Nervous Tissue in Detail
advertisement

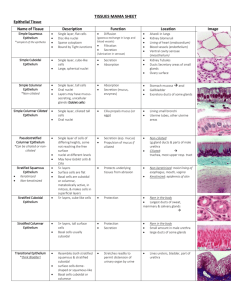
Tissue: Specific Types Epithelial Tissue in Detail Classification of epithelia o According to _____________ “simple” - one cell layer “stratified” – more than one layer of cells (which are named according to the shape of the cells in the apical(base) layer) o According to _____________ “squamous” – wider than tall “cuboidal” – as tall as wide “columnar” - taller than wide Classes of Epithelia Simple Squamous Epithelium o Descriptions: Single layer, flattened cells, simplest of epithelia o Function: Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration Secretes _____________ substances o Location: Air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, lining of ventral body cavity Simple Cuboidal epithelium o Descriptions: Single layered, cube like, large spherical central nuclei o Function: Secretion and absorption o Location: _____________ tubules, ovary surfaces Simple Columnar Epithelium o Descriptions: Single layer, tall, round or oval nuclei, some bear cilia, may contain mucus-secreting glands (_____________ cells) o Function: Absorption, secretion of mucus and enzymes, cilia propels mucus o Location: Nonciliated lines the digestive tract Ciliated lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, parts of uterus. Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium o Descriptions: Single layer w/ _____________ heights, nuclei at different levels, may have goblet cells or cilia o Function: Secretion(especially mucus), propulsion of mucus by ciliary action o Location: Nonciliated in sperm carrying ducts Ciliated lines the trachea and upper respiratory tract. Stratified Squamous Epithelium o Descriptions: (most common stratified) Several layers, surface cells are squamous, basal cells are cuboidal or columnar o Function: _____________ underlying tissues in areas of abrasion o Location: Esophagus, the mouth, outer portion of skin Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium o Descriptions: (rare) Usually two layers of cube-like cells o Function: Protection o Location: _____________ Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands. Stratified Columnar Epithelium o Descriptions: (rare) Several layers thick, columnar with varying in size and shape o Function: Protection, secretion o Location: _____________ Large ducts of glands Transitional Epithelium o Descriptions: Highly modified, several layers of cuboidal or columnar cells o Function: _____________ readily, allowing distention of urinary organs o Location: Lines the ureters, bladder, parts of urethra Bone o Descriptions: Aka: osseous tissue Hard calcified matrix, surrounded by layers of calcium salts in additions to lots of collagen fibers Cells sit in cavities called “_____________” o Function: Protection and support o Location: Skeletal system Hyaline Cartilage o Descriptions: (hyalin=glass) Most common and widespread type Collagen fibers with a _____________ matrix o Function: Supports/reinforces, resilient cushioning o Location: Covers ends of bones in joints, nose, trachea, larynx, embryonic skeleton Elastic Cartilage o Descriptions: Collagen fibers with a rubbery matrix Very elastic o Function: _____________ shape of structure gives flexibility o Location: External ear Epiglottis Connetive Tissue in detail Fibrocartilage o Descriptions: Similar to hyaline but less firm Much like a cushion o Function: Absorbs _____________ shock o Location: Intervertebral discs, discs of knee joint Dense Connective Tissue o Descriptions: Collagen fibers, fibroblasts fill gaps between collagen Strong ropelike structures like _____________ and ligaments o Function: Connect muscles to bones, connect bones at joints, lots of tensile strength o Location: joints Vocab o _____________ – cells that make collagen fibers o Tendons – attach skeletal muscles to bones o Ligaments - connect bones to bones at joints. More stretchy and contain more elastic fibers than tendon Loose CT: Areolar Tissue o Descriptions: Gel-like matrix w/ all three fiber types Very loose network w/ lots of open space o Function: Wraps and cushions organs, a reservoir of water and salts for surrounding tissues, important for _____________ o Location: Under epithelia, around organs, surrounds capillaries Loose CT: Adipose Tissue o Descriptions: (fat) Very similar to areolar tissue ________ cells predominate o Function: Insulates against heat loss, supports and protects organs, reserve food fuel o Location: Under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, abdomen and breast Loose CT: Reticular CT o Descriptions: Network of reticular fibers (similar to fibroblast) Delicate network of interwoven fibers o Function: Form soft internal skeleton that supports other cells such as white blood cells, mast cells o Location: _____________ organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen) Blood o Descriptions: (vascular tissue) Red and white blood cells in a ________ matrix (plasma) Fibers are soluble only seen during clotting o Function: Transportation of gases, nutrients, wastes ect. o Location: Everywhere Muscle Tissue in Detail Skeletal Muscle o Descriptions: Long, cylindrical, obvious striations, multinucleated o Function: Voluntary movement, manipulation of the environment, facial expression Gross body movement o Location: Attached to bones Cardiac Muscle o Descriptions: Branching, striated, uninucleated cells that fit tightly together at junctions called “intercalated disks” o Function: Involuntary control, propels blood into circulation. o Location: Walls of the heart Nervous Tissue in Detail Smooth Muscle o Descriptions: (visceral) No striations, spindle-shaped w/ central nuclei Arranged closely to form sheets o Function: Propelles substances along internal passageways, involuntary control Peristalsis – wavelike motion o Location: Walls of the stomach, bladder, uterus and blood vessels Nervous Tissue o Descriptions: (Neurons) Branching cells, has long extended parts Irritability and conductivity Have “supporting cells” that insulate, support and protect neurons. o Function: Transmits electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors that control their activity o Location: Brain, Spinal cord and nerve