Seahorse Aquaculture
advertisement

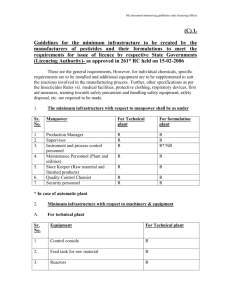
Seahorse Aquaculture Marie Barton University of Alabama 2013 DISL Taxonomy • • • • • • • • • Family: Syngnathidae Hippocampus kuda H. reidi H. erectus H. barbouri H. abdominalis H. breviceps H. comes H. ingens • Captive-bred seahorses first recorded in 2002 • In past decade, risen from 1% of total seahorse trade to 99% today Economic importance, market price, locations, country • Conservation ▫ H. capensis in Hawaii ▫ Mote marine lab • Dried seahorses- traditional medicine ▫ $100-300/kg • Live- ornamental fish ▫ $100-900/animal • Australia, NZ, MX, China, Ireland and UK, India, Indonesia, USA, S. Africa, Thailand, Vietnam ▫ Developed and developing countries Life cycle & larval stages Reproduction in Captivity • Complex mating process ▫ Male courts female with dancing, color change, clicking sounds • Male carries fertilized eggs for 20-30 days • Up to 10 broods/yr • 200-1000 animals/brood • Monogamous Production Methods • Hatchery: Broodstock are kept in cages in calm bay or indoor tanks • Nursery: 1 day after spawning, fry transferred to tank with biofilter, UV sterilization and ozone ▫ Stocked 1-2/L • Growout: 40 days later, transferred to cages or indoor tanks ▫ Initial density 500/m³, after growth 200/m³ Production methods • Large-scale production in Vietnam Hippocampus comes Fry production tank Adult tank Feeds and feeding • Larvae eat plankton, juveniles and adults eat small crustaceans, full grown adults need some small fish too • All prefer live food ▫ Expensive ▫ Conservation growers commonly grow plankton for larvae on site • Most commercial aquaculture uses frozen food ▫ Harder to train/wean but if successful, will be hardier ▫ Artemia • Varied diet important to health ▫ Supplements, alternate live and dead/frozen food Water chemistry and environmental requirements • Pristine water ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Salinity: 15-35 ppt Ammonia and nitrite: 0 ppm Nitrate: <20 ppm DO: 6-8 ppm • Temperature ▫ 20-28°C • pH ▫ 8-8.3 • Tall tank • Current flow in part • Floating space Advantages & Disadvantages • High market value, low production cost • Protected when most vulnerable by male’s pouch • Quick growth in some species ▫ 3-6 months • High fecundity ▫ 1000 babies/brood • Fast gestation ▫ ~8 broods/yr • Some species hardy ▫ Cage raised • Disease susceptible • High risk • Must maintain pristine water conditions if grown indoor • Poor digestion of food ▫ Quick fouling • If stressed at all, no productivity ▫ Easily stressed • Requires much understanding