A-Level H2 Chemistry Worked Solutions 2011
advertisement

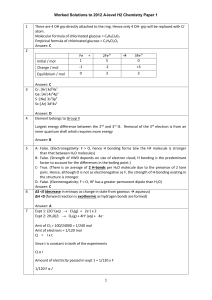
Worked Solutions to 2011 A-level H2 Chemistry Paper 1 1 2 3 4 In TiO2, Titanium exists as Ti4+. Ti: [Ar] 4s2 3d2 = 22 electrons. No. of electrons for each Ti4+ = 22 – 4 = 18 Answer: A Nuclear charge of Ne > F but shielding effect about same for both as electrons are added into the same quantum shell. Therefore, E.N.C of Ne > F thus IE of Ne > F Answer: D 1 mol (Na2CO3)x.y(H2O2) : x mol CO2 : y mol H2O2 0.01 mol (Na2CO3)x.y(H2O2) : 0.048/24 = 0.02 mol CO2 x=2 MnO4- : (H2O2) = 2: 5 Amt of H2O2 = 0.024x 0.05 x 5/2 = 0.03 mol 0.01 mol (Na2CO3)x.y(H2O2) : 0.03 mol H2O2 y=3 Answer: C PV = nRT Since V, n, R const P α T If P x 2 T (in units of K) x 2 Temperature = (27 + 273) x 2 = 600 K Answer: D 5 6 7 8 9 ΔHc = (x + y)/2 Answer: C Lattice energy |(q+. q)/ (r+ + r )| Charge effect is greater that size effect where M2+ and Z2- will form the ionic compound with the most exothermic LE. Since the radii of L+ > J+ and Y- > X-, hence the LE of JX is more exothermic than LY. Hence LE decreases in the order: MZ, JX, LY Answer: C ΔHrxn = ΔHf (products) – ΔHf (reactants) = -2.09 – 0 = -2.09 kJmol-1 ΔSrxn = ΔS (products) – ΔS (reactants) = 44.1 – 51.4 = -7.3 JK-1mol-1 ΔGrxn = ΔH – TΔS = (-2.09 x 1000) – 285(-7.3) J mol-1 Answer: D Anode: 2Cl–(aq) Cl2(aq) + 2e– Cathode: 2H2O(l) + 2e– H2(g) + 2OH–(aq) Cl2 and aqueous NaOH produced during electrolysis can further react to form sodium chlorate(I). Cl2(g) + 2NaOH(aq) NaClO(aq) + NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) Answer: C Metal that will not be easily dissolved (oxidised) should have the highest EoR value Eo(Cu+/Cu) = +0.52 ; Eo(Cu+2/Cu) = +0.34 Eo(Fe2+/Fe) = -0.44 ; Eo(Fe3+/Fe) = -0.04 Eo(Pb2+/Pb) = -0.13 Eo(Zn2+/Zn) = -0.76 Answer: A 1 Worked Solutions to 2011 A-level H2 Chemistry Paper 1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 From the given half equation, all the species are ions. Hence, X must be inert electrode – Pt Y must be solution containing Fe2+ and Fe3+ as the solution must contain all the ions in the half equation. Answer: D Definition of buffer: Buffer maintains the pH at about the same level when small amounts of acid or base is added. Answer: C When [SO2] is const, when [NO2] is increases by 1.33 times, relative rate also increases by 1.33 times. Therefore 1st order w.r.t. NO2. When [SO2] increases from 0.005 to 0.006 (1.2 times), [NO2] increases by 1.2 times, relative rate increases due to SO2 alone is 1.44 / 1.2 = 1.2 times. Therefore 1st order w.r.t. SO2. Answer: B Rate α 1/time Plot concentration of reactant vs rate. The order can be determine from the shape of graph. Answer: B A: Phosphorus exists as P4 whilst sulfur exists as S8. (False) B: Aluminium has the highest electrical conducitivity as it has the most number of delocalised electrons. (False). C: Silicon has the highest melting point (False). Anionic radius trend is as follows: P3- > S2- > Cl- (False) Answer: B Stability of H-X to decomposition depends on H-X bond. Answer: C 2Ca(NO3)2(s) 2CaO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g) Amt of Ca(NO3)2 = 8.2/164 = 0.05 mol Amt of O2 produced = 0.05/2 = 0.025 mol Vol of O2 produced = 0.025 x 24 x 1000 = 600 cm3 Answer: C To produce oxygen gas, hydrogen peroxide must undergo oxidation. Therefore condition must be acidic. Answer: C Enthalpy change of fusion is α melting point W and X has giant structure while Y and Z has simple covalent structure. Also, X has a higher melting point than W hence X must be Si and W Al. Also, since Z has a higher melting point than Y, the size of the electron cloud of Z (S8) must be bigger than Y (P4). Answer: A But-2-yn-ol ABCDAnswer: C True (sp hybridised – C has 2 sigma bonds) True. (–OH gp decolourises KMnO4 due to multiple bonds.) False. (They are sp3 hybridised as C has 3 sigma bonds) True. (C has 4 bp, 0 lp and according to VSEPR theory, shape = tetrahedral) 2 Worked Solutions to 2011 A-level H2 Chemistry Paper 1 20 21 22 23 24 25 CxH2x+2 + (3x+1)/2 O2 xCO2 + (x+1)H2O Number of carbon atoms in alkane = x Moles of oxygen gas = (3x+1)/2 Answer: B In chloroethene, the Cl is next to the C=C. The electrons on Cl can be delocalised into the pi bond of the alkene thus making C-Cl bond stronger (exhibiting partial double bond character) and hence less resistant to hydrolysis. Answer: C Intermediate in SN1 is a carbocation. C is intermediate in Electophilic