Guide to Grammar and Punctuation.
advertisement

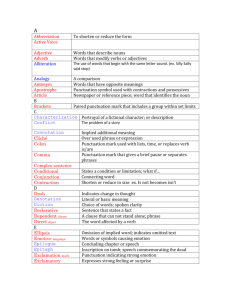
Guide to Grammar and Punctuation St Mary’s CEVA Primary School Year 1 Term Word Sentence Letter Punctuation Full stop Exclamation mark Question mark Singular Plural Description / Meaning A group of sounds together that symbolise something. A sentence begins with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, exclamation mark or question mark. A sentence needs a verb and must make sense on its own. A written a symbol that represents a sound. Upper case letters are used at the start of sentences, days of the week, months of the year and names. The use of certain marks to clarify the meaning of written material by grouping words grammatically into sentences, clauses and phrases. Punctuation marks are used to extend, enhance and end sentences. A full stop marks the end of a sentence. An exclamation sentence (something loud, exciting or dramatic) may end with an exclamation mark. A question sentence ends with a question mark. One thing. More than one thing. A plural word is usually created by adding ‘-s’ (table – tables) although there are irregular plurals (e.g. children; teeth) and plurals that end in ‘-es’ and ‘-ves’. Examples Table; and; run The horse jumped over the fence. The boy walked home. a; b; c A; B; C On Saturday, Frank visited the zoo in Colchester. .,!?“;:‘–()- The horse jumped over the fence. The boy walked home. I have won the lottery! Watch out! Where is the park? What time is lunch? Table; child; wolf; bus Tables; children; wolves; buses Guide to Grammar and Punctuation St Mary’s CEVA Primary School Year 2 Term Verb Description / Meaning Words that denote actions, occurrences or states of being. Past tense When you are writing or talking about something that has already happened. A verb in the past tense usually ends with ‘-ed’. When you are writing or talking about something that is happening at the moment or something that is true now. An adjective describes a noun. Present tense Adjective Noun Suffix A person, place or thing. Proper nouns name a specific person, place or thing and start with a capital letter. A group of letters added to the end of a word to change its meaning. Apostrophe An apostrophe can show possession or ownership. Apostrophe An apostrophe can be used to show when letter have been left out (omission). This makes a ‘contraction’ or shorter form of the words. Commas can be used to separate items in a list (at the end of the list, the word ‘and’ is used in place of a comma). Commas can be used to separate clauses (parts of a sentence). Comma Comma Examples The horse jumped over the fence. The boy is walking home. Frank is cold. Frank was cold. The horse jumped over the fence. The boy walked home. The horse is jumping over the fence. I am sad. The frightened horse jumped over the fence. The small boy walked home. table; boy; Frank; Colchester nice + ly = nicely hope + ful = hopeful cold + er = colder Frank’s football The teacher’s desk The boys’ toilets Would not – wouldn’t I shall – I’ll I have – I’ve I had a tennis ball, reading book, packed lunch and homework diary in my bag. The boy, who had been injured, limped home. At the end of the play, the children clapped loudly. Guide to Grammar and Punctuation St Mary’s CEVA Primary School Year 3 Term Word family conjunction Adverb Preposition Direct speech Inverted commas (speech marks) Prefix Description / Meaning Words that are related in meaning, form or grammar A conjunction is used to join two sentences together or add extra information to a sentence. Examples Run – runner – running Extensive – extent - extend and, but, because, if, although, or, until Fred wore a coat although it was warm outside. An adverb is used to modify or describe a Mary was creeping slowly verb. They tell us how something is down the corridor. happening. Adverbs usually end ‘-ly’. Fred cut out the shapes carefully. A preposition tells us where or when On, between, in, below, inside, something is in relation to something else in a outside, after, before sentence. She hid inside the wardrobe. The actual words of a speaker, quoted using Frank said, “I want to go inverted commas. home.” Inverted commas mark the beginning and end Fred said, “It’s home time!” of direct speech. Inverted commas can be used if quoting a word or phrase. Prefixes are groups of letters added to the start of a word to modify its meaning. Un + happy = unhappy Dis + interested = disinterested Vowel Consonant All words have at least one vowel. There are 