Mitosis/DNA/Genetics Study Guide Things to know for Mitosis (but
advertisement

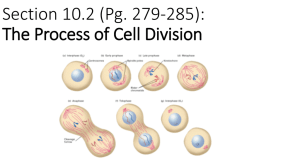
Mitosis/DNA/Genetics Study Guide Things to know for Mitosis (but not limited to) 4 phases Prophase: Nucleus dissolves DNA winds up to make sister chromatids Metaphase: chromosomes line up in along the middle of cell Anaphase: sister chromatids get pulled to either side of cell Telophase: DNA unravels, two nuclei form around DNA, cleavage occurs Cell cycle Interphase: organelle creation and DNA replication; longest part of cell cycle Mitosis: separation of chromosomes Cytokinesis: creation of two new daughter cells; quickest part of cell cycle Vocab: Chromosomes Sister chromatids Chromatin Microtubules Centriole Things to know for DNA (but not limited to) Make up of Nucleotides Each nucleotide has 3 sub-units Phosphate group Simple sugar (deoxyribose) Nitrogen base: there are 4 o Adenine o Thymine o Cytosine o Guanine DNA has two strands joined together at the bases Bases always pair up A –T and C – G Each strand is a connection of nucleotides Phosphate –sugar – phosphate – sugar – phosphate – sugar –etc. The shape is called a Double Helix Sections of DNA are called GENES Chromosomes are DNA strands wound up proteins called HISTONES Things to know for GENETICS (but not limited to) DNA contains all the information that about you. When it is coiled up, it is called chromosomes. GENES are pieces of chromosomes that carry specific information about your physical and behavioral traits HEREDITY is the passing on of genes from parent to offspring GENOTYPE is the description of the inherited traits. They come in ALLELES, such as dominant brown eye allele or recessive blue eye allele. PHENOTYPE is the observable physical characteristics described by the genotype. Know: homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, heterozygous Punnett Squares Possible Test Questions What are the stages of the cell cycle? What happens during interphase? Mitosis? Cytokinesis? What are the phases of mitosis? Explain what happens in each phase of mitosis in terms of the cell membrane, nuclear membrane, DNA, chromosomes, centrioles, and microtubules (spindle fibers). What is the purpose of mitosis? Describe the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction. What are the 3 reasons for cellular division? Why? What is the structure of DNA? How does DNA become chromosomes? What are the individual units of DNA called? How are they arranged? What pairs do nucleotides make? (Know how to spell them.) What are the subunits of a nucleotide? How does each nucleotide connect to the next in a single strand? How do DNA strands connect to each other to from a double strand? Given: AGA CTT ACG TAG, match the complementary strand. How do genotypes differ from phenotypes? What’s the relation between dominant and recessive alleles? Given: Mom has brown hair (Bb), dad has blonde hair (bb). o Create a Punnett square. o Identify the percent of heterozygous alleles. o Identify the percent of homozygous dominant alleles. o Identify the percent of homozygous recessive alleles. o What percentage of offspring are brown haired? o What percentage of offspring are blonde haired? o