Demographic, clinical, radiological and pathology details of the 29
advertisement
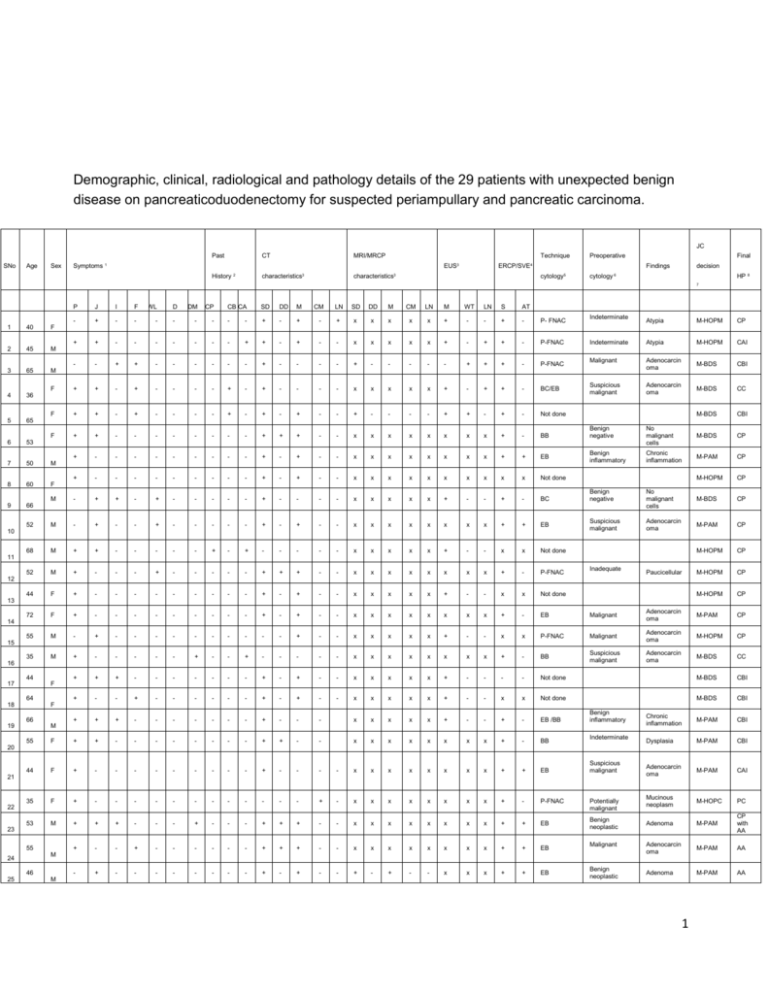
Demographic, clinical, radiological and pathology details of the 29 patients with unexpected benign disease on pancreaticoduodenectomy for suspected periampullary and pancreatic carcinoma. JC Past SNo Age Sex CT MRI/MRCP Technique Symptoms 1 EUS3 History 2 characteristics3 Preoperative ERCP/SVE4 characteristics3 Final Findings cytology5 decision cytology 6 HP 8 7 P J I F WL DM CP CB CA SD DD M CM LN SD DD M CM LN M WT LN S AT - + - - - - - - - - + - + - + x x x x x + - - + - P- FNAC + + - - - - - - - + + - + - - x x x x x + - + + - P-FNAC - - + + - - - - - - + - - - - + - - - - - + + + - P-FNAC F + + - + - - - - + - + - - - - x x x x x + - + + - BC/EB F + + - + - - - - + - + - + - - + - - - - + + - + - Not done 1 40 F 2 45 M 3 65 M 4 36 5 65 F 6 + - - - - - - - - + + + - - x x x x x x x x + - BB Indeterminate Atypia M-HOPM CP Indeterminate Atypia M-HOPM CAI Malignant Adenocarcin oma M-BDS CBI Suspicious malignant Adenocarcin oma M-BDS CC M-BDS CBI Benign negative No malignant cells M-BDS CP Benign inflammatory Chronic inflammation M-PAM CP M-HOPM CP Benign negative No malignant cells M-BDS CP Suspicious malignant Adenocarcin oma M-PAM CP M-HOPM CP M-HOPM CP M-HOPM CP 53 7 50 M 8 60 F 9 + D + - - - - - - - - - + - + - - x x x x x x x x + + EB + - - - - - - - - - + - + - - x x x x x x x x x x Not done M - + + - + - - - - - + - - - - x x x x x + - - + - BC 52 M - + - - + - - - - - + - + - - x x x x x x x x + + EB 68 M + + - - - - - + - + - - - - - x x x x x + - - x x Not done 66 10 11 52 M + - - - + - - - - - + + + - - x x x x x x x x + - P-FNAC 44 F + - - - - - - - - - + - + - - x x x x x + - - x x Not done 72 F + - - - - - - - - - + - + - - x x x x x x x x + - EB Inadequate Paucicellular 12 13 Malignant Adenocarcin oma M-PAM CP 14 P-FNAC Malignant M-HOPM CP 15 Adenocarcin oma Suspicious malignant Adenocarcin oma M-BDS CC M-BDS CBI M-BDS CBI Chronic inflammation M-PAM CBI Dysplasia M-PAM CBI Adenocarcin oma M-PAM CAI Mucinous neoplasm M-HOPC PC Adenoma M-PAM CP with AA Adenocarcin oma M-PAM AA Adenoma M-PAM AA 55 35 M M - + - - - - - - - - - - + - - x x x x x + - - x x + - - - - - + - - + - - - - - x x x x x x x x + - BB + + + - - - - - - - + - + - - x x x x x + - - - - Not done + - - + - - - - - - + - + - - x x x x x + - - x x Not done 16 44 17 F 64 18 F 66 19 + + + - - - - - - - + - - - x x x x x + - - + - EB /BB x x x x x x x x + - BB Benign inflammatory M 55 F + + - - - - - - - - + + - - 44 F + - - - - - - - - - + - - - - x x x x x x x x + + EB 35 F + - - - - - - - - - - - - + - x x x x x x x x + - P-FNAC Indeterminate 20 Suspicious malignant 21 22 Potentially malignant 23 Benign neoplastic 53 M 55 + + - - - + - - - + + + - - x x x x x x x x + + EB + - - + - - - - - - + + + - - x x x x x x x x + + EB - + - - - - - - - - + - + - - + - + - - x x x + + EB Malignant M 24 46 25 + M Benign neoplastic 1 67 26 + 69 27 - + - - - - - - + - + - - + + + - - x x x + + Not done M-PAM AAM Adenoma M-PAM AA + - - - - - - - - - + + + - - x x x x x x x x + + EB Benign neoplastic + - - - - - - - - - - - - + - x x x x x x x x x x P-FNAC Potentially malignant Mucinous neoplasm M-HOPC CL + - - - - - - - - - - - - + - x x x x x x x x x P-FNAC Potentially malignant Mucinous