21 consonant letters A, E, I, O, U B, C, D, F, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, P, Q, R, S, T, V, W, X, Y, Z Clause A clause is either a complete sentence (main clause) or part of a sentence used to add extra information (subordinate clause) Subordinate clause + main clause = complex sentence Subordinate clause A subordinate clause gives us some extra information but may not be a sentence on its own. When the whistle blew, the players shook hands. The boy, who was injured, limped off the pitch. When the whistle blew, the players shook hands. Guide to Grammar and Punctuation St Mary’s CEVA Primary School Year 4 Term Pronoun Possessive pronoun Adverbial Description / Meaning A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun or noun phrase. Examples He, she, it, we they Frank limped home because Frank had hurt his leg. Frank limped home because he had hurt his leg. A pronoun that shows who something It was my football. belongs to. The football was mine. A word or group of words (a clause or phrase) We met by the park entrance. that function as an adverb by modifying the He went fishing after lunch. verb in the sentence. Adverbials describe The horse raced as fast as it how, where or when something happened. could. This year is largely used to consolidate knowledge of grammar and punctuation introduced in Year 3. Guide to Grammar and Punctuation St Mary’s CEVA Primary School Year 5 Term Relative clause Modal verb Relative pronoun Parenthesis Cohesion Determiner Ambiguity Description / Meaning A relative clause is a type of subordinate clause that adds more detail about the noun in the main clause. Modal verbs go before other verbs in a sentence. They include: ‘will’, ‘should’, ‘would’, ‘could’, ‘can’, ‘may’ and ‘must’. A relative pronoun is used to add more detail about a noun or to clarify which noun we are referring to in a sentence. They include: ‘that’, ‘which’, ‘who’, ‘whose’ and ‘where’. Parenthesis is a word or phrase that departs from the main message, adding more detail or information. Parenthesis also refers to the two punctuation marks used to enclose the extra information. Usually we use brackets, dashes or commas. The extra information is not essential for understanding the main message of the sentence. A text has cohesion if its meaning is coherent and it fits together in a way that makes sense. A determiner stands before a noun and any other words that modify the noun. Determiners are: ‘the’, ‘a’, ‘this’, ‘any’, ‘my’, ‘an’. Ambiguity is when an expression can be interpreted in different ways. Examples The book, which was very dusty, fell from the shelf. I shall do my homework on time. The horse, which was frightened, jumped over the fence. Fred got a bike (a bright blue racing bike) for his birthday. On the trip – a visit to the museum – the children behaved well. The horse jumped over a fence. They were cooking apples. Guide to Grammar and Punctuation St Mary’s CEVA Primary School Year 6 Term Active and passive voice Description / Meaning A sentence is written in active voice when the subject of the sentence performs the action in the sentence. A sentence is written in passive voice when the subject of the sentence has an action done to it by someone or something else. The subject of a sentence performs the action (‘does’ the verb). The object of the sentence has the action done to it. A hyphen is used to link words to create compound words. They can be used to link prefixes to words and to link arts of words. Colons can be used: Between two main clauses when the second explains or ‘answers’ the first; To introduce a list; To introduce a quotation (and sometimes to introduce direct speech). Examples The dog bit Ben. (Active) Ben was bitten by the dog. (Passive) Semi-colon A semi-colon can link two complete sentences and turn them into one. The content or ideas in the sentences should be related. Bullet points Bullet points are used to draw attention to important information. They set text out clearly so the reader can see key facts quickly. Synonyms are words with the same or similar meanings. The door was flung open; a shadowy figure stormed in. Wendy was very tired; she had performed in a play the night before. The dog was: loyal affectionate brave Said, muttered, mumbled Subject Object Hyphen Colon Synonym The dog bit Ben. The dog bit Ben. Sugar-free Co-own That is the secret of my success: always be willing to take a risk. The price includes the following: flight to Paris, hotel accommodation and breakfast. He yelled: “Please help us!”