Structured Conversations - Leadership Academy Extended School
advertisement

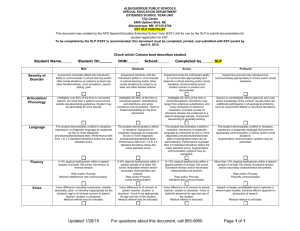
Structured Conversations - Leadership Academy Extended School Year LEGAL BASIS §300.106 Extended School Year Services – Each public agency must ensure that ESY services are available as necessary to provide FAPE, consistent with this section. ESY services must be provided only if a child’s IEP Team determines, on an individual basis, that the services are necessary for the provision of FAPE. In implementing these requirements, a public agency may not limit ESY services to particular categories of disability; or unilaterally limit the type, amount, or duration of those services. §14.132 ESY. ESY means special education and related services that are provided to a child with a disability beyond the normal school year of the public agency; in accordance with the child’s IEP; and at no cost to the parents of the child; and meet the standards of the SEA. Armstrong v. Kline 476F.Supp. 583 (E.D. Pa. 1979) (affirmed in Battle v. Commonwealth of Pennsylvania) Established that for certain handicapped children. . . a program in excess of 180 days is required if they are to attain that level of self-sufficiency that is otherwise possible given an appropriate education. This case provided some standards to be considered in ESY decisions: 1) nature of handicapping condition, 2) severity of handicapping condition, 3) extent of regression or recoupment, and 4) skills in selfsufficiency and independence from caretakers. QUESTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What does your LEA do to ensure individualized ESY programming for students? What action, if any, has to occur if student is absent or does not attend ESY programming at all? How do you determine the amount of time to provide services for ESY?2 Is there more than one type of service delivery model that IEP teams may consider?2 Is there a fee to parents for ESY? FACTS This is how the facts are written on the cards: Students in the Armstrong target group must have an IEP team review of ESY eligibility no later than February 28th of each school year, with a NROEP issued no later than March 31. The Armstrong target group includes autism/pervasive developmental disorder, serious emotional disturbance, severe intellectual disabilities, degenerative impairments with mental involvement, & severe multiple disabilities. 4 Basic Steps: Gather Information, Review 7 Factors and Make Determination, Document Determination in IEP, Issue a NOREP. A NOREP needs to be issued if: Proposing to add ESY services to an IEP that previously did not have it. A NOREP needs to be issued if: Deleting the provision of ESY services from an IEP that previously did have it. 1 A NOREP needs to be issued if: Refusing to initiate the provision of ESY services requested by the parent. Decisions of eligibility for ESY services remain an IEP team decision and are not limited by a formula or single measure. The IEP team must consider the following factors; however, no single factor will be considered determinative: Regression/Recoupment, Mastery, Self-sufficiency/independence, successive interruptions and severity of disability. Reliable Sources of information include progress on IEP goals, progress before and after interruptions to programming, reports by parents, medical or agency reports, observations and opinions, and results of tests (CBA, standardized, criterion-referenced…). Extended School Year is not day care or respite, summer recreation, or any program not required to ensure FAPE. ESY means special education and related services that are provided to a child with a disability beyond the normal school year of the public agency. School year is defined as the first day of July of one year and the 30th of June of the following year. All students with disabilities who qualify for special education services, must be considered for ESP eligibility at each IEP meeting. Students placed in a private school or agency by the LEA through a contractual placement for provision of special education retain all the rights of a child with a disability who is served by a public agency. There is no individual entitlement to services for students who have been placed in private schools by their parents. The ultimate question for an IEP team is not whether FAPE is being provided in the ESY program but whether ESY services are necessary in order to receive FAPE. RESOURCES 1. 2. 3. 4. Basic Education Circulars (BECs) a. BEC 22 Pa. Code 14.132 “Extended School Year Eligibility” b. BEC 34 CFR 300.450 “Special Education Services to Nonpublic School Students” Extended School Year Services in Pennsylvania (2015) http://www.pattan.net/category/Resources/PaTTAN%20Publications/Browse/Single/?id=503d24b08b0332 457f0000c7 State Board of Education Regulations 22 Pa. Code Section 14. 132 Teachers’ Desk Reference: Extended School Year (ESY) (2014) - http://pattan.netwebsite.s3.amazonaws.com/images/2015/06/10/TDR_ESY0615.pdf The following chart will be posted in the center panel: 2 ESY Service to be provided Location Frequency Projected Beginning Date Anticipated Duration Tutorial for parents – AT Device by AT consultant School Library 3, one-hour sessions 7.1.2013 7.24.2013 Direct instruction to parents – Behavior Principles School Library 1, two-hour session 7.1.2013 7.24.2013 Instruction by special educator – Reading & Math Goals Student’s Classroom 2x per week – 45 min 7.1.2013 8.1.2013 Speech/Lang services Student’s Classroom 1 x per week – 30 min. 7.1.2013 8.1.2013 3