neoplasm M-HOPC SC M 19 28 M 64 29 - F M 1 Signs + present, - absent, x not done 2 Symptom A-abdominal pain, J- Jaundice, I-Itching, F-fever, WL- weight loss, D-Diarrhea, DMDiabetes mellitus 3 Past history CA-chronic alcoholic, CB-chronic biliary disease, CP-chronic pancreatitis 4 CT/MRI/EUS characteristics SD- single biliary duct dilatation DD-double duct ie biliary duct and pancreatic duct dilatation M-discrete mass highly suggestive of malignancy, CM- cystic mass head highly suggestive of mucinous neoplasm LN –enlarged lymph nodes WT – wall thickening bile duct 5 ERCP/SVE S-biliary stricture AT-ampullary tumour 6 Technique preoperative pathology P-FNAC-pancreas FNAC, BC-biliary cytology, BB-biliary brushings, EB-Endoscopic ampullary biopsy 7 Preoperative pathology result AA-ampullary adenoma, AAM-ampullary adenomyoma, PCpseudocyst, SC-serous cystadenoma, CL-cystic lymphangioma, CC-choledochal cyst with atypia 8 MDT decision M-HOPM- malignant head of pancreas mass, M-HOPC-mucinous head of pancreas cyst, M-PAM-malignant periampullary mass, M-BDS- malignant bile duct stricture 9 Final pathology result CP- chronic pancreatitis, AA-ampullary adenoma, AAM-ampullary adenomyoma, PC-pseudocyst, SC-serous cystadenoma, CL-cystic lymphangioma, CC-choledochal cyst with atypia CBI- chronic fibrosing biliary duct inflammation, CAI-chronic ampullary inflammation 2 Table 3 Analysis of preoperative diagnostic testing in the 29 patients with unexpected benign disease after pancreaticoduodenectomy for suspected periampullary and pancreatic carcinoma. Procedure n CT scan Discrete mass/ Premalignant cystic mass Double duct sign Biliary duct dilatation MR scan Discrete mass Double duct sign Biliary dilatation ERCP Suspicious biliary stricture EUS Discrete mass Irregular wall thickening Pathology Malignant/ suspicious malignant/ mucinous cystic 29 19 6 23 4 2 2 4 17 17 10 8 2 22 5/4/2 False positive % 65.51% 20.68% 50% 50% 100% 80% 50% 3 Table 4 Analysis of preoperative diagnostic testing in the 29 patients with unexpected benign disease after pancreaticoduodenectomy for suspected periampullary and pancreatic carcinoma. Variable Benign Malignant Age Gender Male Female Surgical procedure PPPD/ Standard Whipples Vascular resection/ Multivisceral resection Blood loss Overall complications Present Absent Postoperative pancreatic fistula Present Absent Significant pancreatic fistula (B/C) Present Absent Mortality No Yes 53.7 53.43 16 13 270 147 28 398 1 19 1051.72 981.38 12 17 36 281 9 (3.1%) 20 7 (2.4%) 22 26 (10.3%) 3 Univaria te P value 0.874 0.299 Multivar iate P value 0.920 0.794 95% CI 0.966 0.651 1.032 3.146 0.780 0.735 0.148 15.057 0.765 0.332 0.497 0.476 1.000 0.443 1.000 5.721 0.019 0.104 0.029 1.391 0.065 0.616 0.267 9.266 0.043 0.341 0.082 1.415 61 (14.6%) 356 51 (12.2%) 366 404 (3.1%) 13 4 Table 5 Distribution of the number of surgeries and percentage of unexpected benign pathologic findings per year during the period of the study. Year of Surgery Total number of pancreaticoduodenectomies performed 13 Total number of patients with unexpected benign pathology 1 Percentage of patients with unexpected benign pathology 7.1 % April to December 2006 January to December 2007 January to December 2008 January to December 2009 January to December 2010 January to December 2011 January to December 