下載此投影片
advertisement
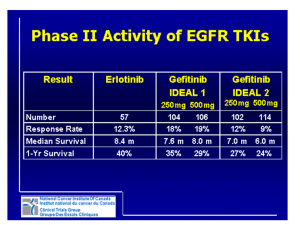
Treatment of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Erlotinib or Gefitinib N Engl J Med. 2011 Mar 10;364(10):947-55. Presentor: CR 周益聖 Supervisor: Vs 顏厥全 財團法人台灣癌症臨床研究發展基金會 1 Outline • • • • • Introduction of lung cancer EGFR in NSCLC Important clinical trials of TKI To know about gefitinib and erlotnib Conclusion with NCCN guideline and regulations of Bureau National health insurance, Taiwan, ROC 2 Lung cancer • Leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide • Estimated 157,300 deaths in the United States in 2010 • 85% of lung cancer are non-small-cell-lung cancer(NSCLC) • Less than 30% respond to platinum based therapy 3 Chemotherapy in NSCLC 4 N Engl J Med 2002;346:92-98 General characteristics N Engl J Med 2002;346:92-98 5 TTP:GC >PC, greater grade 3,4,5 renal toxicity(9% vs. 3%) 6 N Engl J Med 2002;346:92-98 Overall survival 7.8-8.1 months Time to progression 3.1-4.2 months 7 N Engl J Med 2002;346:92-98 EGFR in NSCLC 8 Driver mutations in NSCLC 9 Lancet Oncol 2011; 12: 175–80 HER3 had no tyrosine kinase activity EGFR signaling pathways 10 N Engl J Med 2008; 359:1367-1380 EGFR amplifications 1.Dysplasia (especially of a high grade) 2. Increased lung-cancer risk when detected in the sputum of smoker 3. Poor prognosis 4.Sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors 11 EGFR mutation 12 EGFR mutation Leu Arg Glu Ala (LREA) motif in exon 19 13 N Engl J Med 2005;353:133-44. Gefitinib (Iressa) & Erlotinib(Tarceva) • EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors • Asian, non-smoker, and female • Gefitinib and erlotinib for EGFR mutation N Engl J Med 2008;359:1367-1380 14 Tarceva Tarcev a Placebo Erlotinib in NSCLC(≧2 lines) 15 N Engl J Med 2005; 353:123-132 16 N Engl J Med 2005; 353:123-132 Overall survival HR:0.70 6.7 vs. 4.7 months P<0.001 Progression free survival 2.2 vs 1.8 months P<0.001 17 N Engl J Med 2002;346:92-98 Univariate HR P value Multivariate HR P value 0.7 <0.001 0.7 0.002 0.7 0.8 0.008 0.07 0.8 0.004 0.7 0.9 0.8 0.02 0.7 0.03 0.9 0.4 1.1 0.14 <0.001 0.8 Referrence 0.8 1 0.048 0.89 0.6 0.8 0.06 0.01 0.7 0.01 Treatment Erlotinib Placebo Pathologic subtypes Adenocarcinoma Others EGFR Positive Negative Unknown Smoking Ever Never Unknown Race Asian Others 18 N Engl J Med 2002;346:92-98 EGFR mutation • • • • • • 10% of adenocarcinoma in USA 30-50% of adenocarcinoma in Asia Female & non-smokers Exons 18, 19, and 20 and 21 Transform fibroblasts and lung epithelial cells In transgenic mice->exon 19 deletion or L858R mutation->atypical adenomatous hyperplasia>BAC->invasive adenocarcinoma in 8-10 weeks • >80% : exon 19 or the L858R within exon 21 19 N Engl J Med 2008; 359:1367-1380 Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer(ISEL) Lancet 2005;366:1527-1537 Iressa Placebo Iressa Placebo 20 Overall survival in all populations 5.6 vs. 5.1 months HR:0.89,P=0.087 