Nervous System
advertisement

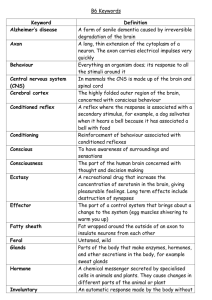
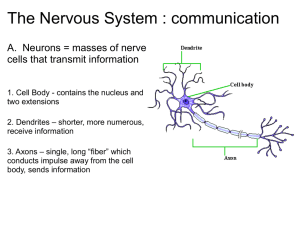
Nervous System Worksheet (Total: 15 points) Student: ___________________________________________________________________________ 1. Which statement is NOT true about the human nervous system? A. The somatic nervous system controls skeletal muscles. B. The autonomic nervous system controls the skin and joints. C. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. D. The somatic nervous system is part of the peripheral nervous system. E. The autonomic nervous system controls glands and smooth muscles of the viscera. 2. The Greek root word meaning "nerve" underlies the term A. neuron. B. cerebellum. C. central. D. cerebrum. E. peripheral. 3. Which statement is NOT true about the cells of the nervous system? A. A neuron can have only one axon. B. A neuroglial cell supports or protects a neuron. C. There may be multiple dendrites on a single cell. D. A dendrite is a cytoplasmic extension of a neuron. E. A dendrite is the cell part that carries an electrical impulse away from the cell body. 4. We can define a nerve impulse as A. an electrical current that moves along one nerve cell as if it were a copper wire. B. a collection of sodium ions that start at the dendrite end and individually move all the way to eventually arrive at the brain. C. a change in sodium ion concentrations on the nerve cell membrane(a change that moves generally from dendrites to axon). D. a change in sodium ion concentrations on the nerve cell membrane(a change that moves generally from axon to dendrites). 5. The Greek root word for "axis" underlies the term A. axon. B. neuron. C. pons. D. dendrite. E. myelin. 6. Dendrites A. carry impulses away from a cell body. B. are always myelinated. C. are found only in the CNS. D. are solely responsible for nervous conduction. E. carry impulses toward a cell body. 7. Use the following key. There is a trigeminal sensory nerve that lets you feel what is happening to your face, and there is a separate facial motor nerve that allows you to control the movements of each side of your face. Also consider that the routes for these two nerves are separate but converge at the same general "facial" region in the brain. You have no facial control but feeling is present (known as Bell palsy). A. blocks at "facial" area of brain B. blocks facial nerve C. blocks trigeminal nerve D. no block 8. Use the following key. There is a trigeminal sensory nerve that lets you feel what is happening to your face, and there is a separate facial motor nerve that allows you to control the movements of each side of your face. Also consider that the routes for these two nerves are separate but converge at the same general "facial" region in the brain. You can neither feel one-half of your face nor control its movement; the physician is concerned about possible stroke or brain tumor. A. blocks at "facial" area of brain B. blocks facial nerve C. blocks trigeminal nerve D. no block 9. The inside of the neuron membrane at rest is A. negatively charged. B. positively charged. C. neutral, or equal to the exterior charge. D. None of the choices are correct, since neurons are never at rest. 10. How fast a person can type or play the piano keys depends upon the ultimate limitation to the number of nerve impulses she or he can send to a muscle per second. This is determined by A. primarily the type of muscle. B. whether the signal is pain, sound, motor, etc. C. the magnitude or strength of the nerve signal. D. the number of neurons and synapses involved. E. the speed with which sodium ions can be pumped back outside the neuron membrane. 11. Which statement is NOT true about the neuron cell membrane? A. The resting potential of a typical neuron is -70 mV within the neuron. B. There is a difference in electrical potential between the sides of the cell membrane. C. There is a voltage difference between the inside and the outside of the cell membrane. D. The resting potential is the difference in electrical potential between the sides of the cell membrane when the cell is at rest. E. The action potential is a rapid change in the electrical potential, making it more negative inside the cell than it was before. 12. In the axon, the nerve impulses travel A. toward the cell body. B. away from the cell body. C. in both directions. D. away from the synapse. 13. Which is NOT a correct association of structure and function? A. axons--outgoing signals B. sensory neuron--delivers signals to control sensory organs such as eye movement C. cell body--nucleus and organelles D. dendrites--incoming signals E. interneuron—conveys signals to other parts of the CNS 14. When a finger or other appendage is severed in an accident, it is possible to surgically rejoin most tissues (bone, skin, etc.) and most will grow back together. However, in a cut through an appendage nerve, it is currently very difficult to reconnect what are primarily severed A. axons. B. synapses. C. cell bodies. D. dendrites. E. interneurons. 15. Which statement is NOT true about the development of an action potential? A. It can be produced by an electric shock or a sudden pH change. B. There is a rapid change in polarity from about -70 mV to about +40 mV. C. The action potential ends when the polarity across the membrane reaches +40 mV. D. Depolarization occurs when sodium gates open and allow sodium ions to enter the cell. E. Potassium gates open after the sodium gates and allow potassium ions to leave the cell. 16. Which statement is NOT true about the action potential of the neuron? A. Large fibers in neurons of some invertebrates carry very rapid nerve impulses. B. The action potential travels the length of the axon in a self-propagating fashion. C. Repolarization occurs as movement of potassium ions occurs across the cell membrane. D. The action potential moves more slowly along a myelinated nerve fiber than along one with no myelin sheath. E. Saltatory conduction occurs from one neurilemmal node to another along a myelinated neuron. 