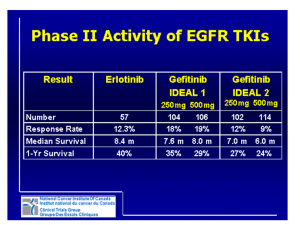
Supplementary Table 2 | Drug rechallenge following progression on
advertisement
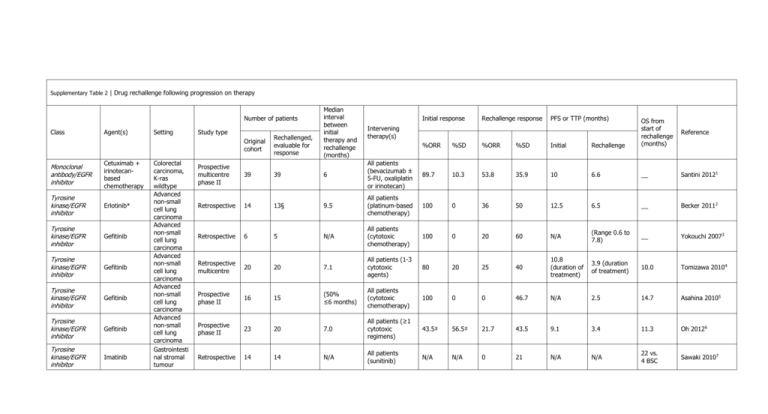
Supplementary Table 2 | Drug rechallenge following progression on therapy Number of patients Class Agent(s) Setting Study type Original cohort Monoclonal antibody/EGFR inhibitor Cetuximab + irinotecanbased chemotherapy Tyrosine kinase/EGFR inhibitor Erlotinib* Tyrosine kinase/EGFR inhibitor Gefitinib Tyrosine kinase/EGFR inhibitor Gefitinib Tyrosine kinase/EGFR inhibitor Gefitinib Tyrosine kinase/EGFR inhibitor Gefitinib Tyrosine kinase/EGFR inhibitor Imatinib Colorectal carcinoma, K-ras wildtype Advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma Advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma Advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma Advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma Advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma Gastrointesti nal stromal tumour Rechallenged, evaluable for response Median interval between initial therapy and rechallenge (months) Intervening therapy(s) Initial response Rechallenge response PFS or TTP (months) %ORR %SD %ORR %SD Initial Rechallenge OS from start of rechallenge (months) 89.7 10.3 53.8 35.9 10 6.6 __ Santini 20121 Reference Prospective multicentre phase II 39 39 6 All patients (bevacizumab ± 5-FU, oxaliplatin or irinotecan) Retrospective 14 13§ 9.5 All patients (platinum-based chemotherapy) 100 0 36 50 12.5 6.5 __ Becker 20112 Retrospective 6 5 N/A All patients (cytotoxic chemotherapy) 100 0 20 60 N/A (Range 0.6 to 7.8) __ Yokouchi 20073 Retrospective multicentre 20 20 7.1 All patients (1-3 cytotoxic agents) 80 20 25 40 10.8 (duration of treatment) 3.9 (duration of treatment) 10.0 Tomizawa 20104 Prospective phase II 16 15 (50% ≤6 months) All patients (cytotoxic chemotherapy) 100 0 0 46.7 N/A 2.5 14.7 Asahina 20105 Prospective phase II 23 20 7.0 All patients (≥1 cytotoxic regimens) 43.5‡ 56.5‡ 21.7 43.5 9.1 3.4 11.3 Oh 20126 Retrospective 14 14 N/A All patients (sunitinib) N/A N/A 0 21 N/A N/A 22 vs. 4 BSC Sawaki 20107 Tyrosine kinase/EGFR inhibitor Imatinib Gastrointesti nal stromal tumour Retrospective multicentre 223 40 9.2‡ All patients (sunitinib) N/A Tyrosine kinase/EGFR inhibitor Imatinib Gastrointesti nal stromal tumour Prospective, single centre, phase III 81 41 N/A All (sunitinib), 40% ≥3 prior TKIs N/A N/A 6 19 DCR 12 weeks 32% (vs. 5% placebo) 25.5‡ 2.9 7.5 Italiano 20128 N/A 1.8 vs. 0.9 placebo 8.2 (vs. 7.5 placebo) Kang 20139 All patients (1-4 therapies, for Tyrosine Metastatic example, kinase/VEGFR Sorafenib renal cell Retrospective 12 8 7.6 18|| 63.6|| 0|| 72.7|| 5.7 5.4 __ Nozawa 201210 sunitinib, inhibitor carcinoma everolimus, thalidomide) All patients Tyrosine kinase Metastatic (sorafenib, ± Retrospective / VEGFR Sunitinib renal cell 23 23# 6.7 bevacizumab, ± 65 29 21 71 13.7 7.2 __ Zama 201011 multicentre inhibitor carcinoma mTOR inhibitor, other) All Tyrosine kinase Metastatic (temsirolimus, / VEGFR Sunitinib renal cell Retrospective 13 13** 13 75 25 15 77 21 6.9 __ Grünwald 201112 everolimus, +4 inhibitor carcinoma sorafenib) Original cohort = patients receiving initial therapy, rechallenged with a drug combination not reflective of ‘true’ rechallenge, or sum of evaluable+non-evaluable patients. Rechallenge patient numbers reflect those patients receiving both initial and rechallenge therapy that were evaluable for response. Other cases are noted. When appropriate