Overall survial in adenocarcinoma 6.3 vs. 5.4 months HR:0.84,P=0.089 21 Lancet 2005;366:1527-1537 Time to treatment failure in all populations 3.0 vs. 2.6 months HR:0.82,P=0.006 22 Lancet 2005;366:1527-1537 Subgroup analysis of Iressa 23 Lancet 2005;366:1527-1537 Iressa PanAsia Study (IPASS) 1.Asia 2.Iressa vs Carboplatin+Paclitaxel 3.First line 24 N Engl J Med 2009;361:947-957 Progression free survival in all populations 5.6 vs. 5.1 months HR:0.74,P<0.001 Progression free survival in EGFR mutation 6.3 vs. 5.4 months HR:0.48,P<0.001 25 N Engl J Med 2009;361:947-957 Progression free survival in EGFR mutation negative 5.6 vs. 5.1 months HR:2.85,P<0.001 Progression free survival in EGFR unknown 6.3 vs. 5.4 months HR:0.68,P<0.001 26 N Engl J Med 2009;361:947-957 Iressa vs. Paclitaxel+carboplatin (1st line) in EGFR mutation 27 N Engl J Med 2010; 362:2380-2388 Progression free survival 10.8 vs. 5.4 months HR:0.30,P<0.001 Overall survival 30.5 vs. 23.6 months P=0.31 28 N Engl J Med 2010; 362:2380-2388 Erlotinib(Tarceva) • Approval from FDA in November,2004 • Approval from European Medicines Agency in June,2005 • Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC • 2nd or 3rd line • 150mg/day PO QD • Bioavailability 100% when taken with food-> more side effect – One hour before or two hours after a meal ( Bioavailability:60%) 29 Gefitinib (Iressa) • Approval from FDA in 2003 • ISEL-> use in who are currently benefiting or have previously benefited in USA • Approval from European Medicines Agency in July,2009 • Any line for NSCLC with EGFR mutations • In first line, inferior to chemotherapy but superior for those with EGFR mutations • ≧2 line, similar to standard chemotherapy • Not effected by food • 250 mg PO QD • Half life: 48 hours • Bioavailability:60% 30 Metabolism • By CYP3A4 – CYP3A5 and CYP1A1( lesser) • Careful with atazanavir, itraconazole, ritonavir,voriconazole, grape fruit juice • Not with CYP3A4 inducers – rifampicin, phenytoin, and St. John’s wort • Cigarrete induces CYP1A1 -> reduces erlotinib • Avoid H2 blocker or PPI (-> reduces gastric PH-> reduce plasma TKI) 31 Follow-up • Radiographic assessment no more frequent than every 6 to 8 weeks • Visit at least monthly • Medications continued as long as – ECOG adequate – No clinical or radiographic progression 32 Dosage • Reduced when rash or diarrhea • Monitor liver function • Discontinued when total bilirubin ≧3X or ALT/AST ≧5X • Erlotinib restated at a reduced dose with decrement of 50mg ( 100mg qd) • Gefitinib restated at initial dose(250mg) 33 Cost • Erlotinib – $4,000/month – NTD 53490/month(1783/#) • Gefitinib – $1,800/month – NTD 41280/month(1376/#) 34 Toxic effects • Discontinuation of drugs due to toxic effects – Erlotinib:5% – Geftinib:2% • Erlotinib – Diarrhea : 55% – Severe diarreha: 6% • Gefitinib – Diarrhea: 27 to 35% • Stopped for up to 14 days until the symptoms resolved • Loperamide 35 Rash • • • • 75% of