17. What keeps a nerve impulse from flowing "backward" in a neuron? A. The synapse receptors form a one-way gate. B. The sodium ions can only move toward a synapse. C. The neurolemmocytes keep impulses flowing in only one direction. D. The axon and dendrite have completely different membrane structures. E. All of the choices are correct. 18. The connection space between the dendrite of one cell and the axon of another cell is called A. a synapse. B. a neurotransmitter. C. an axonic connection. D. a threshold. 19. At a synapse, A. synaptic vesicles fuse with the postsynaptic membrane. B. synaptic vesicles fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane. C. neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft. D. neurotransmitters are actively transported across the synaptic cleft. E. synaptic vesicles fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane, and neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft. 20. The likely effect on a neuron of two excitatory signals and twenty inhibitory signals is A. transmission of a nerve impulse. B. transmission of a nerve impulse releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters at the next synapse. C. prohibiting the axon from firing at all. D. confused integration. 21. Which of the following is NOT true about the myelin sheath? A. It is composed of layers of cellular membrane containing myelin around nerve fibers. B. It gives nerve fibers their white glistening appearance. C. It is surrounded by the neurilemma. D. It decreases the speed of nerve impulse conduction. E. It is formed from Schwann cells. 22. The sodium/potassium pump is primarily responsible for the A. resting potential. B. action potential. C. excretion of salts. D. contraction of muscle fibers. E. maintaining isotonic water balance. 23. Neurotransmitters are molecules that cross the synaptic cleft and A. always inhibit the postsynaptic neuron. B. always excite the postsynaptic neuron. C. either excite or inhibit the postsynaptic neuron. D. integrate the pre-synaptic action potential. E. are carried along the membrane surface of the next neuron. 24. You spray an insect with a common insecticide that destroys the ability of acetylcholinesterase to recycle acetylcholine. What then happens? A. This kills the neuron directly. B. The lack of recycled acetylcholine brings cell metabolism to a halt. C. The insect loses control of body functions as nerve impulses flow continuously. D. This prevents the synapse from restoring its ability to "reset" itself for the next impulse. E. The synapse is prevented from restoring its ability to "reset" itself for the next impulse, therefore, the insect loses control of body functions due to a continuous flow of impulses. 25. Carpal tunnel syndrome is due to damage to one nerve and results in lack of control to the wrist and also numbness. This indicates that the A. nerve contained sensory neurons. B. nerve contained motor neurons. C. nerve contained both sensory and motor neurons. D. damage was to a central body in a ganglion. E. damage was to the spinal cord interneuron. 26. The peripheral nervous system consists of the A. nerves. B. ganglia. C. nerves and ganglia. D. brain and spinal cord. E. brain, spinal cord, and nerves. 27. Spinal nerves contain A. only sensory fibers. B. only motor fibers. C. both sensory and motor fibers. D. only parasympathetic fibers. E. only interneurons forming ganglia. 28. The primary functions of the spinal cord involve A. intelligence and memory. B. speech, taste, smell, vision, hearing. C. reflex actions and communication between the brain and spinal nerves. D. controlling muscle activity and maintaining balance. E. local control and decision-making for local anatomy. 29. A reflex action A. is an automatic, involuntary response. B. does not require the central nervous system. C. is normally controlled consciously. D. has no protective value. E. is only found in humans. 30. The Greek root word for "membranes covering the brain" underlies the term A. medulla oblongata. B. meninges. C. reticular formation. D. diencephalon. E. thalamus. Bonus Questions: 2 points / Q 1. Matching pairs of terms: Somatic nerves Autonomous nerves Part of the autonomous nervous system that controls either the "fight-or-flight" or the resting functions Motor neuron Sensory neuron Chemicals released at the nerve endings and in turn, elicit or inhibit action potential Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system The parts of the synapse that the neurotransmitter is released from or acted upon Afferent pathway Efferent pathway Nerve cells responsible for voluntary motion or for general sensory Excitatory neurotransmitter Inhibitory neurotransmitter Nerves that control voluntary functions or involuntary functions Agonist Antagonist Nervous pathway that conduct signals to the brain or from the brain Presynaptic neuron Postsynaptic neuron Mimicker or blocker of the neurotransmitters 2. The following diagram shows the possible drug action points at the neuronal synapse. Decide the consequence to the neurotransmitter function between increase or decrease, supposing that, in turn, each of the steps in neurotransmission is ENHANCED by a drug. Please consider #2 to #9 and just answer "increase" or "decrease". E.g. Answering #1: Increase. (It means that enhanced transport of neurotransmitter or its precursor from the cell body of the presynaptic neuron results in increase in the transmitter function. But you don't need to explain) #2: Enhanced synthesis of the transmitter #3: Enhanced storage (more vesicles or more molecules in each vesicle) #4: Enhanced metabolism (degradation) of the transmitter #5: Enhanced release of the transmitter #6: Enhanced reuptake of the transmitter by presynaptic neuron #7: Enhanced degradation #8: Enhanced interaction to receptor (more transmitter) #9: Enhanced reaction in postsynaptic neuron (a mimicker)