5259-Rates of Reaction - Triple Science Resource
advertisement

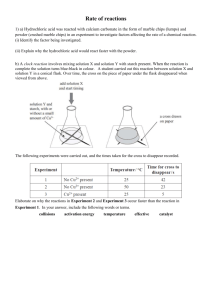
Investigating Rates of Reaction Aim This resource covers a series of 5 lessons during which time students will investigate 5 factors affecting the rate of a chemical reaction, and three methods of investigating rates of reaction. They will be challenged to observe and identify the causes and effects of these factors, as well as to apply How Science Works skills including graph drawing and interpretation, description and explanation of observations. Learning Outcomes Each practical has it’s own learning outcomes, specified below. In addition the following learning outcomes apply: Define rate of reaction Define collision theory List ways of finding the rate of a reaction Explain why a particular method of finding the rate is suitable for a specified reaction Administration Students should work in pairs, and the class should be split into 4 groups. Groups should work on a different practical task, and should rotate through each over 4 hours of lesson time. This should alleviate pressure on equipment, and should allow all students to participate equally. Students will need copies of the instruction sheets and graph paper. Students should be reminded of all safety implications before every session. Some techniques will need to be demonstrated before students attempt them (e.g. use of gas syringes). Suggested timetable: Lessons 1-4: practical tasks on rotation (sheets attached). Students should be encouraged to work independently, to identify patterns in reactivity under the different conditions. They should be encouraged to think about why changing conditions causes the differences they observe. Allow students to come to their own conclusions, but facilitate with questioning – encourage them to think critically about their work. Lesson 5: This lesson should serve as a synoptic session, identifying students ideas about the rates of reaction and introducing collision theory in a more formalised way. Following this, it may be useful for students to return to the explanation part of the practical sheets to include details of collision theory in their explanations of their observations. Name: __________________________ Date: ____________________________ Specification Link: AQA GCSE Chemistry C2.4 Rates of Reacton Edexcel GCSE C2 Chemical Reactions OCR GCSE 21st Century Chemistry A C6 Chemical Synthesis OCR GCSE Gateway Chemistry B C3 Chemical Economics Safety: The teacher should ensure students observe the usual lab safety precautions, with consideration for any additional aspects the group in question might require. Hazcards: 50 Hydrogen peroxide Harmful 60 Manganese and its compounds 47A Hydrochloric acid 95C Sodium thiosulfate 19B Calcium an strontium salts (2) Low Hazard Harmful Corrosive Name: __________________________ Date: ____________________________ Equipment Practical station: A B Effect of catalysts Effect of temperature Hydrogen peroxide Manganese(IV) oxide Finely chopped potato Finely chopped liver Stopwatches (4) Conical flasks (4) Gas syringes with bungs & tubing(4) Clamps & stands Measuring cylinders (25cm3) Hydrochloric acid (0.2mol/dm3) Sodium thiosulfate (0.2mol/dm3) Stopwatches (4) Conical Flasks (4) Water baths at 30, 40 & 50°C Ice bath Measuring cylinders (10cm3) Cotton wool Thermometers Please set up with samples of both solutions in each water/ice bath. C Effect of concentration/pressure Hydrochloric acid (0.2mol/dm3, 0.5 mol/dm3 & 1mol/dm3) Marble chips Stopwatches (4) Conical Flasks (4) Top pan balances (4) Measuring cylinders (25cm3) Cotton wool D Effect of surface area Hydrochloric acid (1mol/dm3) Marble chips (small & large) Stopwatches (4) Conical Flasks (4) Top pan balances (2) Gas syringes with bungs & tubing(4) Clamps & stands Measuring cylinders (25cm3) Learning Objectives Effect of Effect of surface area concentration/pressure State what effect Describe how increasing the Describe how increasing the pressure of surface area | Define catalyst ||| temperature | ||| reacting gases affects the rate of affects the rate of has on the rate of reaction reactions reaction Apply collision Describe the Apply collision theory to explain in effect of theory to explain Describe how a detail how and why increasing in detail how ||| catalyst affects the ||| temperature concentration on surface area rate of a reaction changes the rate the rate of affects the rate of of reaction reaction reaction Apply collision Explain in detail Predict how theory to explain Suggest which why a catalyst temperature would in detail the