Cerusol, Murine ear, Panotic











