YUNUS EMRE TAŞ 11-A 120 THE EFFECT OF SURFACE AREA
advertisement

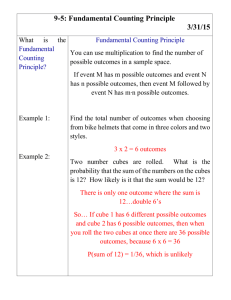
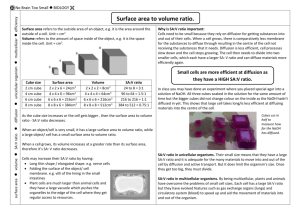
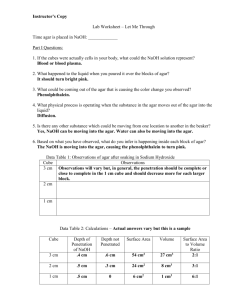
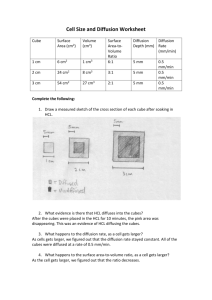
YUNUS EMRE TAŞ 11-A 120 THE EFFECT OF SURFACE AREA VOLUME RATIO ON DISSOLVING OF AGAR IN HYDROCHLORIC ACID RESEARCH QUESTION: What is the effect of surface area volume ratio on dissolving of agar in hydrochloric acid? INTRODUCTION: Diffusion is known as the passive movement of the particles from its higher concentration to its lower concentration without energy. This is the reason why some big molecules cannot diffuse but small ones could diffuse such as monomers, ions, etc. Temperature, size of the molecules, concentration gradient, and surface area to volume ratio are some factors that affect the diffusion rate. With this experiment the effect of surface area to volume ratio on the diffusion rate will be examined. AIM: To see the relation between surface area and volume ratio. HYPOTHESIS: I expect that the one which have the bigger value of surface area volume ratio will dissolve firstly. VARIABLES INDEPENDENT VARIABLES: It is the surface area volume ratio of the agar blocks. DEPENDENT VARIABLES: It is the time taken for the disappearance of the red colour in the block. CONTROLLED VARIABLES: Since the effect of one factor is examined the other factors should be kept constant. Temperature and the concentration of the acid were kept constant. The experiment took place in room temperature and for different sized agar blocks the same concentration of acid is used. APPARATUS: One large block of agar Knife Chopping board 100 cm3 hydrochloric acid 5 beakers (100 ml) Stopwatch METHOD: Cut the large agar block into different cubes that have different dimensions. Add 60 cm3 hydrochloric acid to the each beaker. YUNUS EMRE TAŞ 11-A 120 Put the agar cubes, which have different sizes, into the beakers at the same time and start the time immediately. The time taken for the disappearance of the red colour in the agar cube recorded for each of the agar cube. DATA COLLECTION Agar Cubes Cube 1 Cube 2 Cube 3 Cube 4 Cube 5 Dimensions/cm 0.9x1.5x1.7 0.9x2.2x1.4 0.9x2.0x2.3 0.9x3.1x2.2 0.9x2.4x2.2 Tablo 1: Dimensions of the Agar Cubes Agar Cubes Surface Area/cm2 Volume/cm3 Surface area/Volume Time taken/s (±0.1) Cube 1 Cube 2 Cube 3 10.86 12.64 16.94 2.295 2.772 4.140 4.732 4.560 4.091 310 323 342 Cube 4 Cube 5 23.18 18.57 6.138 4.752 3.776 3.907 380 375 Tablo 2: Surface Area Volume Ratio of the Agar Cubes Time taken/s 450 400 350 300 250 Time taken/s 200 150 100 50 0 0 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 Graph 1: It Shows The Relation Between Surfaca Area Volume Ratio And The Diffusion Rate 5,000 YUNUS EMRE TAŞ 11-A 120 CONCLUSION AND EVALUATION The experiment shows that if the surface area volume ratio gets bigger the diffusion rate increases. It means that when the surface area volume ratio decreases the amount of HCl enters the agar block decreases. So the bigger surface area volume ratio causes increasing diffusion rate. I do not have much time while doing the experiment so I could not repeat the experiment to get accurate values for time and I took the cubes whose surface area volume ratios are very close to each other so the red colour disappears immediately so while I record the time I could catch the real time that the block disappear. It is very difficult the record the time and observe the agar cubes into the acids. I tried to do it but I think I could not ménage it so well so it caused some mistakes and errors.