effect collisions would would be used in affect a reaction of changing not cause a an industrial where particles are concentration or reaction process in a solid state pressure on the rate of reaction Effect of catalysts Effect of temperature Name: __________________________ Date: ____________________________ Experiment A - Measuring the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction Equipment: Hydrogen peroxide Manganese(IV) oxide Potato Liver (optional) Stopwatch Gas syringe & delivery tubes Conical flask 25cm3 measuring cylinder Clamp & stand Safety spectacles Results: Time (s) Procedure: 1. Set up the gas syringe and delivery tubes in a clamp & stand. Gas syringes are delicate, you must have their use demonstrated. 2. Add 25cm3 hydrogen peroxide to the conical flask 3. Add finely chopped potato 4. Swiftly and carefully connect the flask to the gas syringe 5. Start the stopwatch 6. Record the volume of gas released every 10 seconds for 2 minutes. 7. Repeat with a spatula of manganese(IV) oxide and then chopped liver (optional) Draw and label a diagram of your experiment. 3 Volume of gas produced (cm ) Potato Liver MnO2 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Plot these results on a graph. Variables: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variables: Describe your results: Explain what caused the observed effects: Name: __________________________ Date: ____________________________ Experiment B - Measuring the effect of temperature on the rate of a reaction Equipment: Hydrochloric acid (0.2mol/dm3) Sodium thiosulfate (0.2mol/dm3) Stopwatch Conical Flask Water baths at 30, 40 & 50°C Ice bath Measuring cylinder (10cm3) Cotton wool Thermometer Results: Procedure: 1. Place 10cm3 of room temperature 0.2mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid into a conical flask 2. Record the temperature of the solutions 3. Draw an X with a pencil on a piece of plain paper & place underneath the conical flask 4. Add 10cm3 of sodium thiosulfate 5. Start the stopwatch 6. Record how long it takes for the X to be obscured 7. Repeat the experiment with reactants at different temperatures Draw and label a diagram of your experiment. Temp of solutions (°C) Time taken for solution to go cloudy (s) Plot these results on a graph. Variables: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variables: Describe your results: Explain what caused the observed effects: Name: __________________________ Date: ____________________________ Experiment C – Measuring the effect of concentration on the rate of a reaction Equipment: Procedure: 1. Add about 5 marble chips to the conical flask Hydrochloric acid 2. Add 25cm3 of 0.5 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid (0.2mol/dm3, 0.5 mol/dm3 3. Place a plug of cotton wool in the neck of the flask & 1mol/dm3) 4. Place the flask on the balance, record the mass and Marble chips start the stopwatch. Stopwatch 5. Record the mass every 10 seconds for 2 minutes. Conical Flask 6. Repeat for 0.2mol/dm3 and 1mol/dm3 concentrations of Top pan balance hydrochloric acid. Measuring cylinder 3 (25cm ) Cotton wool Results: Draw and label a diagram of your experiment. Mass of reaction vessel (g) Time (s) 0.5mol/dm3 0.2mol/dm3 1mol/dm3 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Plot these results on a graph. Variables: Explain what caused the observed effects: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variables: Describe your results: Name: __________________________ Date: ____________________________ Experiment D – Measuring the effect of surface area on the rate of a reaction Equipment: Procedure: 1. Set up the gas syringe and delivery tubes in a clamp & Hydrochloric acid stand. (1mol/dm3) Gas syringes are delicate, you must have their use Marble chips (small & demonstrated. large) 2. Add 1g of marble chips to the conical flask Stopwatch 3. Add 25cm3 hydrochloric acid Conical Flask 4. Connect the gas syringe and start the stopwatch Top pan balance (shared) 5. Record the volume of gas produced every 10 seconds Gas syringes with bungs & for 2 minutes. tubing 6. Repeat for different sized marble chips Clamps & stands Measuring cylinders (25cm3) Results: Draw and label a diagram of your experiment. Volume of gas produced (cm3) Time (s) Small chips Large chips Powdered 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Plot these results on a graph. Variables: Explain what caused the observed effects: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variables: Describe your results: Name: __________________________ Date: ____________________________