2012 January to December 2013 37 0 0 32 3 8.6 % 45 1 2.2 % 55 3 5.2 % 69 6 8% 67 4 5.6 % 99 11 10 % 5 Figure 2 Percentage of unexpected benign disease at pancreaticoduodenectomy for presumed malignant disease. per year. Percentage of unexpected benign disease 12 Yearwise percentage of unexpected benign disease 10 8 6 4 2 0 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Year 6 Table 6 Details of series in literature of ‘unexpected’ benign disease after pancreaticoduodenectomy for presumed malignant disease Series in literature Indication for PD Thompson et al 1994 (8) Surgery for suspected periampullary malignancy Smith et al 1994 Surgery for primary (Mayo clinic)(9) pancreatic or periampullary malignancy Barens et al 1996 Surgery for suspected (John Hopkins)(10) periampullary malignancy Patients with benign disease 7/20 35% Details of benign disease 29/603 5% Benign bile duct stricture, penetrating duodenal ulcer, metastatic melanoma, ampullary adenoma, intrahepatic druginduced cholestasis and pseudocyst Chronic pancreatitis, serous or mucinous or papillary cystic neoplasm, benign islet cell tumours, ampullary adenoma, duodenal leiomyoma, duodenal villous adenoma, duodenal adenomyoma. Inflammatory lesion in the pancreas or distal common bile duct 108/510 21% van Gulik et al 1997 (Netherlands)(11) Abraham et al 2003 (John Hopkins)(12) Surgery for pancreatic head cancer Weber et al 2003(Memorial Sloan Kettering)(13) Kennedy et al 2006 (Maywood)(14) Kavanagh et al 2008 (Ireland, UK)(15) Surgery for pancreatic head cancer 1287 4.5 % Suspected pancreatic and periampullary cancer Surgery for suspected periampullary malignancy 21/162 12.9 % 8/112 7.1 % Surgery for suspected pancreatic head cancer 14/220 6% 40/447 9.2 % Chronic pancreatitis Pancreatitis (gall stone induced, alcohol induced), chronic pancreatitis, benign biliary tract disease, lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis Pancreatitis Pancreatitis and chronic bile duct inflammation Benign biliary stricture , chronic pancreatitis , choledochal cyst, inflammatory pseudotumour, cystic duodenal wall dysplasia , duodenal 7 de Castro et al 2009 (Netherlands)(17) de la Fuente 2010 (USA)(18) Manzia et al 2010 (UK)(19) Suspicious pancreatic head mass 63/639 9.9 % Surgery for suspected pancreatic malignancy Surgery for suspected pancreatic and periampullary malignancy 37/494 7.4 % 49/459 10.6% Hurtuk et al 2010 (USA)(20) Surgery for suspected periampullary cancer 45/461 9.7% van Heerde 2012 (Netherlands)(21) Surgery for suspected periampullary and pancreatic head malignancy 36/274 13.1 % angiodysplasia , and granular cell neoplasm. Focal chronic pancreatitis, lymphoplasmactic sclerosing pancreatitis Pancreatitis, benign cystadenoma with superimposed pancreatitis Chronic pancreatitis, benign biliary stricture, choledochal cyst, adenomyoma ampulla, inflammation ampulla, papillary hyperplasia, ampullary adenoma, pseudotumour, bile duct papilloma, bile duct vascular malformation, duodenal ulcer Chronic pancreatitis, primary scelorosing cholangitis, choledocholithiasis, isolated bile duct stricture, ampulla of Vater ulcer, duodenal ulcer, distal common bile duct stricture with localized pancreatic fibrosis. Crohns, papillary fibrosis, biliary tract disease, chronic pancreatitis, benign neoplasms 8









