Fluid Mechanics Problem Set: Pressure, Viscosity, and More
advertisement

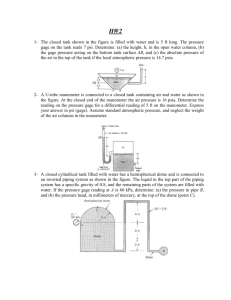
Problem set 2 Chapter 1, Problem 077 1. A 1-m3 volume of water is contained in a rigid container. Estimate the change in the volume of the water when a piston applies a pressure of 28 MPa. V = 0.0130 m3 2. A 10-kg block slides down a smooth inclined surface as shown in Fig. 2-2. Determine the terminal velocity of the block if the 0.1-mm gap between the block and the surface contains SAE 30W oil at 60 °F (dynamic viscosity 0.6 N*s/m2). Assume the velocity distribution in the gap is linear, and the area of the block in contact with the oil is 0.1 m2. Fig. 2-2 Block on an inclined surface. V = 0.0559 m/s 3). An open, clean glass tube, having a diameter of 2.0 mm, is inserted vertically into a dish of mercury at 20˚C. How far will the column of mercury (specific gravity = 13.4) in the tube be depressed if the contact angle is 130o and the surface tension is 0.466 N/m? h = 4.5573×10-3 m. 4). (a) The water strider bug shown in Figure 2-4 is supported on the surface of a pond by surface tension acting along the interface between the water and the bug's legs. Determine the minimum length of this interface needed to support the bug if the surface tension of water is 0.0734 N/m. Assume the bug weighs 8 × 10-4 N and the surface tension force acts vertically upwards. (b) Repeat part (a) if surface tension were to support a person weighing 600 N. Figure 2-4. Water strider bug. Solution (a) Lmin = 10.9 mm (b) Lmin = 8.17×103 m 5) An unknown immiscible liquid seeps into the bottom of an open oil tank. Some measurements indicate that the depth of the unknown liquid is 1.5 m and the depth of the oil (specific weight = 8.5 kN/m3) floating on top is 5.0 m. A pressure gage connected to the bottom of the tank reads 65 kPa. What is the specific gravity of the unknown liquid? Solution SG = 1.53 6) Assume that a person skiing high in the mountains at an attitude of 15,000 ft takes in the same volume of air with each breath as she does while walking at sea level. Determine the ratio of the mass of oxygen inhaled for each breath at this high altitude compared to that at sea level. Assume that the air composition is the same at sea level as it is at 15,000 ft. Density of air at sea level is 2.377×10-3 slugs/ft3 and density of air at 15,000 is 1.496×10-3 slugs/ft3. Solution m15 = 0.629 m0 7) Bourdon gages are commonly used to measure pressure. When such a gage is attached to the closed water tank of Figure 2-7 the gage reads 5 psi. What is the absolute air pressure in the tank? Assume standard atmospheric pressure of 14.7 psi. Figure 2-7 Closed water tank Solution Pair = 19.3 psia 8) A U-tube manometer is connected to a closed tank shown in Figure 2-8. The air pressure in the tank is 0.50 psi and the liquid in the tank is oil ( = 54.0 lbf/ft3). The pressure at point A is 2.0 psi. Determine: (a) the depth of oil, z, and (b) the differential reading , h, on the manometer. Figure 2-8 A closed tank with U-tube manometer. Solution (a) The depth of oil z = 4 ft (b) h = 2.08 ft