weeks converted into months: 1 week = 0.229,984 months, days converted into months: 1 day = 0.0328,549 months. *8 patients received erlotinib to erlotinib, 3 pts sorafenib+erlotinib to erlotinib, 2 pts erlotinib to cetuximab+erlotinib. PFS calculation includes a 14th patient receiving gefitinib to erlotinib. ‡Data based on original cohort of patients/intent to treat population. Patients received initial therapy, but not all were rechallenged (due to lack of PD or patients not evaluable for response). §Patient received initial gefitinib (not true rechallenge, however provided data includes this patient). ||Response rates recalculated using data from 8 evaluable patients rechallenged following PD on sorafenib. #Includes 2 patients with increased dose at rechallenge. **Data includes 2 patients that discontinued initial sunitinib early, prior to PD. Abbreviations: BSC, best supportive care; ORR, overall response rate = PR (partial response) + CR (complete response); PD, progressive disease; PFS, progression-free survival; pts, patients; SD, stable disease; TTP, time to progression. 1. Santini, D. et al. Cetuximab rechallenge in metastatic colorectal cancer patients: how to come away from acquired resistance? Ann. Oncol. 23, 2313–2318 (2012). 2. Becker, A. et al. Retreatment with erlotinib: regain of TKI sensitivity following a drug holiday for patients with NSCLC who initially responded to EGFR-TKI treatment. Eur. J. Cancer 47, 2603–2606 (2011). 3. Yokouchi, H. et al. Clinical benefit of readministration of gefitinib for initial gefitinib-responders with non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 7 (2007). 4. Tomizawa, Y. et al. Effect of gefitinib re-challenge to initial gefitinib responder with non-small cell lung cancer followed by chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 68, 269–272 (2010). 5. Asahina, H. et al. Phase II study of gefitinib readministration in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and previous response to gefitinib. Oncology 79, 423–429 (2010). 6. Oh, I., Ban, H., Kim, K. & Kim, Y. Retreatment of gefitinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who previously controlled to gefitinib: A single-arm, open-label, phase II study. Lung Cancer 77, 121–127 (2012). 7. Sawaki, A., Kanda, T., Komatsu, Y. & Nishida, T. Impact of imatinib plus best supportive care in imatinib- and sunitinib-exposed patients with refractory advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 28, (suppl; abstr 10064) (2010). 8. Italiano, A. et al. Patterns of care, prognosis, and survival in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) refractory to first-line imatinib and second-line sunitinib. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 19, 1551–1559 (2012). 9. Kang, Y. K. et al. Randomized phase III trial of imatinib (IM) rechallenge versus placebo (PL) in patients (pts) with metastatic and/or unresectable gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) after failure of at least both IM and sunitinib (SU): RIGHT study [abstract]. J. Clin. Oncol. suppl; LBA10502 (2013). 10. Nozawa, M. et al. Sorafenib rechallenge in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. BLU Int 110, E228–234 (2012). 11. Zama, I. N. et al. Sunitinib rechallenge in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Cancer 116, 5400–5406 (2010). 12. Grünwald, V. et al. Efficacy of sunitinib re-exposure after failure of an mTOR inhibitor in patients with metastatic RCC. Onkologie 34, 310–314 (2011).