erlotinib 33% of geftinib 7-14 days after initiation of therapy Association with improved OS and PFS – Surrogate indicator of effective EGFR inhibition? – Surrogate indicator of immue based local inflammatory reaction? • • • • • • Follicular and papulopustular Face, scalp, chest, and back Antibiotics, glucocorticoids, and immunomodulators Moisturizing of the skin Avoid acne preparations(benzoyl peroxide) Dose modifications 36 Interstitial lung disease • • • • Less than 1% in white patients About 5% in Japanese patients 1st month of therapy Risk factors – previous chemotherapy – previous radiation to the lungs – preexisting parenchymal lung disease – metastatic lung disease – Concomitant pulmonary infection • TKI permanently discontinued 37 Neutrophilic infiltration of the dermis, involving most prominently the infundibular portion of the hair follicles 38 Areas of uncertainty: other EGFR mutations? 39 Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:7232-7241 Resistance of TKI • Almost for all • Median time to progression: 12 months • Secondary EGFR mutation – T790M in exon 20 in 50%-70% – amplification of the MET oncogene in 30 to 50% • Second generation TKI? – EKB-569 – HKI-272 – XL647 40 J Thorac Oncol 2008;3:S146-9 TKI T790M resistance(Exon20) 41 Amplification of MET oncogene 42 Conclusion 43 NCCN guideline(Version 3.2011) The National Comprehensive Cancer Network 44 home page. (http://www.NCCN.org.) NCCN guideline(Version 3.2011) The National Comprehensive Cancer Network 45 home page. (http://www.NCCN.org.) NCCN guideline(Version 3.2011) All including SCC The National Comprehensive Cancer Network 46 home page. (http://www.NCCN.org.) Erlotinib給付規定 1. 限單獨使用於 (1) 先前已使用過第一線含鉑化學治療,或70歲(含)以上接受過第一線化學治療, 但仍局部惡化或轉移之腺性非小細胞肺癌之第二線用藥。(97/6/1) (2)先前已使用過platinum類及docetaxel或paclitaxel化學治療後,但仍局部惡化 或轉移之非小細胞肺癌之第三線用藥。 2. 需經事前審查核准後使用,若經事前審查核准,因臨床治療需轉換同成份不同含量品 項,得經報備後依臨床狀況轉換使用,惟總使用期限不得超過該次申請事前審查之 療程期限。(97/6/1) (1) 用於第二線用藥:檢具確實患有非小細胞肺癌之病理或細胞檢查報告,並附曾經 接受第一線含鉑化學治療,或70歲(含)以上接受過第一線化學治療之證明,及目前又 有疾病惡化之影像診斷證明(如胸部X光、電腦斷層或其他可作為評估的影像),此 影像證明以可測量(measurable)的病灶為優先,如沒有可以測量的病灶,則可評估 (evaluable)的病灶亦可採用。(97/6/1) (2) 用於第三線用藥:檢具確實患有非小細胞肺癌之病理或細胞檢查報告,並附曾經 接受第一線及第二線化學藥物如platinum(cisplatin或carboplatin)與taxanes (paclitaxel或docetaxel)治療之證明,及目前又有疾病惡化之影像診斷證明(如胸部 X光、電腦斷層或其他可作為評估的影像), 此影像證明以可測量(measurable)的 病灶為優先,如沒有可以測量的病灶,則可評估(evaluable)的病灶亦可採用。 (97/6/1) (3) 每次申請事前審查之療程以三個月為限,每三個月需再次申請,再次申請時並需 附上治療後相關臨床資料,如給藥四週後,需追蹤胸部X光、電腦斷層等影像檢查一 遍,評估療效,往後每四週做胸部X光檢查,每隔八週需追蹤其作為評估藥效的影像 47 (如胸部電腦斷層)。 Geftinib給付規定 1. 限單獨使用於 (1)具有EGFR-TK基因突變之局部侵犯性或轉移性(即第ⅢB期或第 Ⅳ期)之肺腺癌病患之第一線治療。(100/6/1) (2)先前已使用過第一線含鉑化學治療,或70歲(含)以上接受過第 一線化學治療,但仍局部惡化或轉移之肺腺癌。(96/11/1、 100/6/1) 2.需經事前審查核准後使用: (1)用於第一線用藥:檢具確實患有肺腺癌之病理或細胞檢查報告, 及EGFR-TK基因突變檢測報告。(100/6/1) (2)用於第二線用藥:檢具確實患有肺腺癌之病理或細胞檢查報 告,並附曾經接受第一線含鉑化學治療,或70歲(含)以上接受 過第一線化學治療之證明,及目前又有疾病惡化之影像診斷 證明(如胸部X光、電腦斷層或其他可作為評估的影像),此 影像證明以可測量(measurable)的病灶為優先,如沒有可以 測量的病灶,則可評估(evaluable)的病灶亦可採用。 48 Thanks for your attention! 49