Bioc 416 syllabus
advertisement

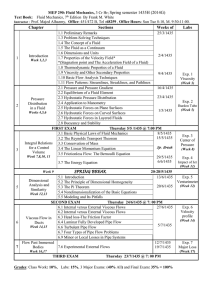
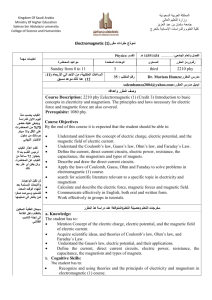
KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE GIRLS’S SECTION Course Syllabus DEPARTMENT: BIOCHEMISTRY COURSE CODE: BIOC 416 COURSE TITLE: CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY NUMBER OF CONTACT HOURS: 4(3,3) E-MAIL:haldoghaither@kau.edu.sa OFFICE: 2-163 OFFICE HOURS: SU, TU& TH (9-10), (12-1) SEMESTER: SPRING 13/14 CLASS TIME: Sections EAR & EBR : SU,TU& TH (10:00-10:50) CLASSROOM: 2165 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. HUDA AL DOGHAITHER 1 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION: The course provides an introduction to the principles and procedures of various tests performed in Clinical Chemistry. It presents the physiological basis, principle and procedures and the clinical significance of test results, including quality control and reference values. Emphasis is placed on basic chemical laboratory techniques, safety, electrolytes, acid-base balance, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and enzymes. II. COURSE PREREQUESITS BIOC 315: Metabolic regulation III. COURSE OBJECTIVES: By the end of this course, students will be able to: A. Demonstrate theoretical comprehension of clinical biochemistry. B. Develop familiarity with clinical biochemical laboratory instrumentations and techniques C. Perform diagnostic techniques, and correlate laboratory findings with disorders. IV. COURSE TOPICS: A. Biochemical investigation in clinical medicine 1. Specimen collection 2. Sample analysis and reporting of results 3. Sources of error 4. The clinical utility of laboratory investigations B. Water, Sodium and Potassium 1. Water and sodium homeostasis 2. Laboratory assessments of water and sodium status 3. Hyponatraemia and hypernatraemia 4. Potassium homeostasis 5. Hypokalaemia and hyperkalaemia C. Hydrogen ion homeostasis and blood gases 1. Respiratory and metabolic acidosis 2. Respiratory and metabolic alkalosis D. The kidneys 1. The biochemical investigation of renal function 2. Renal disorders E. The liver 1.The biochemical assessment of liver function 3. Liver disease F. Thyroid gland 1. Thyroid hormones 2. Tests of thyroid function 3. Disorders of the thyroid G. Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism 1. Introduction to carbohydrate metabolism 2. Measurement of glucose concentrations 3. Diabetes mellitus 2 4. Metabolic complications of diabetes H. Plasma proteins and enzymes 1. Measurement of plasma proteins 2. Immunoglobulins 3. Cytokines 4. Plasma enzymes I. Lipids, lipoproteins and cardiovascular diseases 1. Triglycerides, cholesterol and phospholipids 2. Classifications of lipoproteins 3. Reference ranges and laboratory investigations 4. Disorders of lipid metabolism 5. The management of lipid disorders 6. Lipoprotein deficiency 7. Myocardial infraction 8. Heart failure 9. Hypertension J. Inherited metabolic disorders 1. Glucose6- phosphatase deficiency 2. Galactosaemia 3. Phenylketonuria 4. Steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency 5. Cystic fibrosis V. LAB COMPONENTS: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Introduction to clinical laboratories and blood collection Liver function tests: Measurement of Alanine transaminase (ALT) Liver function tests: Measurement bilirubin Kidney function tests: Measurement of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) Kidney function tests: Measurement of creatinine and creatinine clearance Lipid profile: Measurement of Total cholesterol and triglycerides Diabetic profile tests: Measurement of blood glucose Urine analysis: Identification of normal physical and chemical urine constituent I. Urine analysis: Identification of pathological urine constituent J. Urine microscopic examination VI. TEACHING LEARNING STRATEGIES: To do well, students should attend class and take very detailed notes. You should rely on your lecture notes rather than the text as your primary study resource. You will be responsible for everything covered in lecture, but not responsible for material that is covered in the text but not in lecture. It is not possible to cover all the topics in the text. To get most out of the lectures, it is recommended you read the text before lecture, and then reread the text in more detail after the lecture to make sure you understand all concepts. The lectures move quite rapidly, so reading the text before lecture will improve your comprehension. Always go over your lecture notes within a day of the lecture. 3 VII. POLICIES: Attendance & Tardiness: Any student missing a class/classes will be counted absent and her absence will fall within the 25% absence range It is the student’s responsibility to make sure she is not missing any exam, quizzes or any other course class assignments. All students are responsible for work missed during their absence. The course instructor is NOT obliged to repeat her lecture or coursework missed by the student due to her absence. Students are expected to meet the following Be punctual in coming to class. You will be marked absent if you enter the class after five minutes of starting time. Absenteeism for more than 25% of allocated course lectures, will entitle the instructor to stop you from attending the final exam.” You will receive an F grade. Turn off mobile telephones during classes. If a mobile rings during class it will be taken from the student and returned only at the end of the semester. Do not leave the classroom except in case of emergency and when the instructor gives you the permission to do so. There might be a quiz after each chapter (topic) is finished. These quizzes will not be repeated. Any late/missed assignments will not be accepted after the due date, automatically resulting in a zero. Food and drink are not allowed in the class. VIII. COURSE EVALUATION/GRADING: Indicator Points 10 20 10 25 35 100 Test 1 Midterm exam Test 2 Lab Final exam Total IX. GRADING SCALE: 95-100 90-94 85-89 80-84 75-79 70-74 65-69 60-64 60 = A+ =A = B+ = B = C+ = C = D+ = D =F X. TEXTS & MATERIALS Marshall, W. and Bangert, S. (2008). Clinical chemistry (6th ed.). Edinburgh, London: Mosby Elsevier. ISBN 0723434557 4 XI. COURSE PLAN: Week Date Subject/Topic References 1 25-29/3/1435 2 2-6/4/1435 3 9-13/4/1435 4 16-20/4/1435 5 23-27/4/1435 6 1-5/5/1435 7 8-12/5/1435 Urine analysis 8 15-19/5/1435 The liver: The biochemical assessment of liver function MIDTERM BREAK Exams Syllabus Introduction to clinical biochemistry Biochemical investigation in clinical medicine Chapter 1 Water, Sodium and Potassium Chapter 2 Hydrogen ion homeostasis and blood gases Chapter 3 The kidneys Chapter 4 Test 1 Tuesday 25/4/1435 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 20-28/5/1435 9 29/5 - 3/6/1435 The liver: Liver disease 10 6-10/6/1435 Thyroid gland 11 13-17/6/1435 12 20-24/6/1435 Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism Plasma proteins and Enzymes 13 27/6 - 2/7/1435 14 5-9/7/1435 15 12-16/7/1435 Chapter 5 Chapter 9 Lipids, lipoproteins and cardiovascular diseases Inherited metabolic disorders Revision Final exams 25/7-7/8/1435 5 Midterm Exam Tuesday 8/6/1435 Chapter 11 Chapter 13 Chapter 14 Test 2 Tuesday 29/6/1435 Chapter 16 Final Lab exams