Substitution; D is intermediate in SN2 (transition state formed); A is an intermediate in a nucleophilic addition mechanism. Answer: B The reactant will undergo ester hydrolysis (there is heat from steam and acid). H2O will also add across double bond (EA). Note in C: a diol cannot be formed through EA unless its through mild oxidation. Answer: B Ease of nucleophilic substitution reaction according to classes of halogeno compounds are: Acyl Chlorides > Alkyl chlorides > Aryl chlorides Ease of nucleophilic substitution reaction for reaction within the same class of compounds are: R-Cl < R-Br < R-I Answer: B Cl2 should not be aq. as water will cause the AlCl3 to be hydrolysed. (recall: chemical periodicity – reaction of AlCl3 with water to form an acidic solution). Answer: C 26 27 Answer: A X is The alkyl halide undergoes NS with ammonia to form a substituted amine. 3 Worked Solutions to 2011 A-level H2 Chemistry Paper 1 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 The amine above then undergoes an intermolecular NS with the acid chloride to form A. (Note: C and D are not possible as they are ionic compound which should be soluble in water.) Answer: A React with Na : alcohol, phenol OR -COOH group present React with 2,4DNPH: ketone or aldehyde (X, Y, Z reacts with Na; only Y reacts with 2,4 DNPH) Answer: D When pKa (2.1 and 4.1) < pH (7) glutamic acid exists in a basic medium. Hence, all acidic groups are deprotonated. When pKa (9.5) > pH (7) glutamic acid exists in an acidic medium. Hence all basic groups are protonated. Answer: B With HCl and heat, -amide group will undergo hydrolysis, leaving –NH3+ on oseltamivir -amine group (basic) will react with acid to form –NH3+ -ester group will undergo hydrolysis, leaving –COOH on oseltamivir Answer: B Only 1 (by definition or relative molecular mass) Answer: D (only 1) Option 1 – True. Hydrogen gas must be at standard conditions i.e. 1 atm , 298 K Option 2 – True. The cell produces a current but when the electrodes are connected through a high-resistance voltmeter, the current in the external circuit is virtually zero and the cell registers its maximum potential difference, (E0). Option 3 – False. A concentration of 1mol dm-3 solution is required. pH = 1 infers [H+] = 10-1 mol dm-3. Answer: B ( 1 and 2) Option 1 – True. Same empirical formula (C6H5NO)n where n= 1 for Z and n= 2 for X Option 2 – True. X and Y have the same molecular formula C12H10N2O2 but different arrangement of atoms hence they are isomers. Option 3. – True. Since (C6H5NO)n n= 1 for Z and n= 2 for Y, Mr of Y is twice that of Z. Answer: A (1, 2 and 3) Option 1. Correct – since it is zero order, rate does not change with time Option 2. Correct – rate constant only depends on temp Option 3. Wrong - rate constant will change with temp, hence the graph will linearly increasing. Answer: B ( 1 and 2) AlCl3 (s) + aq [Al(H2O)6]3+ (aq) + 3 Cl- (aq) [Al(H2O)6]3+ (aq) + H2O (l) [Al(H2O)5OH]2+ (aq) + H3O+ (aq) AlCl3 undergoes hydroylsis, making it acidic. 1. Wrong. Not due to the reaction of chloride and water as chloride is a weak conjugate base that does not hydrolyse in water. 2. Correct. Al3+ has high charge/ mass (similar to charge/surface area), causing it to undergo hydrolysis in water. 4 Worked Solutions to 2011 A-level H2 Chemistry Paper 1 3. Correct. One of the O-H bonds in H2O of is broken in [Al(H2O)6]3+ to release the H+ Answer: C ( 2 and 3) 36 37 NaBr and conc sulphuric acid will react as follows: KBr + H2SO4 HBr + KHSO4 2 HBr + H2SO4 SO2 + Br2 + 2H2O Answer: B ( 1 and 2) 1. Correct. 2. Wrong. Only 1 ester group 3. Wrong. Only 3 chiral centres Answer: D (1 only) 38 39 40 Only 1 is correct. CO and NO (both pollutants) are converted to more harmless gases, CO2 and N2. Option 2 and 3 are wrong because harmful gases are produced – CO, NO2 and SO3 Answer: D (1 only) Baeyer’s test – Mn is reduced from +7 (in MnO4-) to +4 (in MnO2) Fehling’s test – Cu is reduced from +2 (in Cu2+) to +1 (in Cu2O) Tollen’s test – Ag is reduced from +1 (in [Ag(NH3)]+ to 0 (in Ag) Answer: A (1, 2 and 3) 1. Correct. The non-polar R group (–CH3 group) in alanine can interact with each other by VDW 2. Correct. The polar R group ( –CH2OH group) in serine can interact by H-bonding with the – COOH gp of another amino acid 3. Wrong. The R groups do not contain -NH2 and –COOH group.Hence ionic bonding is not present. Answer: B (1 and 2) END 5 Worked Solutions to 2011 A-level H2 Chemistry Paper 1 6